エージェントのカスタマイズ¶
エージェントを開発するには、agentic_workflowのソースコードを編集する必要があります。 開発プロセスにおいて、エージェントのテストやデプロイに役立つさまざまなツールやコマンドが提供されています。
Generic Baseテンプレート
generic_base`テンプレートを使用して、任意のフレームワークを使用してエージェントを構築することができます。しかし、このテンプレートには定義済みのエージェントコードが含まれていないため、エージェントのロジックと構造を自分で実装する必要があります。
エージェントコードの修正¶
エージェント開発の最初のステップは、目的の機能を実装するようにエージェントコードを修正することです。 メインのエージェントコードは、アプリケーションプロジェクトのagent/agentic_workflowディレクトリにあります。
agentic_workflow/
├── __init__.py # Package initialization
├── agent.py # Main agent implementation, including prompts
├── custom.py # DataRobot integration hooks
├── config.py # Configuration management
├── mcp_client.py # MCP server integration (optional, for tool use)
└── model-metadata.yaml # Agent metadata configuration
| ファイル | 説明 |
|---|---|
__init__.py |
ディレクトリをPythonパッケージとして識別し、インポートを有効にします。 |
model-metadata.yaml |
エージェントの設定、ランタイムパラメーター、デプロイ設定を定義します。 |
custom.py |
エージェントを実行するためのDataRobot統合フック(load_model、chat)を実装します。 |
agent.py |
ワークフローのコアロジックとフレームワーク固有の実装を持つ、メインのMyAgentクラスが含まれています。 |
config.py |
環境変数、ランタイムパラメーター、およびDataRobotの資格情報からの設定読み込みを管理します。 |
mcp_client.py |
ツール連携のためのMCPサーバー接続管理を提供します(オプション。MCPツールを使用する場合にのみ必要です)。 |
修正が必要なメインクラスはagent.pyにあります。 開発対象のフレームワークに基づく実装の詳細については、このクラスを参照してください。
エージェントテンプレートには、2つのエージェントと2つのタスクを含む簡単な例が用意されています。 必要に応じて、このコードを修正して、エージェント、タスク、およびツールを追加できます。 各エージェントはLLMプロバイダーに接続され、LLMプロバイダーはagent.pyファイルのllmプロパティで指定されます。 このプロパティを修正することで、LLMプロバイダーやその設定を変更できます。 詳細については、LLMプロバイダーの設定に関するドキュメントを参照してください。 エージェントワークフローのテンプレートの全体的な構造については、エージェントのコンポーネントに関するドキュメントを参照してください。
datarobot_genai package
エージェントテンプレートは、datarobot_genaiパッケージを使用して開発を効率化します。 このパッケージは、LLM設定、回答形式、DataRobotサービスとの連携など、エージェントの実装を簡素化するヘルパー関数と基本クラスを提供します。 テンプレートにはこのパッケージが自動的に含まれるため、別途インストールする必要はありません。
エージェントプロンプトの修正¶
各エージェントテンプレートは、プロンプトの定義とカスタマイズに異なるアプローチを使用します。 選択したフレームワークでプロンプトを変更する方法を理解することは、エージェントの動作を特定のユースケースに合わせるために非常に重要です。
CrewAI テンプレートでは、プロンプトはagent.pyファイル内のMyAgentクラスのいくつかのプロパティを通して定義されます。
- エージェントのプロンプト:role
、goal、backstory`プロパティを使用して定義されます。 - タスクプロンプト:description
とexpected_output`プロパティを使用して定義されます。
@property
def agent_planner(self) -> Agent:
return Agent(
role="Content Planner",
goal="Plan engaging and factually accurate content on {topic}",
backstory="You're working on planning a blog article about the topic: {topic}. You collect "
"information that helps the audience learn something and make informed decisions. Your work is "
"the basis for the Content Writer to write an article on this topic.",
allow_delegation=False,
verbose=self.verbose,
llm=self.llm,
)
CrewAIエージェントのプロンプトを修正するには:
- **エージェントの動作を更新する:エージェント定義の
role、goal、backstoryプロパティを変更します。 - 変数を使用する:
{topic}やその他の変数をプロンプトの動的なコンテンツに利用します。
@property
def task_plan(self) -> Task:
return Task(
description=(
"1. Prioritize the latest trends, key players, and noteworthy news on {topic}.\n"
"2. Identify the target audience, considering their interests and pain points.\n"
"3. Develop a detailed content outline including an introduction, key points, and a call to action.\n"
"4. Include SEO keywords and relevant data or sources."
