GenAI feature considerations¶
The following sections describe things to consider when working with generative AI capabilities in DataRobot. Note that as the product continues to develop, some considerations may change. See Troubleshooting for an overview of common errors and their handling.
Trial users: See the considerations specific to the DataRobot free trial, including supported LLM base models.
Availability¶
The sections below describe support for the various elements (LLMs, embeddings, data types, sharing) that are part of GenAI model creation. See also:
LLM availability¶
Note the following when working with LLMs and the LLM gateway:
Availability of the LLM gateway is based on your pricing package. When enabled, the specific LLMs available via the LLM gateway are ultimately controlled by the organization administrator. If you see an LLM listed below but do not see it as a selection option when building LLM blueprints, contact your administrator. See also the LLM gateway service documentation for information on the DataRobot API endpoint that can be used to interface with external LLM providers. LLM availability through the LLM gateway service is restricted to non-government regions.
To integrate with LLMs not available through the LLM gateway service, see the notebook that outlines how to build and validate an external LLM integration using the DataRobot Python client.
All LLMs that are part of the LLM gateway are disabled by default and can only be enabled by the organization administrator. To enable an LLM for a user or org, search for LLM_ in the Feature access page; it will return the full list of available LLMs. These LLMs are supported for production usage in the DataRobot platform.
Additionally, an org admin can toggle Enable Fast-Track LLMs, also in Feature access, to gain access to the newest LLMs from external LLM providers. These LLMs have not yet gone through the full DataRobot testing and approval process and are not recommended for production usage.
Provider region availability information applies only to DataRobot's managed multi-tenant SaaS environments. It is not relevant for self-hosted (single-tenant SaaS, VPC, and on-premise) deployments where the provider region is dependent on the installation configuration.
The following tables list LLMs by provider.
In the tables below, which lists LLM availability by provider, note the following:
| Indicator | Explanation |
|---|---|
| † | Due to EU regulations, model access is disabled for Cloud users on the EU platform. |
| ‡ | Due to JP regulations, model access is disabled for Cloud users on the JP platform. |
| Δ | The model ID the playground uses for calling the LLM provider's services. This value is also the recommended value for the model parameter when using the Bolt-on Governance API for deployed LLM blueprints. |
| © | Meta Llama is licensed under the Meta Llama 4 Community License, Copyright © Meta Platforms, Inc. All Rights Reserved. |
Amazon Bedrock¶
Amazon Bedrock LLM availability
| Type | Max context window | Max completion tokens | Chat model ID Δ | Provider region availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropic Claude 2.1 | 200,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-v2:1 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3 Haiku | 200,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3 Opus† | 200,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-opus-20240229-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3 Sonnet | 200,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Haiku v1† | 200,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet v1 | 200,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet v2† | 200,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude 3.7 Sonnet v1 | 200,000 | 131,072 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude Opus 4† | 200,000 | 32,768 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-opus-4-20250514-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4† | 200,000 | 65,536 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0 |
|
| Anthropic Claude Opus 4.1† | 200,000 | 32,000 | bedrock/anthropic.claude-opus-4-1-20250805-v1:0 |
|
| Cohere Command R† | 128,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/cohere.command-r-v1:0 |
|
| Cohere Command R Plus† | 128,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/cohere.command-r-plus-v1:0 |
