トレースの実装¶
OpenTelemetry(OTel)は、エージェントに包括的なオブザーバビリティを提供し、エージェントの実行をリアルタイムで監視、トレース、デバッグすることができます。 このガイドでは、エージェントツールにカスタムトレースを追加して、詳細な実行情報を取得する方法を説明します。
OpenTelemetryによるトレースは、以下のことに役立ちます。
- エージェントのパフォーマンスと実行フローを監視する。
- 詳細な実行トレースを追跡することで、問題をデバッグする。
- ツールの実行パターンとタイミングを把握する。
- ツールのカスタム属性とメタデータを確認する。
エージェントテンプレートには、CrewAI、LangGraph、Llama-Indexなどのフレームワーク向けのOpenTelemetry計装がすでに含まれています。 この計装により、以下のスパンが自動的に取得されます。
- エージェントの実行
- ツールの起動
- LLM APIの呼び出し
- HTTPリクエスト
ツールにカスタムスパンやカスタム属性を追加することで、このデフォルトトレースを強化することができます。
ツールにカスタムトレースを追加する¶
OpenTelemetryのカスタムトレースをツールに追加して、ツールの実行に関する追加情報を取得します。 これにより、ユースケースに固有のカスタム属性、中間出力、実行の詳細を追跡できます。
ツールにカスタムトレースを追加する基本的なパターンは以下のとおりです。
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
# Within your tool's execution
with tracer.start_as_current_span("my_custom_span_name"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
current_span.set_attribute("custom.attribute", "value")
# Your tool logic here
result = perform_tool_action()
# Optionally add more attributes about the result
current_span.set_attribute("result.status", "success")
current_span.set_attribute("result.size", len(result))
return result
ツール例¶
OpenTelemetryのカスタムトレースをエージェントツールに追加する方法については、以下のコード例を参照してください。
import requests
from crewai.tools import BaseTool
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
class WeatherTool(BaseTool):
name = "weather_tool"
description = (
"Fetches the current weather for a specified city. "
"Requires an API key from OpenWeatherMap."
)
def run(self, city: str) -> str:
with tracer.start_as_current_span("weather_tool_fetch"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
# Set custom attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.city", city)
current_span.set_attribute("weather.api", "openweathermap")
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY" # Replace with your API key
base_url = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
params = {"q": city, "appid": api_key, "units": "metric"}
try:
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
weather = data['weather'][0]
main = data['main']
# Add result attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.temperature", main['temp'])
current_span.set_attribute("weather.condition", weather['main'])
result = (
f"Current weather in {data['name']}, {data['sys']['country']}:\n"
f"Temperature: {main['temp']}°C (feels like {main['feels_like']}°C)\n"
f"Condition: {weather['main']} - {weather['description']}\n"
f"Humidity: {main['humidity']}%\n"
f"Pressure: {main['pressure']} hPa"
)
return result
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
current_span.set_attribute("weather.error", str(e))
return f"Error fetching weather data: {str(e)}"
import requests
from langchain_core.tools import Tool
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
class WeatherTool(Tool):
name = "weather_tool"
description = (
"Fetches the current weather for a specified city. "
"Requires an API key from OpenWeatherMap."
)
def run(self, city: str) -> str:
with tracer.start_as_current_span("weather_tool_fetch"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
# Set custom attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.city", city)
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY" # Replace with your API key
base_url = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
params = {"q": city, "appid": api_key, "units": "metric"}
try:
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
# Add result attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.temperature", data['main']['temp'])
result = f"Temperature in {city}: {data['main']['temp']}°C"
return result
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
current_span.set_attribute("weather.error", str(e))
return f"Error: {str(e)}"
import requests
from llama_index.tools import BaseTool
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
class WeatherTool(BaseTool):
name = "weather_tool"
description = (
"Fetches the current weather for a specified city. "
"Requires an API key from OpenWeatherMap."