),
expected_output="A comprehensive content plan document with an outline, audience analysis, SEO keywords, "
"and resources.",
agent=self.agent_planner,
)
CrewAIのタスクプロンプトを修正するには:
- タスク指示のカスタマイズ:タスク定義の
descriptionプロパティを更新します。 - 期待される出力の変更:要件に合わせて
expected_outputプロパティを修正します。 - 変数を使用する:
{topic}やその他の変数をプロンプトの動的なコンテンツに利用します。
より高度なCrewAIプロンプトエンジニアリング技術については、CrewAIエージェントのドキュメントとCrewAIタスクのドキュメントを参照してください。
LangGraphテンプレートでは、プロンプトはdatarobot_genaiパッケージのmake_system_promptヘルパー関数を使用して定義されます。
from datarobot_genai.core.agents import make_system_prompt
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
@property
def agent_planner(self) -> Any:
return create_react_agent(
self.llm(preferred_model="datarobot/azure/gpt-5-mini-2025-08-07"),
tools=self.mcp_tools,
prompt=make_system_prompt(
"You are a content planner. You are working with a content writer colleague.\n"
"You're working on planning a blog article about the topic. You collect information that helps the "
"audience learn something and make informed decisions. Your work is the basis for the Content Writer "
"to write an article on this topic.\n"
"1. Prioritize the latest trends, key players, and noteworthy news on the topic.\n"
"2. Identify the target audience, considering their interests and pain points.\n"
"3. Develop a detailed content outline including an introduction, key points, and a call to action.\n"
"4. Include SEO keywords and relevant data or sources."
),
name="Planner Agent",
)
LangGraphのプロンプトを修正するには:
- システムプロンプトを更新する:エージェントの定義で
make_system_prompt()に渡される文字列を変更します。 - タスク固有の指示を追加する:システムプロンプト文字列内に詳細な指示を含めます。
- **エージェントの動作を変更するプロンプトの内容を更新して、エージェントがタスクをどのように解釈し、どのように反応するかを変更します。
より高度なLangGraphプロンプトエンジニアリング技術については、LangGraphのドキュメントを参照してください。
LlamaIndexテンプレートでは、プロンプトはMyAgentクラス内のFunctionAgent定義のsystem_promptパラメーターを使って定義されます。
@property
def research_agent(self) -> FunctionAgent:
return FunctionAgent(
name="ResearchAgent",
description="Useful for finding information on a given topic and recording notes on the topic.",
system_prompt=(
"You are the ResearchAgent that can find information on a given topic and record notes on the topic. "
"Once notes are recorded and you are satisfied, you should hand off control to the "
"WriteAgent to write a report on the topic. You should have at least some notes on a topic "
"before handing off control to the WriteAgent."
),
llm=self.llm,
tools=[self.record_notes],
can_handoff_to=["WriteAgent"],
)
LlamaIndexのプロンプトを修正するには:
- システムプロンプトを更新する:
FunctionAgentの定義でsystem_prompt文字列を変更します。 - エージェントの説明をカスタマイズする:エージェントの識別方法を変更するために
descriptionパラメーターを更新します。 - ハンドオフ動作の変更:エージェントのワークフローを制御するために、
can_handoff_toリストとシステムプロンプトを更新しました。 - ツール固有の説明を追加する:特定の道具をいつ、どのように使うかについての指示を含めます。
より高度なLlamaIndexプロンプトエンジニアリングのテクニックについては、LlamaIndexプロンプトエンジニアリングのドキュメントを参照してください。
NAT(NVIDIA NeMo Agent Toolkit)のテンプレートでは、プロンプトはworkflow.yamlファイルで、関数定義内のsystem_promptフィールドを使用して定義されます。
functions:
planner:
_type: chat_completion
llm_name: datarobot_llm
system_prompt: |
You are a content planner. You are working with a content writer colleague.
You're working on planning a blog article about the topic.
You collect information that helps the audience learn something and make informed decisions.
Your work is the basis for the Content Writer to write an article on this topic.