|
| DeepSeek R1 v1† | 128,000 | 32,768 | bedrock/deepseek.r1-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3 8B Instruct v1†© | 8,192 | 2,048 | bedrock/meta.llama3-8b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3 70B Instruct v1†© | 8,192 | 2,048 | bedrock/meta.llama3-70b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.1 8B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-1-8b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.1 70B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-1-70b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.1 405B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 4,096 | bedrock/meta.llama3-1-405b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.2 1B Instruct v1© | 131,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-2-1b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.2 3B Instruct v1© | 131,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-2-3b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.2 11B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-2-11b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.2 90B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-2-90b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 3.3 70B Instruct v1†© | 128,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama3-3-70b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 4 Maverick 17B Instruct v1†© | 1,000,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama4-maverick-17b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Meta Llama 4 Scout 17B Instruct v1†© | 3,500,000 | 8,192 | bedrock/meta.llama4-scout-17b-instruct-v1:0 |
|
| Mistral Mistral 7B Instruct v0† | 32,768 | 8,192 | bedrock/mistral.mistral-7b-instruct-v0:2 |
|
| Mistral Mistral Large 2402 v1† | 32,768 | 8,192 | bedrock/mistral.mistral-large-2402-v1:0 |
|
| Mistral Mistral Small 2402 v1† | 32,768 | 8,192 | bedrock/mistral.mistral-small-2402-v1:0 |
|
| Mistral Mixtral 8x7B Instruct v0† | 32,768 | 4,096 | bedrock/mistral.mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0:1 |
|
| Amazon Nova Lite | 300,000 | 10,000 | bedrock/amazon.nova-lite-v1:0 |
|
| Amazon Nova Micro | 128,000 | 10,000 | bedrock/amazon.nova-micro-v1:0 |
|
| Amazon Nova Premier† | 1,000,000 | 32,000 | bedrock/amazon.nova-premier-v1:0 |
|
| Amazon Nova Pro | 300,000 | 10,000 | bedrock/amazon.nova-pro-v1:0 |
|
| Amazon Titan | 8,192 | 8,192 | bedrock/amazon.titan-text-express-v1 |
|
| OpenAI gpt-oss-120b | 131,072 | 128,000 | bedrock/openai.gpt-oss-120b-1:0 |
|
| OpenAI gpt-oss-20b | 131,072 | 128,000 | bedrock/openai.gpt-oss-20b-1:0 |
|
Anthropic¶
Anthropic LLM availability
| Type | Max context window | Max completion tokens | Chat model ID Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropic Claude 3 Haiku | 200,000 | 4,096 | anthropic/claude-3-haiku-20240307 |
| Anthropic Claude 3 Opus | 200,000 | 4,096 | anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229 |
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Haiku | 200,000 | 8,192 | anthropic/claude-3-5-haiku-20241022 |
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet v1 | 200,000 | 8,192 | anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620 |
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet v2 | 200,000 | 8,192 | anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 |
| Anthropic Claude 3.7 Sonnet | 200,000 | 64,000 | anthropic/claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219 |
| Anthropic Claude Opus 4 | 200,000 | 32,000 | anthropic/claude-opus-4-20250514 |
| Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4 | 200,000 | 64,000 | anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514 |
Azure OpenAI¶
Azure OpenAI LLM availability
| Type | Max context window | Max completion tokens | Chat model ID Δ | Provider region availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI GPT-4o mini | 128,000 | 16,384 | azure/gpt-4o-mini |
|
| OpenAI GPT-4o | 128,000 | 16,384 | azure/gpt-4o-2024-11-20 |
|
| OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo | 128,000 | 4,096 | azure/gpt-4-turbo |
|
| OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo | 16,385 | 4,096 | azure/gpt-35-turbo |
|
| OpenAI o3-mini | 200,000 | 100,000 | azure/o3-mini |
|
| OpenAI o4-mini | 200,000 | 100,000 | azure/o4-mini |
