Manage applications¶
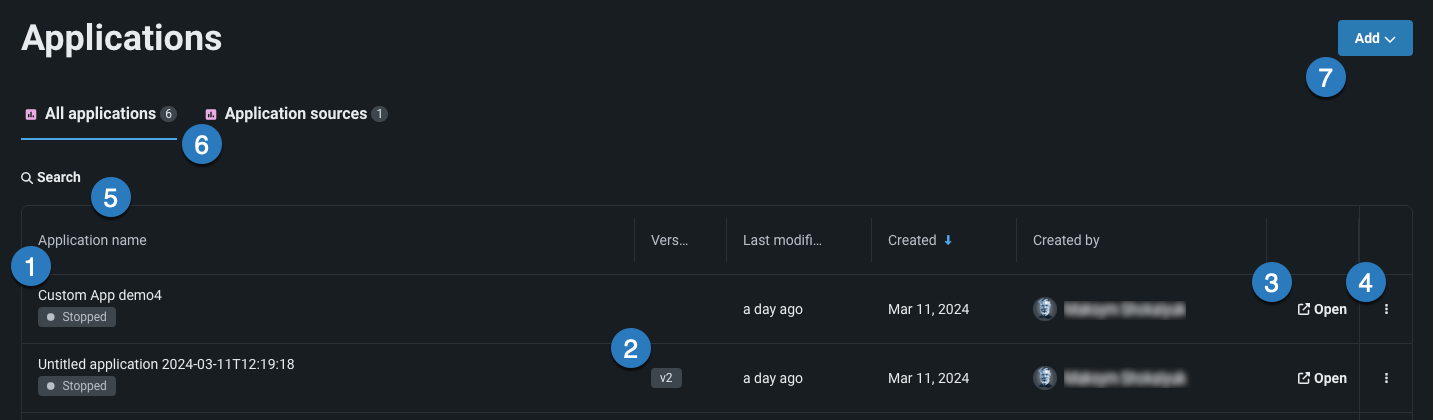
The Applications page in Registry lists all applications available to you in the All applications tab. The table below describes the elements and available actions from this page:
| Element | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Application name | The application name. |
| 2 | Version | Lists the version number of the application or source. |
| 3 | Open | Click to open an application or source. |
| 4 | Actions menu | From the Actions menu, you can:
|
| 5 | Search | Use to find a specific application in the list. |
| 6 | Application tabs | Choose to view built applications or application sources. |
| 7 | Add dropdown | Use the Add dropdown to upload an application or create a new application source. |
Share applications¶
The sharing capability allows you to manage permissions and share an application with users, groups, and organizations, as well as recipients outside of DataRobot. This is useful, for example, for allowing others to use your application without requiring them to have the expertise to create one.
Warning
When multiple users have access to the same application, it's possible that each user can see, edit, and overwrite changes or predictions made by another user, as well as view their uploaded datasets. This behavior depends on the nature of the application.
To access sharing functionality in the All applications tab, click the Actions menu next to the app you want to share and select Share .
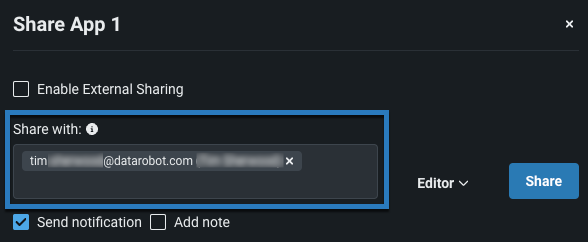
This opens the Share dialog, which lists each associated user and their role. Editors can share an application with one or more users or groups, or the entire organization. Additionally, you can share an application externally with a sharing link.
-
Enter a username, group, or organization in the Share with field.
-
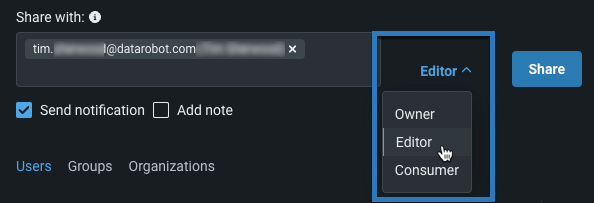
Choose a role for permissions from the dropdown.