1. Prioritize the latest trends, key players, and noteworthy news on the topic.
2. Identify the target audience, considering their interests and pain points.
3. Develop a detailed content outline including an introduction, key points, and a call to action.
4. Include SEO keywords and relevant data or sources.
NATのプロンプトを変更するには:
- システムプロンプトを更新する:
workflow.yaml内の関数定義のsystem_promptフィールドを変更します。 - 関数ごとにLLMを設定する:
workflow.yamlのllmsセクションで定義されたLLMを参照するように、llm_nameフィールドを設定します。 - ワークフローの構造を変更する:
workflowセクションを更新して、実行順序とツールリストを変更します。 - 新しい関数を追加する:
functionsセクションに追加の関数を定義して、エージェントの機能を拡張します。
より高度なNATの使用方法については、NVIDIA NeMo Agent Toolkitのドキュメントを参照してください。
迅速な修正のためのベストプラクティス
どのフレームワークでもプロンプトを修正する場合:
- **具体的に:エージェントに達成してほしいことを明確かつ詳細に指示します。
- Use consistent formatting:ワークフロー内のすべてのエージェントで一貫したプロンプト構造を維持します。
- インクリメンタルにテストする:より大きな変更を実装する前に、小さな変更を行い、それをテストします。
- **コンテキストを考慮する:プロンプトがマルチエージェントワークフローでうまく機能するようにします。
- ドキュメントの変更:将来の参照とチームコラボレーションのために、迅速な変更を追跡します。
ストリーミングレスポンスを有効にする¶
ストリーミングを使用すると、エージェントは、完全なレスポンスを待機することなく、生成されたレスポンスを段階的に送信できます。 これにより、進捗状況がリアルタイムで表示され、認識される遅延が短縮されて、エージェントのアクションが発生したときにユーザーが確認できるようになるため、ユーザーエクスペリエンスが向上します。
ストリーミングのサポートは、エージェントフレームワークによって異なります。 ストリーミングの実装には3つのレベルがあります。
- チャンクストリーミング:LLMからの各チャンクは、生成時にストリーミングされます(トークンや部分テキストなど)。
- ステップストリーミング:各サブエージェントからのレスポンスは、準備ができた時点でストリーミングされます。
- イベントストリーミング:個々のイベント(新しいステップの開始、ツールの呼び出し、推論)がストリーミングされます。
| フレームワーク | ストリーミング | 備考 |
|---|---|---|
| LangGraph | 有効 | stream=Trueが渡されると、チャンクレベルのストリーミングが自動的に有効になります。 基本クラスであるLangGraphAgentが、ストリーミングレスポンスを処理します。 |
| Generic Base | サポートされています | すべてのストリーミングレベル(チャンク、ステップ、イベント)にカスタム実装が必要です。 チャンクストリーミングのサンプルコードがagent.pyに用意されています。 |
| CrewAI | サポートされています | すべてのストリーミングレベル(チャンク、ステップ、イベント)にカスタム実装が必要です。 イベントリスナーは、エージェント実行とツール使用のイベントを段階的にキャプチャします。これにより、カスタムコードを用いたステップおよびイベントのストリーミングが容易になります。 チャンクストリーミングには、LLMから直接ストリーミングするためのカスタム実装が必要です。 |
| LlamaIndex | サポートされています | すべてのストリーミングレベル(チャンク、ステップ、イベント)にカスタム実装が必要です。 フレームワークはエージェントを段階的に実行するため、カスタムコードを用いたステップストリーミングが容易になります。 チャンクとイベントのストリーミングには、カスタム実装が必要です。 |
| NAT | サポートされています | すべてのストリーミングレベル(チャンク、ステップ、イベント)にカスタム実装が必要です。 |