|
| OpenAI o1 | 200,000 | 100,000 | azure/o1 |
|
| OpenAI o3 | 200,000 | 100,000 | azure/o3 |
|
| OpenAI o1-mini† | 128,000 | 65,536 | azure/o1-mini |
|
| OpenAI GPT-5 | 400,000 | 128,000 | azure/gpt-5-2025-08-07 |
|
| OpenAI GPT-5 mini | 400,000 | 128,000 | azure/gpt-5-mini-2025-08-07 |
|
| OpenAI GPT-5 nano | 400,000 | 128,000 | azure/gpt-5-nano-2025-08-07 |
|
Google VertexAI¶
Google VertexAI LLM availability
| Type | Max context window | Max completion tokens | Chat model ID Δ | Provider region availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claude 3 Haiku | 200,000 | 4,096 | vertex_ai/claude-3-haiku@20240307 |
|
| Claude 3 Opus† | 200,000 | 4,096 | vertex_ai/claude-3-opus@20240229 |
|
| Claude 3.5 Haiku† | 200,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/claude-3-5-haiku@20241022 |
|
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | 200,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/claude-3-5-sonnet@20240620 |
|
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet v2 | 200,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/claude-3-5-sonnet-v2@20241022 |
|
| Claude 3.7 Sonnet | 200,000 | 64,000 | vertex_ai/claude-3-7-sonnet@20250219 |
|
| Claude Opus 4† | 200,000 | 32,000 | vertex_ai/claude-opus-4@20250514 |
|
| Claude Sonnet 4 | 200,000 | 64,000 | vertex_ai/claude-sonnet-4@20250514 |
|
| Claude Opus 4.1† | 200,000 | 32,000 | vertex_ai/claude-opus-4-1@20250805 |
|
| Google Gemini 1.5 Flash | 1,048,576 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/gemini-1.5-flash-002 |
|
| Google Gemini 1.5 Pro | 1,048,576 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/gemini-1.5-pro-002 |
|
| Google Gemini 2.0 Flash | 1,048,576 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/gemini-2.0-flash-001 |
|
| Google Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite | 1,048,576 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/gemini-2.0-flash-lite-001 |
|
| Llama 3.1 8B Instruct MAAS† © | 128,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-3.1-8b-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 3.1 70B Instruct MAAS† © | 128,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-3.1-70b-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 3.1 405B Instruct MAAS† © | 128,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-3.1-405b-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 3.2 90B Vision Instruct† © | 128,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-3.2-90b-vision-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 3.3 70B Instruct† © | 128,000 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-3.3-70b-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 4 Maverick 17B 128E Instruct MAAS† © | 524,288 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-4-maverick-17b-128e-instruct-maas |
|
| Llama 4 Scout 17B 16E Instruct MAAS† © | 1,310,720 | 8,192 | vertex_ai/meta/llama-4-scout-17b-16e-instruct-maas |
|
| Mistral CodeStral 2501 | 32,000 | 32,000 | vertex_ai/codestral-2501 |
|
| Mistral Large 2411 | 128,000 | 128,000 | vertex_ai/mistral-large-2411 |
|
| OpenAI gpt-oss-120b | 131,072 | 32,768 | vertex_ai/openai/gpt-oss-120b-maas |
|
| OpenAI gpt-oss-20b | 131,072 | 32,768 | vertex_ai/openai/gpt-oss-20b-maas |
|
Deprecated and retired LLMs¶
In the quickly advancing agentic AI landscape, LLMs are constantly improving, with new versions replacing older models. To address this, DataRobot's LLM deprecation process marks LLMs and LLM blueprints with a badge to indicate upcoming changes. The goal is to help protect experiments and deployments from unexpected removal of provider support. Note that retirement dates are set by the provider and are subject to change.
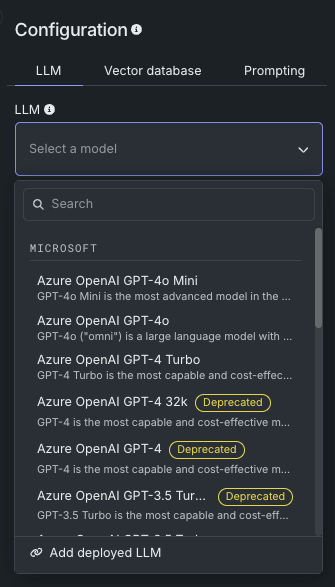
Badges for deprecated LLMs are shown in the LLM blueprint creation panel:
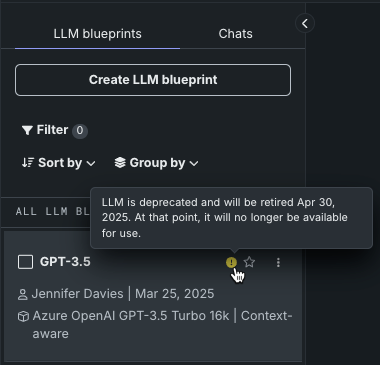
Or if built, affected LLM blueprints are marked with a warning or notice, with dates provided on hover:
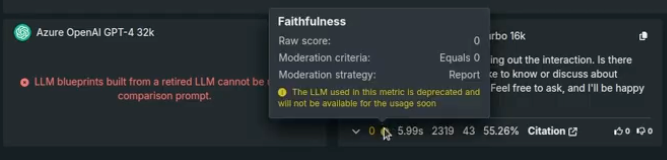
Once LLM blueprints are built, they are displayed in the LLM blueprints tab. Deprecated or retired LLM blueprints are marked with a warning or notice, with dates provided on hover:
-
When an LLM is in the deprecation process, support for the LLM will be removed in 90 days. Badges and warnings are present, but functionality is not restricted.