-
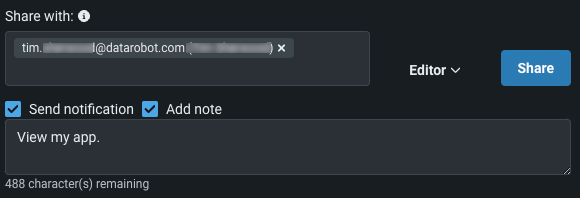
Select Send notification to send an email notification and Add note to add additional details to the notification.
-
Click Share. If you are sharing with a group or organization, the app is shared with—and the role is applied to—every member of the designated group or organization.
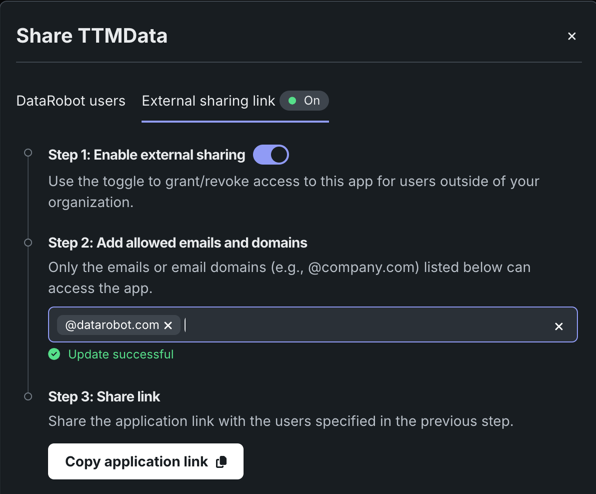
External sharing allows you to share applications with end-users who don't have access to DataRobot via a link. To share an application with non-DataRobot users:
- Click the External sharing link tab. The icon next to the tab name indicates whether or not external sharing is currently enabled.
- Toggle on Enable external sharing. Additional fields appear below.
-
Add all of the email domains and addresses you want to be able to access the application. Note that the emails and domains must be formatted correctly (e.g., @datarobot.com) and only those listed here can access the app via the sharing link.
-
Click Copy application link and send this link to all of the users specified in the previous step. They will receive an email invitation from DataRobot and require this link for verification. Email invitations expire one hour after they are sent to a user. After a user accepts authentication, the authentication token created expires after 30 days.
Revoking application access
You can revoke all access to the sharing link at any time by toggling off Enable external sharing. You can also revoke individual access by removing email domains and addresses from the allowed field.
Self-managed external sharing
For self-managed users externally sharing an application, note that you need to configure a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server in order to share the application with external users.
You can also programmatically share applications using the DRApps CLI.
The following actions are also available in the Share dialog:
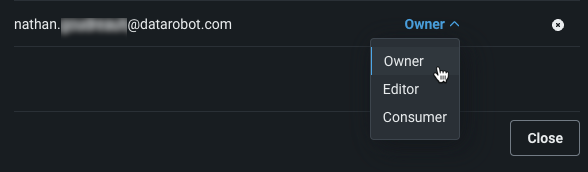
- To remove a user, click the X button to the right of their role.
-
To re-assign a user's role, click the assigned role and assign a new one from the dropdown.
Application API keys¶
In addition to sharing applications, you may want to grant the ability for users to access and use data from within an application. An application API key grants an application the necessary access to the DataRobot Public API. Sharing roles grant control over the application as an entity within DataRobot, while application API keys grant control over the requests the app can make when a user accesses it.
When a user accesses application, the application web server receives a request from their browser. The application API key is included in the header of the request made to the application in order for them to use it.
An application key is automatically created when you build an application. Follow to the steps below to configure an application API key:
-
To edit the scope of access the key grants, navigate to the application source and create a new version.
