Generative AI service¶
Enabling the service¶
In order to enable the service, edit the values.yaml file. Set enabled: true for two services (core and LLM gateway), and set up object storage:
buzok-onprem:
# -- Enable Generative AI core sub-chart
enabled: true
buzok-llm-gateway:
# -- Enable Generative AI LLM gateway sub-chart
enabled: true
Additionally, enable the LLM_GATEWAY feature flag (a.k.a. "Enable consumption based pricing access to LLMs in production") in the core configuration by adding the following environment variable.
Important
ENABLE_LLM_GATEWAY must be set to false for STS organizations with DR-provided credentials and without consumption based pricing. Contact Customer Support for details.
core:
config_env_vars:
ENABLE_LLM_GATEWAY: true
Refer to the next section for large language model (LLM) access configuration.
Storage and encryption configuration¶
The Generative AI Service uses global DataRobot settings. For details, refer to the Object Storage Configuration guide.
If you define a FILE_STORAGE_PREFIX in global DataRobot settings, in all storage types Generative AI Service uses that prefix and append genai/ to it when storing its files.
Large language models (llm) configuration¶
The Generative AI (GenAI) service supports managed LLMs from the following providers: Azure OpenAI, Amazon Bedrock, Google Vertex AI, Anthropic, Cerebras, TogetherAI. In order to enable these models, you need to provision LLM resources using specified providers.
Refer to the LLM vendor documentation for provisioning LLM resources (links are subject to change over time):
Once LLMs are configured on the provider side, set up provider credentials in the GenAI service (credentials used to access LLMs in Azure/GCP/AWS/etc). For customer-managed credentials (always used for self-managed, and often, single tenant SaaS installations)—to provide the most flexibility and security—it's recommended to use secure configurations in DataRobot. In certain cases, for instance a single tenant SaaS environment with DataRobot-managed credentials, a DataRobot admin sets up credentials directly in values.yaml.
Set up credentials via secure configurations¶
Prior to installation, ensure the respective provider is enabled under the llmGateway configuration section within the buzok-llm-gateway sub-chart, for example:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
<supported-provider>:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-<provider>-llm-credentials
Note
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-<provider>-llm-credentials is only needed when Secure Configuration setup is used.
List of supported providers and corresponding LLM credentials secure config names:
anthropic:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-anthropic-llm-credentials
aws:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-aws-llm-credentials
azure:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-azure-llm-credentials
cerebras:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-cerebras-llm-credentials
google:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-gcp-llm-credentials
togetherai:
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-togetherai-llm-credentials
Note
The following providers secure configs may be listed but aren't yet supported:
- cohere (genai-cohere-llm-credentials)
- openai (genai-openai-llm-credentials)
- groq (genai-groq-llm-credentials)
After installation is complete, perform the following steps to provide model credentials to DataRobot Generative AI:
- Format access credentials into a JSON using the structure described in the next sections (LLM provider dependent)
