Create and manage prompts¶
Prompts are a fundamental part of interacting with, and generating outputs from, LLMs and agents. Access the prompt management system from the Prompts tile within Registry for a centralized, version-controlled, and integrated system for prototyping, experimenting, deploying, and monitoring prompts as agent components.
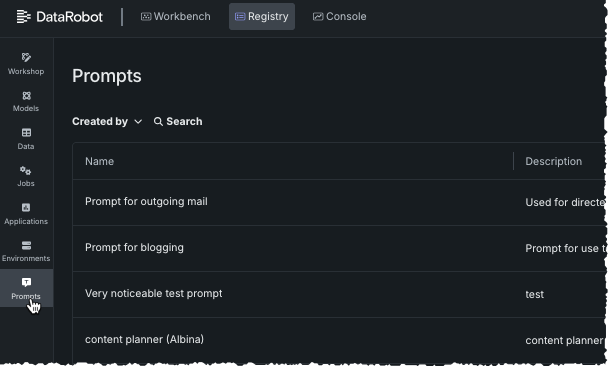
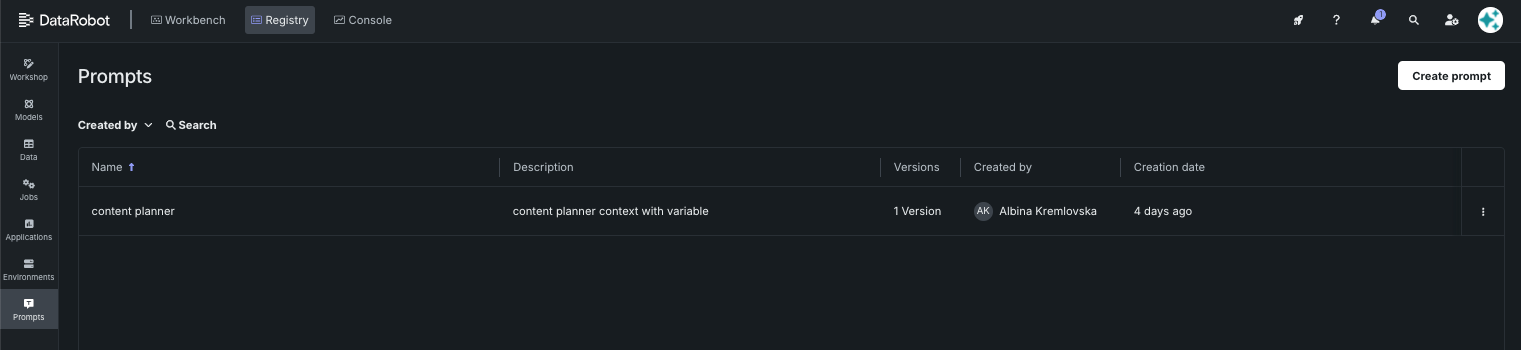
The Prompts tile initially lists all saved and shared prompts. Click an entry for configuration details.
The system supports:
- Creating prompts.
- Versioning capabilities, for iterating on to prompts.
- Managing prompts by comparing and sharing prompts with users or organizations.
- Calling a prompt in an agent.
Details: Prompt management benefits
Managing prompts as simple text files creates significant risks and inefficiencies in building production-grade AI agents. DataRobot's prompt management system addresses the major issues, as described in the table below.