-
When retired, assets created from the retired model are still viewable, but the creation of new assets is prevented. Retired LLMs cannot be used in single or comparison prompts.
Some evaluation metrics, for example faithfulness and correctness, use an LLM in their configuration. For those, messages are displayed when viewing or configuring the metrics, as well as in the prompt response.
If an LLM has been deployed, because DataRobot does not have control over the credentials used for the underlying LLM, the deployment will fail to return predictions. If this happens, replace the deployed LLM with a new model.
The following LLMs are currently, or will soon be, deprecated and removed:
| LLM | Retirement date |
|---|---|
| Anthropic Claude 2.1 | Retired |
| Anthropic Claude 3 Sonnet | Retired |
| Cohere Command Light Text v14 | Retired |
| Cohere Command Text v14 | Retired |
| Titan | Retired |
| LLM | Retirement date |
|---|---|
| GPT-3.5 Turbo | October 15, 2025 |
| GPT-3.5 Turbo 16k | Retired |
| GPT-4 | Retired |
| GPT-4 32k | Retired |
| GPT-4 Turbo | October 15, 2025 |
| GPT-4o Mini | August 16, 2025 |
| o1-mini | October 27, 2025 |
| LLM | Retirement date |
|---|---|
| Bison | Retired |
| Gemini 1.5 Flash | September 24, 2025 |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | September 24, 2025 |
If an LLM has been deployed, because DataRobot does not have control over the credentials used for the underlying LLM, the deployment will fail to return predictions. If this happens, replace the deployed LLM with a new model.
Embeddings availability¶
DataRobot supports the following types of embeddings for encoding data; all are transformer models trained on a mixture of supervised and unsupervised data.
| Embedding type | Description | Language |
|---|---|---|
| cl-nagoya/sup-simcse-ja-base | A medium-sized language model from the Nagoya University Graduate School of Informatics ("Japanese SimCSE Technical Report"). It is a fast model for Japanese RAG.
|
Japanese |
| huggingface.co/intfloat/multilingual-e5-base | A medium-sized language model from Microsoft Research ("Weakly-Supervised Contrastive Pre-training on large MultiLingual corpus") used for multilingual RAG performance across multiple languages.
|
100+, see ISO 639 |
| huggingface.co/intfloat/multilingual-e5-small | A smaller-sized language model from Microsoft Research ("Weakly-Supervised Contrastive Pre-training on large MultiLingual corpus") used for multilingual RAG performance with faster performance than the MULTILINGUAL_E5_BASE. This embedding model is good for low-latency applications.
|
100+, see ISO 639 |
| intfloat/e5-base-v2 | A medium-sized language model from Microsoft Research ("Weakly-Supervised Contrastive Pre-training on large English Corpus") for medium-to-high RAG performance. With fewer parameters and a smaller architecture, it is faster than E5_LARGE_V2.
|
English |
| intfloat/e5-large-v2 | A large language model from Microsoft Research ("Weakly-Supervised Contrastive Pre-training on large English Corpus") designed for optimal RAG performance. It is classified as slow due to its architecture and size.
|
English |
| jinaai/jina-embedding-t-en-v1 | A tiny language model trained using Jina AI's Linnaeus-Clean dataset. It is pre-trained on the English corpus and is the fastest, and default, embedding model offered by DataRobot.
|
English |
| jinaai/jina-embedding-s-en-v2 | Part of the Jina Embeddings v2 family, this embedding model is the optimal choice for long-document embeddings (large chunk sizes, up to 8192).
|
English |
| sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 | A small language model fine-tuned on a 1B sentence-pairs dataset. It is relatively fast and pre-trained on the English corpus. It is not recommend for RAG, however, as it was trained on old data.