- In the DataRobot Secure Configuration admin UI, create new Secure Configuration with a name and type described in the next sections
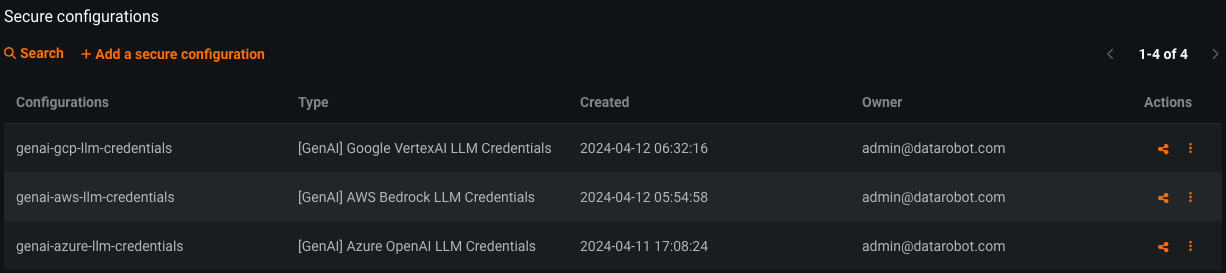
- Paste formatted JSON credentials into the configuration value
- Share the newly created Secure Configuration with the GenAI Admin system user (
genai-admin@datarobot.com), which is automatically created during installation. The configuration must be shared with either Owner or Editor role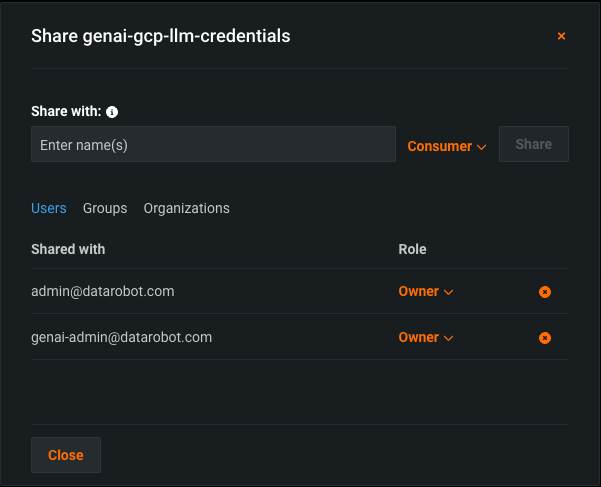
The Generative AI Service caches credentials retrieved from Secure Configuration for a short period of time; when rotating these credentials it may take a couple of minutes for the new credentials to be used.
Set up credentials directly during installation¶
Note
In this case, updating credentials requires reinstalling/updating DataRobot and the credentials are visible for the person performing the installation. This is considered a less secure and flexible way of setting up credentials for the GenAI service.
Credentials can be specified directly in the buzok-llm-gateway configuration section. Secure configuration won't be used in this case. The example below is how a configuration for AWS credentials (exact keys differ for various providers, see provider-specific sections below for credentials structure details):
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
aws:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: ""
credentials:
endpoints:
- region: "<aws_region>"
access_key_id: "<aws_access_key_id>"
secret_access_key: "<aws_secret_access_key>"
Azure OpenAI Models¶
Azure OpenAI models must be configured with specific deployment names, where deployment name can be equal to the model name. For example, a deployment for the gpt-35-turbo-16k model can be named gpt-35-turbo-16k. Note that deployment names can be different from the actual model name, such as creating a deployment named gpt-4o-2024-11-20 for the model gpt-4o.
After configuring Azure OpenAI LLM deployment, format the credentials using the following JSON structure:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "<region-code>",
"api_type": "azure",
"api_base": "https://<your-llm-deployment-endpoint>.openai.azure.com/",
"api_version": "2024-10-21",
"api_key": "<your-api-key>"
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] Azure OpenAI LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-azure-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
Note
Currently, "2024-10-21" is the latest stable version of the Azure API. To use the latest models, you may need to use a preview version of the API. Refer to the official Azure API documentation for details on Azure Inference API versions.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
azure:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-azure-llm-credentials
Amazon Bedrock models¶
The Generative AI Service supports the various first-party (e.g. Amazon Nova) and third-party (e.g. Anthropic Claude, Meta Llama, and Mistral) models from Amazon Bedrock.
There are two options of setting up Amazon Bedrock models: using IAM roles and using static AWS credentials.
Using IAM roles (IRSA) is recommended as a more secure option because it uses dynamic short-lived AWS credentials. However, if your Kubernetes cluster isn't in AWS cloud, setting up this authorization mechanism requires setting up Workload Identity Federation. For this reason, the Generative AI Service also supports using static AWS credentials. For security reasons, when using static credentials, it's recommended to create a separate AWS user that only has permissions to access AWS Bedrock.