インフラストラクチャのサポート
すべてのエージェントテンプレートには、ストリーミングレスポンスを処理できるインフラストラクチャがcustom.pyに含まれています。 カスタム実装を必要とするフレームワーク(Generic Base、CrewAI、LlamaIndex、NAT)の場合、ストリーミングが要求されたときにAsyncGeneratorを返すようにエージェントのinvoke()メソッドを変更する必要があります。 エージェントのinvoke()メソッドがAsyncGeneratorを返すと、インフラストラクチャは自動的にそれを適切なストリーミングレスポンス形式に変換します。 is_streamingヘルパー関数は、from datarobot_genai.core.agents import is_streamingをインポートすることで、datarobot_genaiパッケージを通じて、すべてのフレームワークテンプレートで利用できます。 この関数は、チャット補完のリクエストボディパラメーターにstream=Trueが含まれているかどうかを確認します。
エージェントにストリーミングが実装されている場合は、ローカルでテストするとき(CLIを使用)、またはデプロイされたエージェントで予測を行うとき(APIを使用)にストリーミングを有効にします。
エージェントCLIを実行する際には、--streamフラグを使用します。
task agent:cli -- execute --user_prompt 'Write a document about the history of AI.' --stream
構造化クエリーでストリーミングを使うこともできます。
task agent:cli -- execute --user_prompt '{"topic":"Generative AI"}' --stream
APIを呼び出す際、補完パラメーターにstream=Trueを設定します。
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
base_url=CHAT_API_URL,
api_key=API_KEY,
)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="datarobot-deployed-llm",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What would it take to colonize Mars?"},
],
stream=True, # Enable streaming
)
# Process streaming response
for chunk in completion:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content, end="", flush=True)
ローカル開発中のエージェントのテスト¶
テンプレートで提供される開発サーバを使用して、ローカルでエージェントをテストすることができます。 これにより、DataRobotにデプロイすることなく、エージェントコードを実行してデバッグすることができます。
エージェントにテストクエリーを送信するには、開発サーバーが稼働している必要があります。 手動で起動するか、自動起動オプションを使用します。
複数のテストを実行する場合は、開発サーバーを手動で起動します。 開発サーバーは継続的に実行され、ターミナルをブロックするため、1つのターミナルで起動します。
task agent:dev
このターミナルは起動したままにしておきます。 その後、別のターミナルでテストコマンドを実行します。
task agent:cli -- execute --user_prompt 'Write a document about the history of AI.'
エージェントのワークフローが要求した場合、構造化クエリーをプロンプトとして送信することもできます。
task agent:cli -- execute --user_prompt '{"topic":"Generative AI"}'
単一のテスト用に開発サーバーを自動起動します。 START_DEV=1を使用して、開発サーバーを自動的に起動および停止します。
task agent:cli START_DEV=1 -- execute --user_prompt 'Write a document about the history of AI.'
エージェントのワークフローが要求した場合、構造化クエリーをプロンプトとして送信することもできます。