)
def _run(self, city: str) -> str:
with tracer.start_as_current_span("weather_tool_fetch"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
# Set custom attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.city", city)
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY" # Replace with your API key
base_url = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
params = {"q": city, "appid": api_key, "units": "metric"}
try:
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
# Add result attributes
current_span.set_attribute("weather.temperature", data['main']['temp'])
result = f"Temperature in {city}: {data['main']['temp']}°C"
return result
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
current_span.set_attribute("weather.error", str(e))
return f"Error: {str(e)}"
ネストされたスパンの作成¶
ネストされたスパンを作成して、複数のステップからなる複雑なツールの実行を表します。
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
def complex_tool_workflow(input_data):
with tracer.start_as_current_span("complex_tool_main"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
current_span.set_attribute("input.size", len(input_data))
# First step in the workflow
with tracer.start_as_current_span("data_processing"):
processed_data = process_data(input_data)
trace.get_current_span().set_attribute("processed_items", len(processed_data))
# Second step in the workflow
with tracer.start_as_current_span("data_validation"):
validated_data = validate_data(processed_data)
trace.get_current_span().set_attribute("validated_items", len(validated_data))
# Third step in the workflow
with tracer.start_as_current_span("result_generation"):
result = generate_result(validated_data)
current_span.set_attribute("result.size", len(result))
return result
スパンにイベントを追加する¶
スパンにイベントを追加して、ツール実行の重要なタイミングをマークします。
from opentelemetry import trace
from datetime import datetime
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
def tool_with_events():
with tracer.start_as_current_span("tool_execution"):
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
# Add an event for when processing starts
current_span.add_event(