|
English |
* Input Dimension = max_sequence_length
Multilingual language support for E5-base and E5-small, see also ISO 639
Supported languages:
"Afrikaans",
"Amharic",
"Arabic",
"Assamese",
"Azerbaijani",
"Belarusian",
"Bulgarian",
"Bengali",
"Breton",
"Bosnian",
"Catalan",
"Czech",
"Welsh",
"Danish",
"German",
"Greek",
"English",
"Esperanto",
"Spanish",
"Estonian",
"Basque",
"Persian",
"Finnish",
"French",
"Western Frisian",
"Irish",
"Scottish Gaelic",
"Galician",
"Gujarati",
"Hausa",
"Hebrew",
"Hindi",
"Croatian",
"Hungarian",
"Armenian",
"Indonesian",
"Icelandic",
"Italian",
"Japanese",
"Javanese",
"Georgian",
"Kazakh",
"Khmer",
"Kannada",
"Korean",
"Kurdish",
"Kyrgyz",
"Latin",
"Lao",
"Lithuanian",
"Latvian",
"Malagasy",
"Macedonian",
"Malayalam",
"Mongolian",
"Marathi",
"Malay",
"Burmese",
"Nepali",
"Dutch",
"Norwegian",
"Oromo",
"Oriya",
"Panjabi",
"Polish",
"Pashto",
"Portuguese",
"Romanian",
"Russian",
"Sanskrit",
"Sindhi",
"Sinhala",
"Slovak",
"Slovenian",
"Somali",
"Albanian",
"Serbian",
"Sundanese",
"Swedish",
"Swahili",
"Tamil",
"Telugu",
"Thai",
"Tagalog",
"Turkish",
"Uyghur",
"Ukrainian",
"Urdu",
"Uzbek",
"Vietnamese",
"Xhosa",
"Yiddish",
"Chinese"
Sharing and permissions¶
The following table describes GenAI component-related user permissions. All roles (Consumer, Editor, Owner) refer to the user's role in the Use Case; access to various function are based on the Use Case roles. For example, because sharing is handled on the Use Case level, you cannot share only a vector database (vector databases do not define any sharing rules).
Permissions for GenAI functions
| Function | Use Case Consumer | Use Case Editor | Use Case Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vector database | |||
| Vector database creators | |||
| Create vector database | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Create vector database version | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Edit vector database info | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Delete vector database | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Vector database non-creators | |||
| Edit vector database info | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| Delete vector database | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| Playground | |||
| Playground creators | |||
| Create playground | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Rename playground | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Edit playground description | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Delete playground | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Playground non-creators | |||
| Edit playground description | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| Delete playground | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| Playground → Assessment tab | |||
| Configure assessment | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Enable/disable assessment metrics | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Playground → Tracing tab | |||
| Download log | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Upload to AI Catalog | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| LLM blueprint created by others (shared Use Case) | |||
| Configure | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Send prompts (from Configuration) | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Generate aggregated metrics | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Create conversation (from Comparison) | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Upvote/downvote responses | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Star/favorite | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Copy to new LLM blueprint | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Delete | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Register | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
Supported dataset types¶
When uploading datasets for use in creating a vector database, the supported formats are either .zip or .csv. Two columns are mandatory for the files—document and document_file_path. Additional metadata columns, up to 50, can be added for use in filtering during prompt queries. Note that for purposes of metadata filtering, document_file_path is displayed as source.
For .zip files, DataRobot processes the file to create a .csv version that contains text columns (document) with an associated reference ID (document_file_path) column. All content in the text column is treated as strings. The reference ID column is created automatically when the .zip is uploaded. All files should be either in the root of the archive or in a single folder inside an archive. Using a folder tree hierarchy is not supported.
Regarding file types, DataRobot provides the following support:
-
.txtdocuments -
PDF documents
- Text-based PDFs are supported.
- To extract text from image-based PDFs, you must use the Python API client. Extracting text from image-based PDFs via the GUI is not fully supported.
- Documents with mixed image and text content are supported; only the text is parsed.
- Single documents consisting only of images result in empty documents and are ignored.
- Datasets consisting of image-only documents (no text) are not processable.
-
.docxdocuments are supported but older.docformat is not supported. -
.mddocuments, and the.markdownvariant, are supported. -
A mix of all supported document types in a single dataset is allowed.
