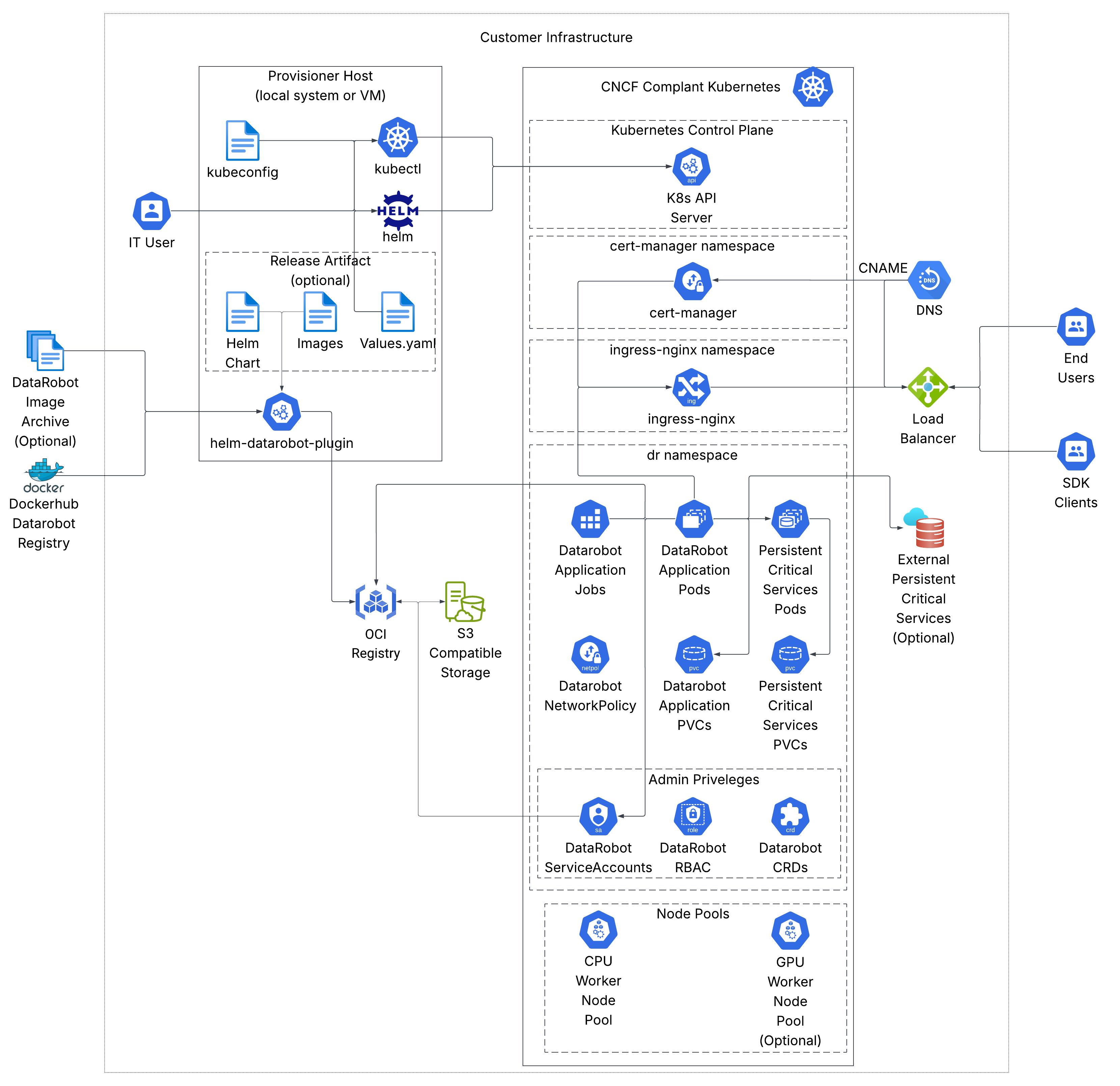
Architecture overview¶
Self-managed platform deployments allow you to deploy DataRobot on your own managed VPC or physical hardware clusters for additional security controls and physical isolation.
The following diagram represents a simplified architecture overview:
System landscape and context¶
The DataRobot platform is used by:
- End-users accessing the graphical user interface (GUI) from a web browser.
- SDK clients, which provide programmatic access to the platform via a REST API.
The DataRobot platform is installed by:
- Users in IT who rely on the Provisioner host to carry out the various steps required for DataRobot platform installation, such as executing commands via
kubectlandhelm. - Optionally, the DataRobot Image Archive can be used as a source for DataRobot artifacts instead of Docker Hub for restricted or air-gapped environments.
The DataRobot platform is deployed on a CNCF-Compliant Kubernetes cluster, residing in the dr namespace. The platform relies on the following cluster components:
- StorageClasses for persistent storage.
- Cloud native certificate manager (cert-manager) to acquire valid certificates.
- NGINX Ingress controller (ingress-nginx) and DNS setup with a Fully-Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) to allow users to access application.
- Network policy engine.
- Set of DataRobot CRDs, RBAC, and associated ServiceAccounts to grant access to S3-Compatible Storage and OCI Registry (admin privileges).
The DataRobot platform is architecturally composed of the following generalized components:
- The DataRobot Application Pods constitute a set of internal subcomponents.
- The DataRobot Application Jobs are a collection of platform jobs, such as LRS and Workers.
- Persistent Critical Services (PCS): Services providing persistent storage and middleware for caching, distributed messaging, and coordination. This includes Mongo, PostgreSQL, Redis, and RabbitMQ services. It can be replaced with external Persistent Critical Services (PCS) based on cloud solutions.