task agent:cli START_DEV=1 -- execute --user_prompt '{"topic":"Generative AI"}'
このコマンドはエージェントをローカルで実行し、出力をコンソールに表示すします。 異なる入力やシナリオをテストするためにクエリーを変更することができます。
実行時依存関係を用いた高速イテレーション
開発を迅速に行うために、実行時依存関係を使用してDockerイメージを再構築することなく、Pythonの依存関係を追加できます。 このプロセスにより、イテレーションの速度が向上します。 実行時依存関係の追加の詳細については、Pythonパッケージの追加に関するドキュメントを参照してください。
DataRobot LLMプレイグラウンドでテスト用のエージェントを構築する¶
DataRobot LLMプレイグラウンドを使って改良できるカスタムモデルを作成するには:
dr task dev
このコマンドは、DataRobotでカスタムモデルを作成するためにPulumiインフラストラクチャを実行しますが、完全なプロダクションデプロイは作成しません。 これにより、反復的なクラウド開発とテストが大幅に高速化されます。 コマンドの詳細については、CLIドキュメントのdr taskおよびdr runを参照してください。
DataRobot LLMプレイグラウンドでエージェントを扱う例については、エージェントプレイグラウンドのドキュメントを参照してください。
ビルドコマンドに関する注意事項
dr task devコマンドを実行すると、既存のデプロイがすべて削除されます。 削除された場合は、dr task deployを使用して再作成できますが、新しいデプロイのデプロイIDは異なります。
本番用エージェントのデプロイ¶
完全な運用レベルのデプロイを作成するには:
dr task deploy
このコマンドはカスタムモデルを構築し、必要なインフラストラクチャを備えた本番用デプロイを作成するため、時間はかかりますが、完全な本番環境を提供します。 その他のオプションについては、CLIのtaskおよびrunコマンドを参照してください。 デプロイは、完全な監視、ロギング、スケーリング機能を含む標準的なDataRobotデプロイです。 DataRobotのデプロイの詳細については、デプロイのドキュメントを参照してください。
デプロイされたエージェントのログとトレースを確認する¶
エージェントがデプロイされたら、DataRobot UIでOpenTelemetry (OTel)のログとトレースを見ることができます。
ログを表示するには、デプロイタブでデプロイを検索してクリックし、アクティビティログタブ、ログの順にクリックします。 ログはOpenTelemetry形式で表示され、ログレベル(INFO、DEBUG、WARN、ERROR)、期間指定によるフィルター(直近 15 分、直近 1 時間、直近 1 日、またはカスタム範囲)、およびサードパーティ製のオブザーバビリティツール(Datadogなど)と連携するためのOTelログAPI経由でのエクスポート機能が含まれます。
アクセスと保持
ログはすべてのデプロイタイプで利用可能です。 デプロイで「オーナー」ロールと「ユーザー」ロールを持つユーザーのみが、これらのログを表示できます。 ログは30日間保存されます。
エージェントへのリクエストのエンドツーエンドのパスをたどるトレースを表示するには、デプロイのサービスの正常性タブで、予測の合計数チャートの右上隅にあるトレースを表示をクリックします。 トレーステーブルには、タイムスタンプ、ステータス、トレースID、期間、スパン数、コスト、プロンプト、補完などのトレース情報が表示されます。 トレース行をクリックすると、チャートまたはリスト形式で詳細なスパンが表示されます。これにより、LLM APIの呼び出し、ツールの起動、エージェントのアクションなど、エージェントの実行における個々のステップを確認できます。
詳細については、ログのドキュメントとトレースのドキュメントを参照してください。
Pulumiを使って手動でエージェントをデプロイする¶
必要に応じて、Pulumiコマンドを手動で実行して、Pulumiコードのデバッグや改良を行うことができます。
# Load environment variables
set -o allexport && source .env
# For build mode only (custom model without deployment)
export AGENT_DEPLOY=0
# Or for full deployment mode (default)
# export AGENT_DEPLOY=1
# Navigate to the infrastructure directory
cd ./infra