| Problem | Prompt management system solution |
|---|---|
| Versioning conflicts | Versioning, which is essential for tracking changes, ensures reproducibility, facilitates rollbacks to stable versions, and creates a clear audit trail for collaboration, debugging, and compliance. |
| Lack of consistency | Templates allow you to standardize and reuse prompt structures, separating static instructions from dynamic data. The result is faster iteration, consistency, and easier updates without changing application code. |
| Compliance violations | Governance provides a controlled process for creating, testing, and deploying prompts. This ensures quality, security, and compliance through centralized registries and approval workflows, which is vital for enterprises. Governance also helps mitigate security risks, such as prompt injection attacks or data leakage, by enforcing policies on the types of data that can be included in a prompt. For large organizations, centralized management and oversight prevent the proliferation of inconsistent or low-quality prompts and provide a comprehensive view of how LLMs are being used across the company. |
| Standalone testing | Integrated platforms enable experimentation and evaluation with data-driven prompt engineering. A/B, side-by-side testing and performance tracking (cost, latency, quality) help to identify the most effective prompts. |
Create prompts¶
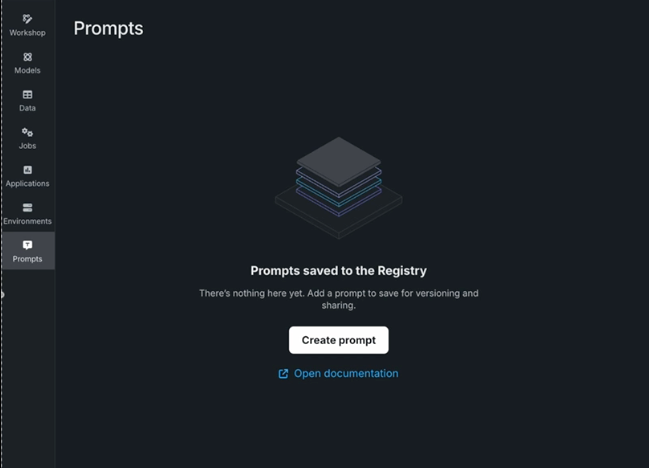
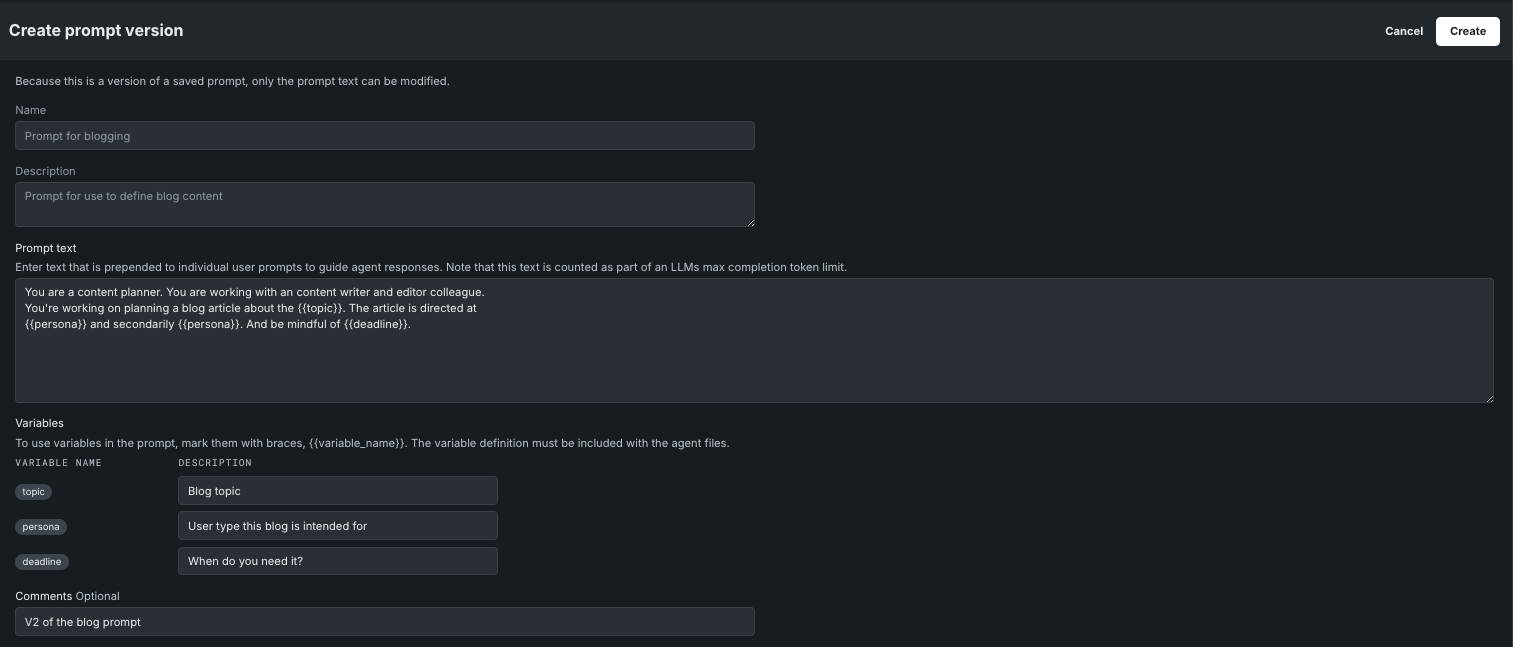
To create a prompt, open Registry > Prompt. The prompt library opens with a Create prompt button available.