After enabling model access in AWS Bedrock, format the credentials using the following JSON structure for using static credentials:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "<your-aws-region, e.g. us-east-1>",
"access_key_id": "<your-aws-key-id>",
"secret_access_key": "<your-aws-secret-access-key>",
"session_token": null,
}
]
}
Use the following JSON structure when using a role different from IRSA (ensure there is a policy that allows IRSA to assume this role):
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "<your-aws-region, e.g. us-east-1>",
"role_arn": "<your-aws-role-arn>"
}
]
}
Using IRSA to access Bedrock is available in 11.1.2 and later. Set "use_web_identity": true to use AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity from the pod's service account token.
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "<your-aws-region, e.g. us-east-1>",
"role_arn": "<your-aws-role-arn>",
"use_web_identity": true
}
]
}
Using FIPS-enabled endpoints is available in 11.1.2 and later. Set "use_fips_endpoint": true to do that. Note, that model availability may vary between FIPS-enabled and regular endpoints.
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "<your-aws-region, e.g. us-east-1>",
"role_arn": "<your-aws-role-arn>",
"use_fips_endpoint": true
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] AWS Bedrock LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-aws-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
aws:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-aws-llm-credentials
Google Vertex AI models¶
The Generative AI Service supports multiple models from Google Vertex AI, including first-party Gemini models and third-party Claude/Llama/Mistral models.
After provisioning the model, you should receive a json file with access credentials. Format contents of this file into the following JSON structure to provide credentials to DataRobot Generative AI:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "us-central1",
"service_account_info": {
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "<your-project-id>",
"private_key_id": "<your-private-key>",
"private_key": "----- <your-private-key>-----\n",
"client_email": "<your-email>.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "<your-client-id>",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://<your-cert-url>.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"universe_domain": "googleapis.com"
}
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] Google VertexAI LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-gcp-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
google:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-gcp-llm-credentials
Anthropic models¶
The Generative AI Service provides first-party integration with Anthropic, giving access to various Claude models.
To configure access to Anthropic, the API Key has to be provided:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "us",
"api_key": "<your-anthropic-api-key>"
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] Anthropic LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-anthropic-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
anthropic:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-anthropic-llm-credentials
Cerebras Models¶
The Generative AI Service provides integration with Cerebras, giving access to high-performance inference models.
To configure access to Cerebras, sign in to the Cerebras platform and create a new API key. Format the credentials using the following JSON structure:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "global",
"api_key": "<your-cerebras-api-key>"
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] Cerebras LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-cerebras-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
cerebras:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-cerebras-llm-credentials
Together AI models¶
The Generative AI Service provides integration with TogetherAI, offering access to a wide range of open-source language models.
To configure access to TogetherAI, sign in to the TogetherAI console and create a new API key. Format the credentials using the following JSON structure:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region": "global",
"api_key": "<your-togetherai-api-key>"
}
]
}
When creating a Secure Configuration with these credentials, use the [GenAI] TogetherAI LLM Credentials configuration type, and use genai-togetherai-llm-credentials as the configuration name.
The provider Secure Configuration section should look like:
buzok-llm-gateway:
enabled: true
llmGateway:
providers:
togetherai:
enabled: true
credentialsSecureConfigName: genai-togetherai-llm-credentials
LLM Catalog updates¶
Occasionally you may be required to update some information on LLMs in a catalog (e.g., set retirement_date or modify available_regions). In this release it can be done by manually updating the buzok-llm-gateway-catalog config map in the Kubernetes cluster after deployment. Once the config map is updated, restart the buzok-llm-gateway-app deployment to apply changes.
Warning
don't modify the LLM catalog unless absolutely necessary to avoid unintentional misconfiguration.
Note
Because changes are done to configmap in Kubernetes, they're not persisted during a redeploy. Make sure to get and keep a copy of the modified Kubernetes resource and reapply it after redeployment.
Refreshing LLM catalog cache¶
The LLM Catalog cache has a TTL (time-to-live) of 1 hour and refreshes automatically every hour. If you need to manually refresh the LLM catalog cache, such as after configuring new LLM provider credentials, you can do so by restarting the buzok-llm-gateway-app deployment in your Kubernetes cluster. This forces the service to update the LLM Catalog data using the latest configured LLM credentials.