"Processing started",
{"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat()}
)
# Your tool logic
intermediate_result = perform_action()
# Add an event for mid-execution
current_span.add_event(
"Intermediate result ready",
{"result_count": len(intermediate_result)}
)
# More processing
final_result = complete_processing(intermediate_result)
# Add final event
current_span.add_event(
"Processing completed",
{"output_size": len(final_result)}
)
return final_result
エージェントにカスタムトレースを追加する¶
カスタムトレースを設定して、構成や環境の詳細を含むエージェントの起動方法を取り込むことができます。 ランタイムパラメーター(環境変数など)をスパンに表示するには、以下の手順に従います。
-
.envファイルを更新して、以下の環境変数を含め、ローカル開発時およびモデルをパッケージ化する際に使用できるようにします。EXAMPLE_ENV_VAR=my_example_value -
writer_agent/agentic_workflow/model-metadata.yamlにパラメーターを追加して、エージェントの実行時に挿入できるようにします。runtimeParameterDefinitions: - fieldName: EXAMPLE_ENV_VAR type: string defaultValue: SET_VIA_PULUMI_OR_MANUALLY -
infra/infra/llm.pyを更新して、ランタイムパラメーターをカスタムモデル環境に転送します。custom_model_runtime_parameters = [ # ...existing parameters... datarobot.CustomModelRuntimeParameterValueArgs( key="EXAMPLE_ENV_VAR", type="string", value=os.environ.get("EXAMPLE_ENV_VAR"), ), ] -
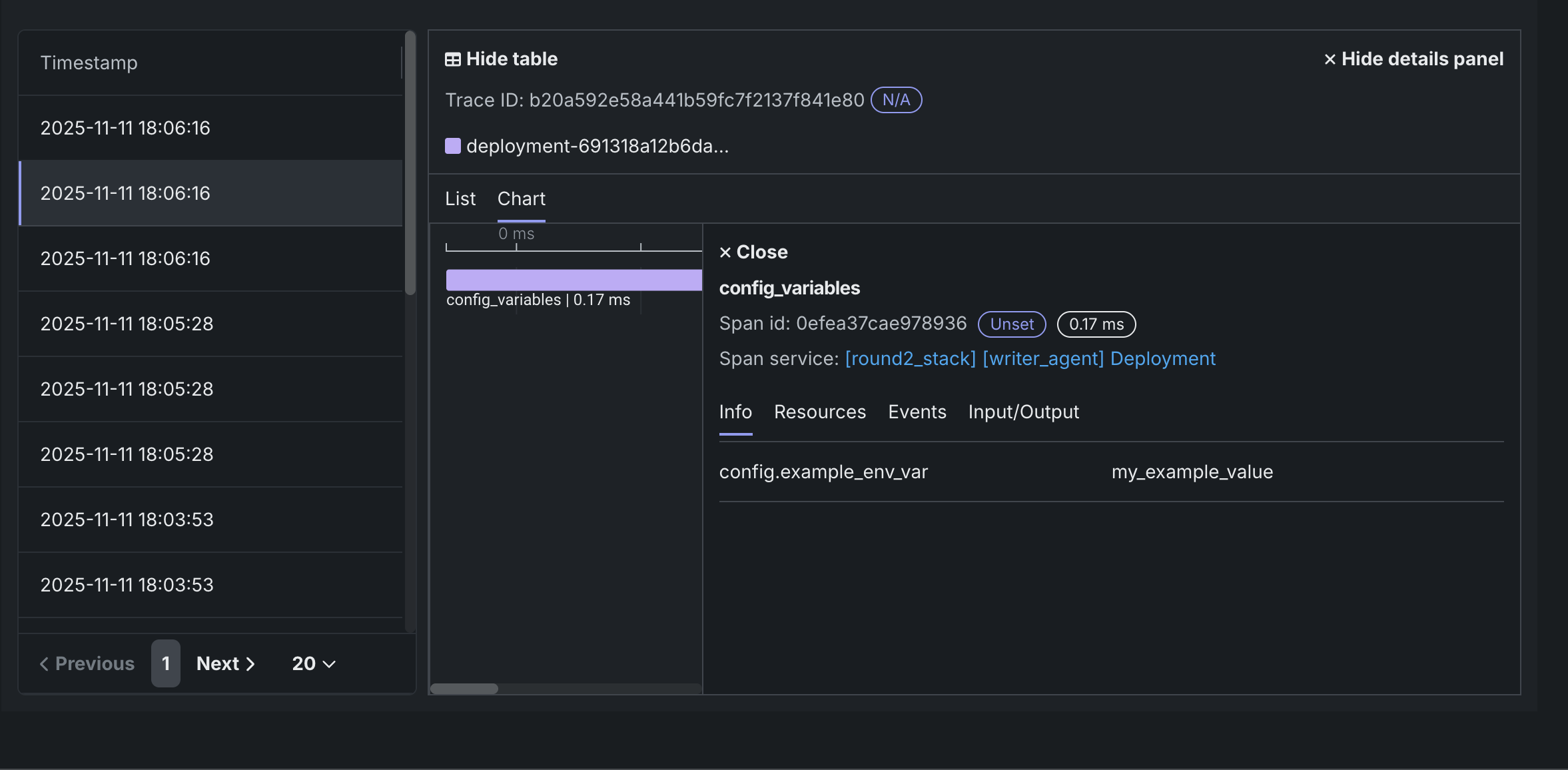
設定読み込みコードをスパンで囲み、
set_attributeとadd_eventに値を付加します。@property def agent_planner(self) -> Any: with tracer.start_as_current_span("config_variables"): current_span = trace.get_current_span() current_span.set_attribute("config.example_env_var", config.example_env_var) current_span.add_event("config attribute set on span") # ...agent code continued...
エージェントをデプロイして実行すると、トレースビジュアライザーは config.example_env_var=my_example_valueなどの属性を持つconfig_variablesスパンを表示します。 これにより、ランタイムパラメーターやその他の環境値が正しく読み込まれたことを簡単に確認できます。
ベストプラクティス¶
- わかりやすいスパン名を使用する:
- スパンには明確でわかりやすい名前を使います(たとえば、
"span1"ではなく"weather_fetch")。 - 必要に応じて、スパン名にツール名を含めます。
- スパンには明確でわかりやすい名前を使います(たとえば、
- 意味のある属性を設定する:
- 実行に関するコンテキストを提供する属性を追加します。
- 一貫性のある属性命名規則を使用します(例:
tool.input、tool.output、tool.error)。 - サイズ、カウント、ステータスなどの関連するメタデータを含めます。
- スパンを適切に使用する:
- すべてのコード行ではなく、重要な操作のためにスパンを作成します。
- 各スパンは、意味のある作業単位を表す必要があります。
- サブ操作を表すには、ネストされたスパンを使用します。