General considerations¶
-
If a multilingual dataset exceeds the limit associated with the multilingual model, DataRobot defaults to using the
jinaai/jina-embedding-t-en-v1embedding model. -
Deployments created from custom models with training data attached that have extra columns cannot be used unless column filtering is disabled on the custom model.
-
When using LLMs that are either BYO or deployed from the playground and require a runtime parameter to point to the endpoint associated with their credentials: Be aware of the vendor's model versioning and end-of-life schedules. As a best practice, use only endpoints that are generally available when deploying to production. (Models provided in the playground manage this for you.)
-
Note that an API key named
[Internal] DR API Access for GenAI Experimentationis created for you when you access the playground or vector database in the UI. -
When using GPUs, BYO embeddings functionality is available for self-managed users only. Note that when many users run vector database creation jobs in parallel, if using BYO embeddings, LLM playground functionality may be degraded until vector database creation jobs complete. Using CPUs with a custom model that contains the embeddings model is supported in all environments.
-
Only one aggregated metric job can run at a time. If an aggregation job is currently running, the Configure aggregation button is disabled and the "Aggregation job in progress; try again when it completes" tooltip appears.
Playground considerations¶
-
Playgrounds can be shared for viewing, and users with editor or owner access can perform additional actions within the shared playground, such as creating blueprints. While non-creators cannot prompt an LLM blueprint in the playground, they can make a copy and submit prompts to that copy.
-
You can only prompt LLM blueprints that you created (i.e., in both configuration and comparison view). To see the results of prompting another user’s LLM blueprint in a shared Use Case, copy the blueprint, and then you can chat with the same settings applied.
-
Each user can submit 5000 LLM prompts per day across all LLMs, where deleted prompts and responses are also counted. However, only successful prompt response pairs are counted and bring-your-own (BYO) LLM calls are not part of the count. Limits for trial users are different, as described here.
Vector database considerations¶
The following describes considerations related to vector databases. See also the supported dataset types, below.
GPU usage for Self-Managed users
When working with datasets over 1GB, Self-Managed users who do not have GPU usage configured on their cluster may experience serious delays. Email DataRobot Support, or visit the Support site, for installation guidance.
-
Creation:
-
By default, DataRobot uses the Facebook AI Similarity Search (FAISS) vector database.
-
For internal (FAISS) vector databases, a 10GB dataset limit is applied during vector database creation and resulting vector database asset size (text after extraction).
-
The following apply to Pinecone or Elasticsearch connected (external) vector databases:
- They support up to 100GB.
- You cannot create a version (child) from a connected vector database.
- You cannot create a connected vector database from a parent vector database.
- You can add data to a connected vector database “in place” without creating a new version.
-
-
Deployment:
- When deploying vector databases for 10GB datasets, the vector database custom model may require more RAM than the default of 4GB. The custom model resource allocation settings are configurable by the organization administrator.
-
Token budget:
-
When determining the number of contexts to retrieve from the vector database, DataRobot allocates 3/4 of the excess token budget (the context size for the LLM) to retrieved documents and the rest to chat history (if applicable).
-
The token budget is comprised of system prompt, user prompt, and max completion length. The excess token budget is
context size - (max completion length + system prompt + user prompt). -
If there is no chat history, the whole excess budget is used for document retrieval. Similarly, if there is no vector database, excess budget is used for history.
-
-
Chunking:
- Vector database creation with semantic chunking can fail when individual documents in the dataset contain very large texts. The exact limits are not known, but if you experience the error, use recursive chunking instead.
-
-
Metadata filtering is only supported in RAG playgrounds.
-
Metadata filtering only supports exact pattern matching (no partial strings or relative expressions).
-
When multiple strings are entered, DataRobot applies an implicit AND. No other operators are supported.
-
Vector databases created before the introduction of metadata filtering do not support this feature. To use filtering with them, create a version from the original and configure the LLM blueprint to use the new vector database instead.
-
The following are internal column names and should not be used to define metadata column:
chunk_id,start_index,page,similarity_score,pagebreak_indices,content,_doc_vector, andchunk_size. -
For purposes of metadata filtering, the
document_file_pathcolumn name is displayed assource. -
Metadata filtering for BYO vector databases, like all BYO functionality, requires additional configuration. Because the BYO component must be a standalone drop-in replacements for DataRobot internal vector databases, it must implement the complete vector database functionality: handle an input dataframe containing columns for the
queryand search parametersk,filterandadd_neighbor_chunks, and return the matching most similar documents, including potential metadata in an unstructured format.