Disabling internet-dependent features¶
The Generative AI service in DataRobot, by default, relies on internet connectivity to interact with various Language Model (LLM) types for chat prompting. However, in scenarios where internet access is restricted, the availability of specific LLM types can be managed by organization administrators.
Administrators have the ability to disable selected LLM types via DataRobot UI. Each LLM type is controlled by a dedicated feature flag. A few examples of such flags are listed below, but full list is available under Generative AI section on DataRobot Feature Flags configuration UI.
- Disable Azure OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo (
DISABLE_LLM_AZURE_OPENAI_GPT_35_TURBO): Controls access to Azure OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo. - Disable Anthropic Claude 2 (
DISABLE_LLM_AWS_ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE_2): Controls access to Anthropic Claude 2. - Disable Google Bison (
DISABLE_LLM_GCP_BISON): Controls access to Google Bison.
All of the above LLM types require internet access. When disabled, the respective LLMs isn't available in the LLM selection list when configuring an LLM blueprint in a playground.
The only LLM model type that doesn't require internet access is the custom model type. Access to custom models is also controlled by a dedicated "Disable Custom Model LLMs in the LLM playground" (DISABLE_LLM_CUSTOM_MODEL) feature flag. This can be disabled like any other LLM type if necessary.
Connected vector database (vdb) configuration¶
The Generative AI Service supports connected VDBs from the following vendors: Pinecone, Elasticsearch. The connection is configured when the VDB is created by the user supplying an API token credential for Pinecone or a basic or API token credential and a URL or cloud ID for their Elasticsearch instance.
By default the Generative AI service has network egress access to the necessary endpoints, but if there is a network configuration restricting this access one or more of the following patterns would need to be added to an allowlist:
1. *.pinecone.io and *.*.*.pinecone.io for Pinecone
2. *.*.*.elastic-cloud.com for Elasticsearch Cloud instances
3. URL for an on premise Elasticsearch instance
4. URL for a hosted or managed Elasticsearch instance
Static files migration¶
The Generative AI Service uses embedding models for the creation of Vector Databases and the augmentation of LLM queries. The service expects the weights for these models in blob storage. During the deployment of the service, a migration job is executed, downloading a tar archive (and checksum file) with the weights of the embedding models from DataRobot CDN and stores them in the blob storage.
For offline installations without access to the internet, the deployment requires additional steps from you.
Install in offline clusters¶
You have two options:
- You disable the migration job to run during the deployment, upload the files to a worker pod and trigger the migration script manually.
- You make the files available to the migration job through a self-hosted HTTP server, serving the files to the migration job.
Option 1: Execute the migration script manually¶
- Find the static files archive URL in the chart:
> helm template /path/to/datarobot/chart.tgz --set buzok-onprem.enabled=true | grep "genai.cdn"
- https://genai.cdn.app.datarobot.com/weights/datarobot-genai-weights-2024-01-12-18.tar.xz
-
Disable the migration job in the
values.yamlfile.buzok-onprem: buzok-worker: jobs: job-migration-static-files: enable: false -
Install DataRobot including the Generative AI service.
-
Download the tar archive and the checksum file to your machine. The checksum URL is the archive URL with an appended
.sha256sum.export ARCHIVE_URL="THE_ARCHIVE_URL_FROM_STEP_ONE" curl -fLo datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz $ARCHIVE_URL curl -fLo datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz.sha256sum $ARCHIVE_URL.sha256sum -
Find a running worker pod.
kubectl -n <k8s-namespace> -l role=buzok-worker-app-io get pods -
Copy the downloaded files into the worker pod.
export POD_NAME="WORKER_POD_NAME_FROM_THE_PREVIOUS_STEP" kubectl -n <k8s-namespace> cp datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz $POD_NAME:/app/ephemeral kubectl -n <k8s-namespace> cp datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz.sha256sum $POD_NAME:/app/ephemeral -
Execute the migration script:
kubectl exec -n <k8s-namespace> $POD_NAME -- bash engine/docker_entrypoint.sh python -m worker.scripts.migrate_static_files with-this-file /app/ephemeral/datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz
Option 2: Make files accessible through a self-hosted HTTP server¶
For this method you needs an HTTP server that's accessible from pods running in the Kubernetes cluster. It can be the machine you use to install DataRobot, or some other machine accessible by the cluster. Be aware that you could run into networking issues, and you are advised to verify that pods can access your HTTP server before you proceed with the installation.