-
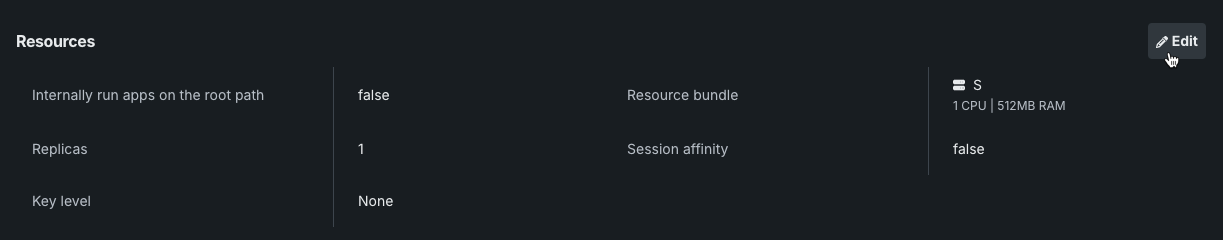
In the Resources section, click Edit.
-
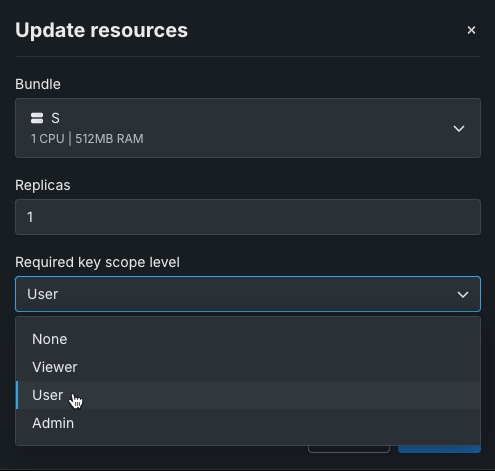
From the Update resources modal, you can edit the degree of access for the application API key using the Required key scope level dropdown. Select a role that defines the degree of access the application has to DataRobot's public API when using the key.
The role types have the following access:
Role Access None No access. When you select this role, DataRobot does not supply an application API key. Viewer Read-only User Create, read, and write Admin Create, read, write, and delete -
After choosing a role, click Update. When you build an application from the source you configured, it will automatically provide an application API key with the scope of access defined by the selected role.
When a user accesses and uses an application, the application API key is included in the header of the request made by the application.
Scoped tokens¶
Scoped tokens provide more granular control (in the form of roles) over the permissions and resources when access to an application is shared with users.
You can set up the application to work with the owner API key (through the DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN env variable) and the visitor API key (through the x-datarobot-api-key request header). The examples below show the local developer scoped tokens experience for both Streamlit and FastAPI.
# Work with owner API key
endpoint = os.environ.get("DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT")
owner_api_key = os.environ.get("DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN") # owner API key
with datarobot.Client(token=visitor_api_key, endpoint=endpoint) as client:
deployments = datarobot.Deployment.list() # get list of visitor datasets
# Work with visitor API key
## Streamlit
endpoint = os.environ.get("DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT")
headers = streamlit.context.headers # request headers
visitor_api_key = headers.get('x-datarobot-api-key') # visitor API key from request headers
with datarobot.Client(token=visitor_api_key, endpoint=endpoint) as client:
datasets = datarobot.Dataset.list() # get list of visitor datasets
## FastAPI
_router = fastapi.APIRouter(tags=["Datasets"])
@_router.get("/datasets")
async def chat_completion(request: fastapi.Request) -> Any:
endpoint = os.environ.get("DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT")
visitor_api_key = request.headers.get('x-datarobot-api-key') # visitor API key from request headers
with datarobot.Client(token=visitor_api_key, endpoint=endpoint) as client:
datasets = datarobot.Dataset.list() # get list of visitor datasets
Link to a Use Case¶
To link an application to a Workbench Use Case, in the application's actions menu , click Link to Use Cases:
In the Link to Use Case modal, select one of the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Select Use Case | Click the Use Case name dropdown list to select an existing Use Case, then click Link to Use Case. |
| Create Use Case | Enter a new Use Case name and an optional Description, then click Create Use Case to create a new Use Case in Workbench. |
| Managed linked Use Cases | Click the minus icon next to a Use Case to unlink it from the asset, then click Unlink selected. |
Delete an application¶
If you have the appropriate permissions, you can delete an application by opening the Actions menu and clicking Delete ().