-
See also supported dataset types.
Playground deployment considerations¶
Consider the following when registering and deploying LLMs from the playground:
-
Setting API keys through the DataRobot credential management system is supported. Those credentials are accessed as environment variables in a deployment.
-
Registration and deployment is supported for:
-
All base LLMs in the playground.
-
LLMs with vector databases.
-
-
The creation of a custom model version from an LLM blueprint associated with a large vector database (500MB+) can be time-consuming. You can leave the workshop while the model is created and will not lose your progress.
Bolt-on Governance API¶
-
When using the Bolt-on Governance API with a deployed LLM blueprint, see LLM availability for the recommended values of the
modelparameter. Alternatively, specify a reserved value,model="datarobot-deployed-llm", to let the LLM blueprint select the relevant model ID automatically when calling the LLM provider's services. In Workbench, when adding a deployed LLM that implements thechatfunction, the playground uses the Bolt-on Governance API as the preferred communication method. Enter the Chat model ID associated with the LLM blueprint to set themodelparameter for requests from the playground to the deployed LLM. Alternatively, enterdatarobot-deployed-llmto let the LLM blueprint select the relevant model ID automatically when calling the LLM provider's services. -
Configuring evaluation and moderation for the custom model negates the effect of streaming responses in the chat completion API, since guardrails evaluate the complete response of the LLM and return the response text in one chunk.
-
The following OpenAI parameters are not supported in the Bolt-on Governance API:
functions,tool,tool_choice,logprobs,top_logprobs.
LLM evaluation and moderation¶
The following describes considerations related to LLM evaluation and moderation:
-
You can generate synthetic datasets in both the UI and API. Use GPT-4, if possible, as it best follows the format DataRobot expects for output format. Otherwise, the LLM might not generate question-answer pairs.
-
Metrics:
-
For NeMo metrics, the
blocked_terms.txtfile is shared between the prompt and response metrics. As a result, modifyingblocked_terms.txtin the prompt metric will modify it for the response metric and vice versa. -
All metrics can be copied and duplicates can exist, with the following exception: Only two NeMo stay on topic metrics can exist in a custom model, one for input and one for output (NeMo metric prompt and one NeMo response metric).
-
The Faithfulness and Correctness metrics will return 0 if the LLM you chose does not produce the correct output format.
-
When transferring metrics to a production environment, if the guard for a metric is not enabled in the playground it is transferred as a report guard to production.
-
-
Moderations:
-
The Report moderation method triggers a warning for an evaluation metric when the guard condition is met. The Report and block moderation method triggers a warning and displays a moderation message, defined for each metric. The Replace moderation method is not available in the playground.
-
When a playground evaluation metric and moderation configuration is sent to the workshop, the evaluation metric is created as a custom metric, including the guard condition (if enabled). Moderation settings do not need to be configured for a playground evaluation metric to create a custom metric and log the base metric scores during the export to the workshop.
-
When a playground evaluation metric and moderation configuration is sent to the workshop, the moderation configuration is applied after the first custom model version is created. As a result, any evaluation metric exported from the playground includes a second custom model version containing the moderation configuration. This additional step must be complete, and the second version of the custom model must be available, before the custom model is ready to be used with moderations.
-
-
Aggregation:
-
In the evaluation dataset aggregation table, the Current configuration only toggle compares only those metrics sharing the configuration currently displayed in LLM tab of the Configuration sidebar. Old aggregation records may not contain the LLM blueprint configurations used and will default to the LLM blueprint configuration migration that occurred in September 2024. All new aggregation records moving forward track the LLM blueprint configuration used for computation.
-
If multiple LLM blueprints are part of a request, DataRobot computes aggregation blueprint-by-blueprint, sequentially, to avoid LLM limit issues.
-
Trial user considerations¶
The following considerations apply only to DataRobot free trial users:
-
You can create up to 15 vector databases, computed across multiple Use Cases. Deleted vector databases are included in this count.
-
You can make 1000 LLM API calls, where deleted prompts and responses are also counted. However, only successful prompt response pairs are counted.