- Find the static files archive URL in the chart:
> helm template /path/to/datarobot/chart.tgz --set buzok-onprem.enabled=true | grep "genai.cdn"
- https://genai.cdn.app.datarobot.com/weights/datarobot-genai-weights-2024-01-12-18.tar.xz
-
Download the tar archive and the checksum file to your HTTP server. The checksum URL is the archive URL with an appended
.sha256sum.export ARCHIVE_URL="THE_ARCHIVE_URL_FROM_STEP_ONE" curl -fLo datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz $ARCHIVE_URL curl -fLo datarobot-genai-weights.tar.xz.sha256sum $ARCHIVE_URL.sha256sum -
If you don't have an HTTP server running yet, you can start one e.g. via
python3 -m http.server 8080. - (Optional) Test if pods can access your HTTP server.
-
Override the
staticFilesArchiveUrlin yourvalues.yamlfile.buzok-onprem: buzok-worker: staticFilesArchiveUrl: "YOUR_NEW_URL" -
Proceed with the installation of the Generative AI service.
- (Optional) Remove the HTTP server or the files from it. After the installation you don't have to serve them anymore.
Troubleshooting static files migration¶
If the static file migration job fails, or when you change the file storage settings (for example, storage prefix), you need to force the job to rerun by taking the following steps. This section assumes your cluster has internet access. If this isn't the case, refer to the options mentioned above.
- Find the static files archive URL in the chart:
> helm template /path/to/datarobot/chart.tgz --set buzok-onprem.enabled=true | grep "genai.cdn"
- https://genai.cdn.app.datarobot.com/weights/datarobot-genai-weights-2024-01-12-18.tar.xz
-
Find a CPU worker pod:
kubectl -n <k8s-namespace> -l role=buzok-worker-app-io get pods -
Exec into the pod and force re-run the migration:
kubectl exec -n <k8s-namespace> -it <pod-name> -- bash engine/docker_entrypoint.sh bash
# Run the following command inside the pod
FORCE_STATIC_FILE_MIGRATION=true python -m worker.scripts.migrate_static_files with-this-url <datarobot-genai-weights-file-url>
Migration of execution environments¶
Generative AI supports generation of custom models, but this requires execution environments installed on a cluster. Execution environments are automatically installed or updated with a migration job during the deployment of the Generative AI service.
For offline installations without access to the internet, the deployment requires additional steps.
Install in offline clusters¶
This job requires an external network connection: the execution environments pull additional dependencies from the internet. If there is no internet access, the job fails. You can install the execution environments manually from a prebuilt package.
- Disable the migration job in the
values.yamlfile:
buzok-onprem:
buzok-worker:
jobs:
job-migration-execution-environments:
enable: false
- Find the environment version id in the chart:
> helm template /path/to/datarobot/chart.tgz --set buzok-onprem.enabled=true | grep CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID:
CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID: "660577ba61d4c9b498e6bdaf"
- Download and unpack the pre-built image from the DataRobot CDN:
export CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID=<CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID>
curl -O https://genai.cdn.app.datarobot.com/execution-environments/execution-environments-v$CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID.tar.gz
tar -xvf execution-environments-v$CUSTOM_MODEL_ENVIRONMENT_VERSION_ID.tar.gz
- Obtain API token for GenAI service account:
GENAI_API_TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret buzok-secrets -o jsonpath='{.data.DATAROBOT_ADMIN_V2_API_TOKEN}' | base64 -d)
- Install the pre-built image using a generated script:
source installer_env/bin/activate
python install_public_environments.py <V2_API_ENDPOINT> $GENAI_API_TOKEN
You have to use
V2_API_TOKENspecifically from thebuzok-secretssecret: it has necessary permissions, and this service account should be the owner of the execution environment for GenAI. If you create the environment using any other user, DataRobot won't be able to update it automatically.