Click Create prompt and complete the fields. All fields support a maximum of 5000 characters.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter a name for the prompt. The name must contain only letters, numbers, underscores (_), dashes (-), spaces, and brackets. |
| Description | Enter a description for the prompt. The description is for developer information; it displays on the prompt library landing page and the individual prompt details page. |
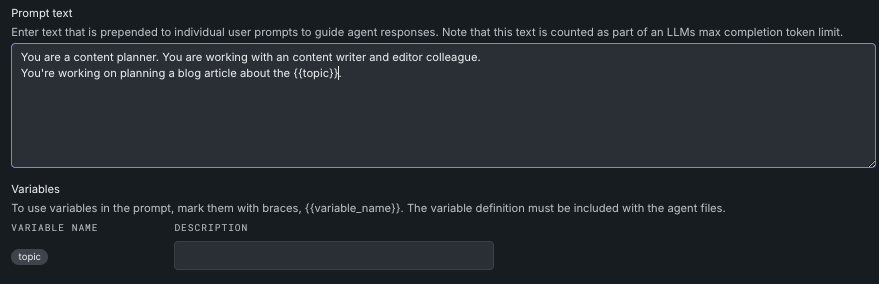
| Prompt text | Enter the text that will be included with each individual user prompt. Prompt text can contain variables, as described below. Note that text entered in this field is counted as part of an LLM's max completion token limit. You can use a maximum of 100 variables in a single prompt. |
| Variables | Enter a variable name marked with double braces {{ variable_name }}. The variable definition must be included with the agent files and must contain only letters, numbers, and underscores (_). Variable character limits are:
|
| Comments (optional) | Enter text to display on individual prompt details page. |
If you are not using variables, click Create. Otherwise see the section on adding variables.
Also, see prompt versioning for details on modifying existing prompts.
Add variables¶
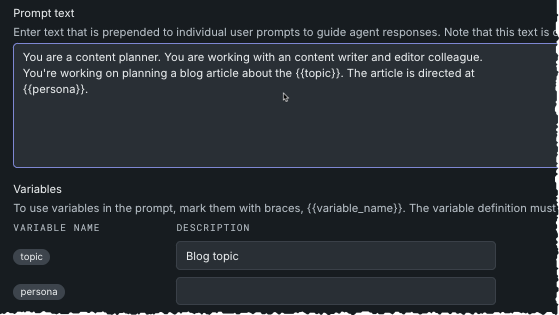
If you enter a variable in the Prompt text field, the Variables section expands to include a description field. The description is required; the content of this field displays on the individual prompt details page. It does not define the variable. Variable must be defined in the MyAgent class of the agents.py file.
To include a variable:
-
Define the variable(s) in
agents.py. Note that this step does not have to be completed first but must be completed before testing the prompt. -
Enter the prompt text, indicating a variable using double brackets ({{ }}) around the variable name. With each variable you reference, an entry for that variable is included in the Variables section.
You can use the same variable multiple times in the prompt text.
-
Click Create.
View defined prompts¶
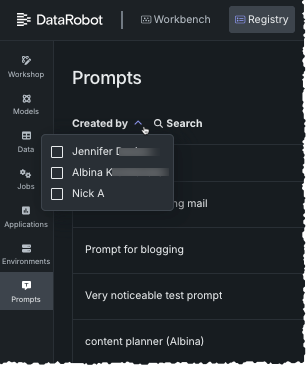
When you click the Prompts tile in Registry, the prompt library opens listing all prompts created by, or shared with, you. You can search for the prompt name or use the Created by filter to search by creator.