# Run Pulumi deployment
pulumi up
環境変数 AGENT_DEPLOYは、Pulumi がカスタムモデルのみを作成するか(AGENT_DEPLOY=0)、カスタムモデルとプロダクションデプロイの両方を作成するか(AGENT_DEPLOY=1)を制御します。 設定されていない場合、Pulumiはデフォルトでフルデプロイモードになります。
Pulumiは、作成または更新するリソースを確認するよう促します。
デプロイされたエージェントワークフローで予測を行う¶
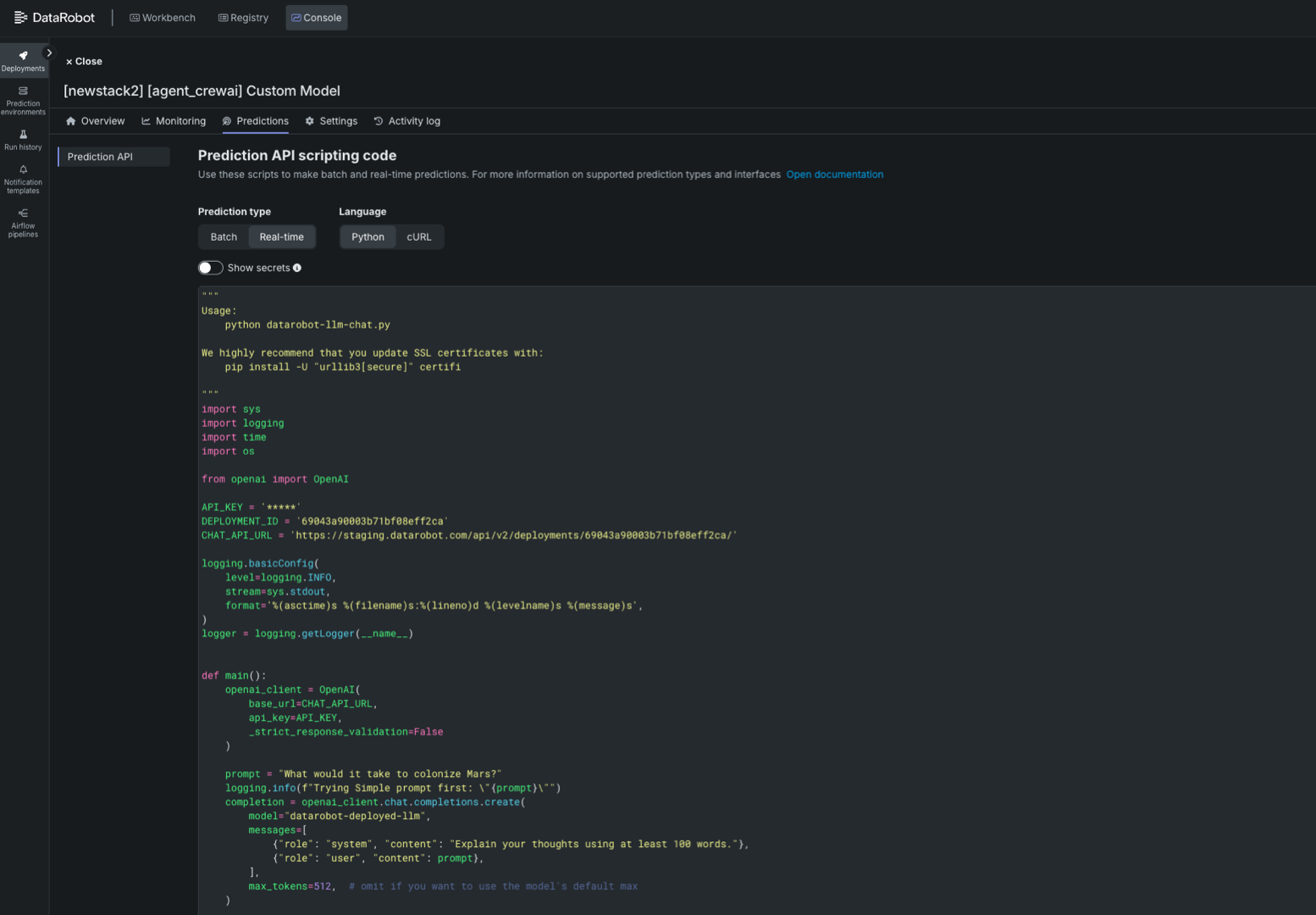
エージェントワークフローがデプロイされたら、デプロイの予測 > 予測APIタブからリアルタイムの予測スニペットにアクセスします。 デプロイ予測の詳細については、予測APIスニペットに関するドキュメントを参照してください。
あるいは、以下のスクリプトを修正して、デプロイされたエージェントワークフローを予測し、変数API_KEY、DEPLOYMENT_ID、CHAT_API_URLのプレースホルダーを置き換えることもできます。
import sys
import logging
import time
import os
from openai import OpenAI
API_KEY = '<API_KEY>' # Your API Key
DEPLOYMENT_ID = '<DEPLOYMENT_ID>' # The agentic workflow deployment ID
CHAT_API_URL = '<CHAT_API_URL>' # The chat API URL for the agentic workflow deployment
# For example, 'https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2/deployments/68824e9aa1946013exfc3415/'
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
stream=sys.stdout,
format='%(asctime)s %(filename)s:%(lineno)d %(levelname)s %(message)s',
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def main():
openai_client = OpenAI(
base_url=CHAT_API_URL,
api_key=API_KEY,
_strict_response_validation=False
)
prompt = "What would it take to colonize Mars?"
logging.info(f"Trying Simple prompt first: \"{prompt}\"")
completion = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="datarobot-deployed-llm",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Explain your thoughts using at least 100 words."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
],
max_tokens=512, # omit if you want to use the model's default max
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main())
次のステップ¶
デプロイ後、エージェントはDataRobot環境で利用できるようになります。 以下を実行することが可能です。
- task agent:cli -- execute-deployment`を使用して、デプロイしたエージェントをテストします。
- エージェントを他のDataRobotサービスと連携します。
- DataRobotのダッシュボードで使用状況とパフォーマンスを監視します。
このリポジトリで提供される例の範囲を超えたエージェントプラットフォーム固有の支援については、各フレームワークの公式ドキュメントを参照してください。
また、特定のフレームワーク向けのパブリックリポジトリには、より複雑なエージェントの構築、ツールの追加、ワークフローやタスクの定義に役立つ、多くの例やドキュメントが用意されています。