Troubleshooting execution environments¶
In case automated or manual installation of execution environments fails or timeouts, you can find logs in the job:
kubectl logs job.batch/buzok-worker-job-migration-execution-environments-<revision>
If the job installation timeouts waiting for environment build, check logs of the build service:
kubectl logs deployment/build-service | grep ERROR
kubectl logs deployment/queue-exec-manager-build-service | grep ERROR
In case of a recoverable error, you can retry the installation with the same execution environment version id.
GPU Configuration¶
Warning
GPU configuration for the Generative AI service has changed in 10.2. When upgrading from an earlier version of DataRobot with the Generative AI feature enabled, follow the guide below to configure from scratch.
The Generative AI service supports the usage of GPUs for the creation of Vector Databases. It doesn't require dedicated nodes and uses shared cluster resources for this type of workloads targeting GPUs. GPUs are able to significantly reduce the time required to build Vector Databases. However, they could be also significantly more expensive than regular instances. The Generative AI service is able to run with or without GPU nodes. You have the chance to fully decide on yourself if you want to use them.
The following table shows the time it takes to creates a Vector Database for different sized datasets. Dataset size indicates the size of the uncompressed text file that makes up the dataset. For the GPU runtime, an instance with a Nvidia T4 GPU was used. For the CPU runtime, 5 cores of a 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPU was used.
| Dataset size | Embedding Model | CPU runtime | GPU runtime | GPU x times faster than CPU | Creation time improvement on GPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 MB | jinaai/jina-embedding-t-en-v1 | 00h 02m | 00h 00m | 7 | 00h 01m |
| 6 MB | intfloat/multilingual-e5-base | 00h 20m | 00h 01m | 11 | 00h 18m |
| 6 MB | intfloat/e5-large-v2 | 01h 20m | 00h 06m | 12 | 01h 14m |
| 47 MB | jinaai/jina-embedding-t-en-v1 | 00h 14m | 00h 02m | 7 | 00h 12m |
| 47 MB | intfloat/multilingual-e5-base | 02h 14m | 00h 12m | 11 | 02h 02m |
| 47 MB | intfloat/e5-large-v2 | 09h 08m | 00h 44m | 12 | 08h 24m |
| 200 MB | jinaai/jina-embedding-t-en-v1 | 01h 08m | 00h 10m | 7 | 00h 58m |
| 200 MB | intfloat/multilingual-e5-base | 09h 22m | 00h 53m | 11 | 08h 28m |
GPU Requirements¶
If you plan to utilize GPUs, be aware of the following requirements for the GPU nodes, based on maximum dataset size of 10Gb:
- Nvidia GPU with one of these compute capabilities: 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.6 8.9 9.0 10.0 See this website for a list of GPUs and their compute capabilities.
- 16GiB of GPU memory
- 50GiB of RAM
- 75GiB of storage
- X86-64 processor with at least 2 CPU cores
Enable the use of GPUs¶
After you have prepared your Kubernetes cluster and your GPU nodes (see general GPU instructions), enable the usage of GPU nodes for the Generative AI service in the values.yaml file of the DataRobot helm chart. First, update core settings and describe GPU nodes that should be used by the Generative AI service.
core:
config_env_vars:
# An array of supported GPU types configured for worker job pods. Used to map vram and GPU
# capabilities to the tolerations and node selectors Kubernetes administrators have set on GPU
# enabled node groups.
# NOTE: This setting is a JSON-formatted string. Ensure it's properly formatted.
KUBEWORKERS_GPU_SUPPORTED_TYPES: |-
[
{
"priority": 1,
"description": "gpu-node",
"nodeSelectors": ["datarobot.com/node-capability: gpu"],
"tolerations": ["nvidia.com/gpu=true:NoExecute"],
"vram": 16,
"capabilities": ["7.5"]
}
]
Enable GPUs for VDB creation in Buzok configuration. Default configuration is requested in this case (16 Gb vRAM, CUDA capabilities ["7.5"] - should match configuration/capabilities of GPU nodes in cluster described in KUBEWORKERS_GPU_SUPPORTED_TYPES).