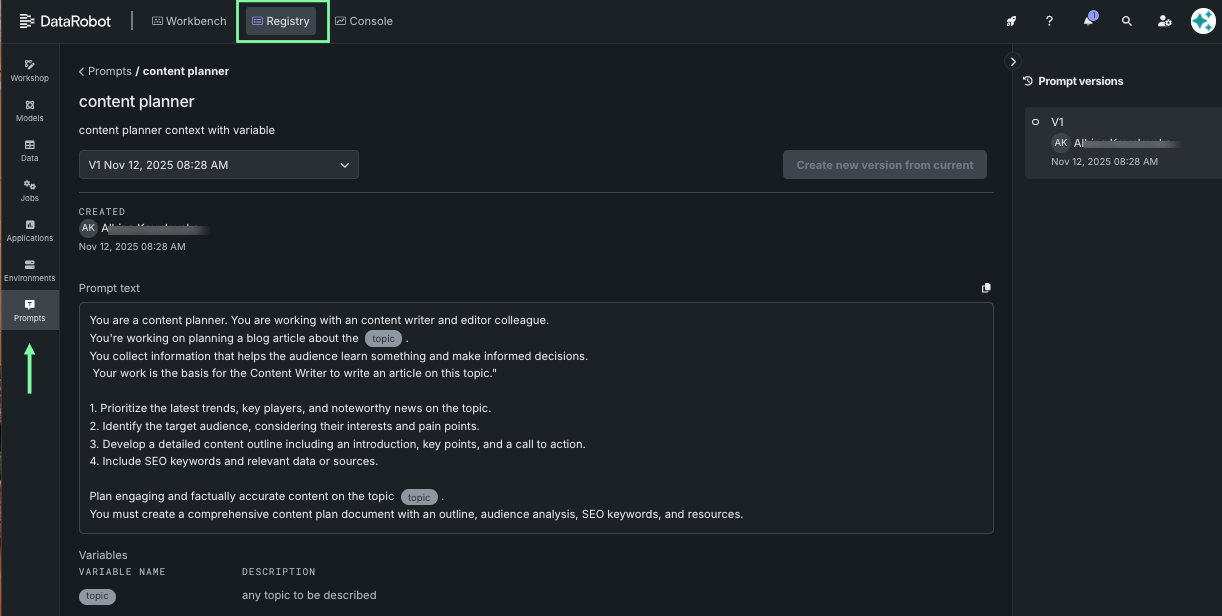
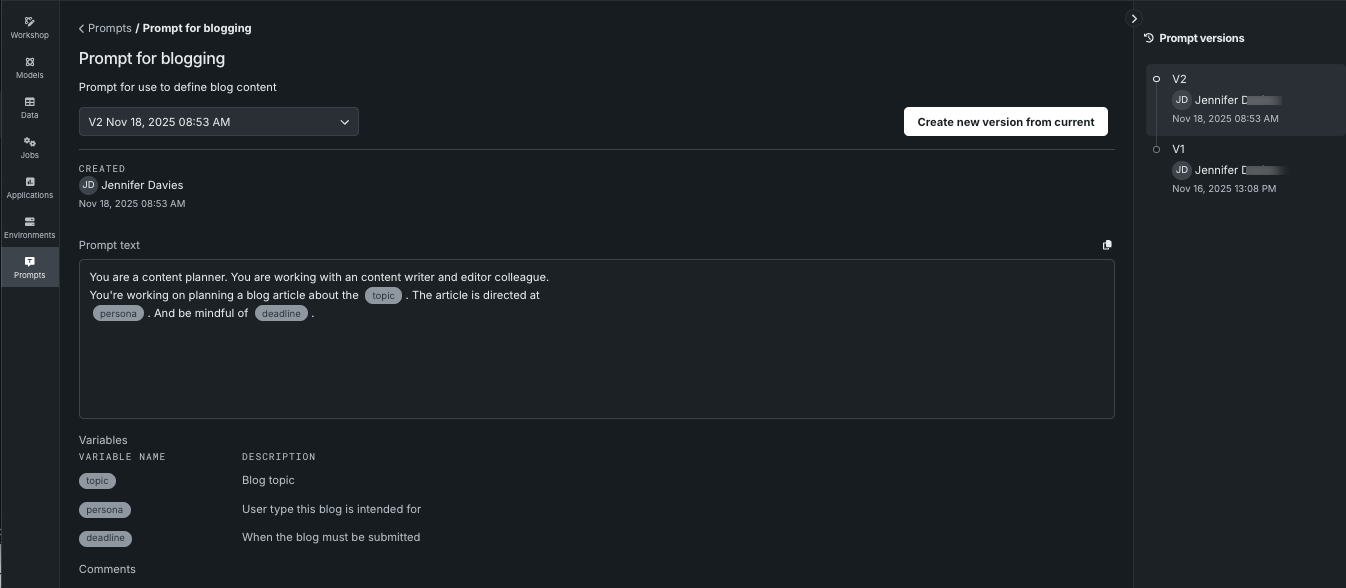
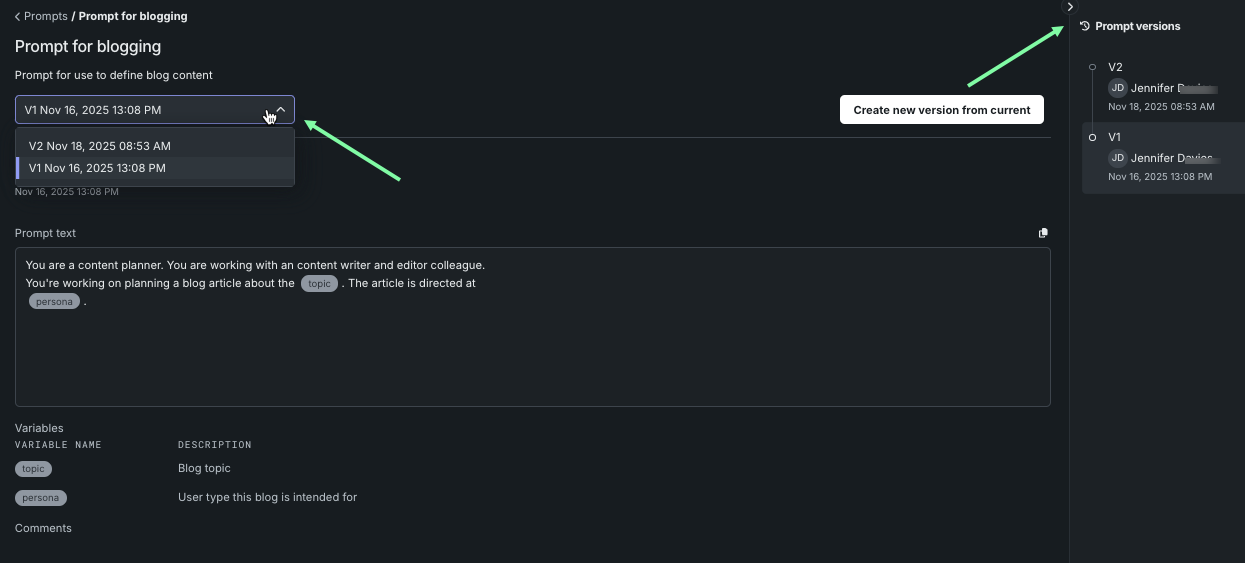
Click an entry to see details of the newest version of the prompt. A list of all versions is displayed in the right panel. To view a different version, click a version in the panel or use the dropdown.
The prompt displayed is read-only. To modify it, create a new version.
Create prompt versions¶
Prompt versioning is vital for managing changes to prompts over time, as even small alterations can significantly impact an LLM's output. This practice ensures reproducibility, allowing teams to link specific model outputs to the exact prompt version that generated them, and facilitates quick rollbacks to stable versions if new changes degrade performance.
To version prompts:
-
Click on the prompt you want to modify from the table list of prompts on the Prompts tile in Registry. The display shows the most recent version of the prompt; it is read-only.
-
Click Create new version from current in the upper right to open the canvas for creating a new version of the prompt. The existing prompt text, variables, and comments area are now editable. The name and description are not.
-
Modify the text and variables, as needed. Be sure that all description fields are complete.
-
Click Create. The new prompt is displayed in the versions panel.
Manage prompts¶
Once you have created prompts, or prompts have been shared with you, you can sort, compare, and share them. Access the prompt management system from the Prompts tile within Registry.
Filter table listing¶
You can filter the prompt table to list only those prompts created by certain users. To do so, select prompt creators from the Created by dropdown.
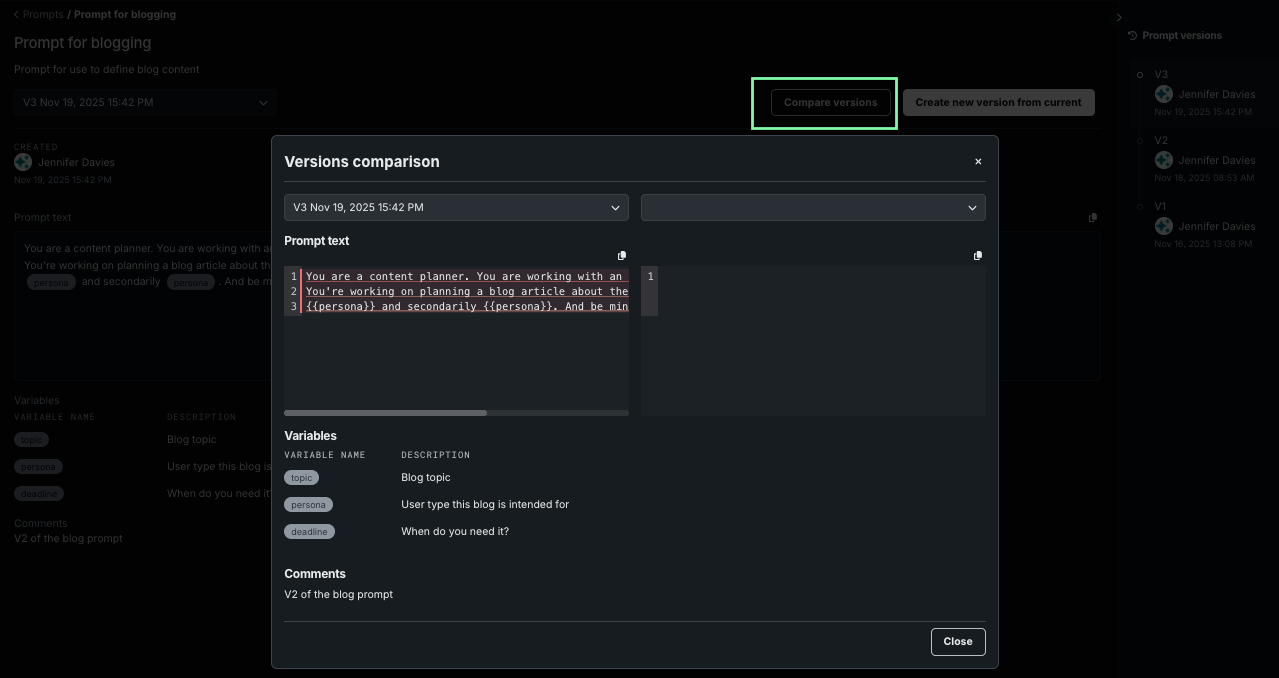
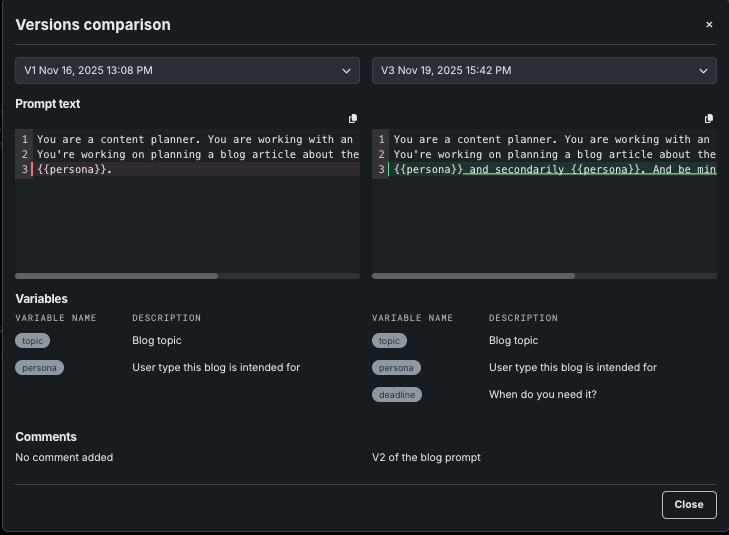
Compare versions¶
Use the Compare versions functionality to review changes made between versions. To compare:
-
Select the prompt from the table listing. The latest version of the prompt opens.
-
Click Compare versions to open the comparison modal.
-
Using the dropdowns, select the versions to compare.
Color helps to identify changes in the prompt text; use the scrollbars to see complete entries. Changes in variable and comments are also indicated.
Share prompts¶
You can share prompts with a user, group, or organization. An owner can share, change roles, or create new versions from the existing prompt. To share the prompt, click the Action menu and choose Share prompt.
The standard sharing modal appears.