buzok-onprem:
buzok-worker:
computeApi:
enableGpuForVDB: true
In case your cluster has configured GPUs that have other set of CUDA Capabilities or less vRAM, you can customize these like below:
buzok-onprem:
buzok-worker:
computeApi:
enableGpuForVDB: true
jobResourcesMapOverrides:
jobs:
create_vector_database:
gpu_vram: "8"
gpu_capabilities:
- "8.0"
Finally, to explicitly override all settings for a particular GenAI job executed via Compute API, you can do that using jobResourceMap parameter (for example, here's how overriding settings for create_vector_database_with_custom_embeddings job would look like):
buzok-onprem:
buzok-worker:
computeApi:
jobResourcesMapOverrides:
jobs:
create_vector_database_with_custom_embeddings:
cpu_request: "1"
cpu_limit: "2"
memory_request: 26Gi
memory_limit: 32Gi
storage_request: 75Gi
gpu_enabled: false
env:
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE: "0"
TDQM_DISABLE: "1"
DEVICE_FOR_NEURAL_NETWORK_COMPUTATIONS: cpu
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: none
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: none
Here is a short description of configuration fields above:
- cpu_request / cpu_limit - CPU cores required (passed to K8s on job creation)
- memory_request / memory_limit - RAM required (passed to K8s on job creation)
- storage_request - disk space required (passed to K8s on job creation)
- gpu_enabled (false by default) - enables request for GPUs for the job (used by DR Kubeworkers Controller)
- gpu_vram - VRAM required (used by DR Kubeworkers Controller).
- gpu_capabilities - compute capabilities required by the job to execute. Refer to section above for details on capabilities supported by Vector Database creation job and different GPU models.
- env - environment variables to set for a job. Usually these don't require any modifications. Just use one of sets below depending on GPU usage:
- For jobs using GPU:
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE: "0" # Disables TensorFloat-32 precision on Nvidia GPUs
TDQM_DISABLE: "1" # Disables logs from certain libraries
DEVICE_FOR_NEURAL_NETWORK_COMPUTATIONS: cuda # Internal instruction to enable use of GPU in PyTorch
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES and CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES are used to explicitly prevent job from using GPU, even if pod is scheduled on GPU-enabled node):
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE: "0" # Disables TensorFloat-32 precision on Nvidia GPUs
TDQM_DISABLE: "1" # Disables logs from certain libraries
DEVICE_FOR_NEURAL_NETWORK_COMPUTATIONS: cpu # Internal instruction to use CPU in PyTorch
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: none # Used to restrict GPU access at the container level
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: none # Used to hide GPU from application inside container
If job requests gpu (gpu_enabled: true) - VRAM and GPU capabilities settings are used by DataRobot Kubeworkers Controller to match job request with one of nodegroups described in KUBEWORKERS_GPU_SUPPORTED_TYPES (job's VRAM request must be lesser/equal than nodegroup's, requested capabilities must be a subset of nodegroup's). Other request settings (CPU/RAM/Storage) are handled directly by K8s, as well as nodeSelectors and tolerations from selected nodegroup.
Installation runtime¶
Installing an umbrella chart with Generative AI service enabled takes up to 15-20 minutes. Add
--timeout 20m0s to helm commands to avoid timeouts.
The runtime is mainly increased due to 2 heavy migrations: static files and execution environments. they're set to run post-upgrade, so helms run them sequentially and tracks their status. If needed, one can disable hooks usage to run migration jobs in parallel:
buzok-onprem:
buzok-worker:
runMigrationsPostInstall: false
Note
This option speeds up installation, but be aware that Helm doesn't track the status of migrations and the installation script doesn't report their failure. You must manually track that those jobs are completed.