Troubleshooting the Worker Queue¶
If you expect to be able to increase your worker count but cannot, the reasons may be:
- You have hit your worker limit.
- Your workers are part of a shared pool.
- Your workers are in use by another project.
Worker limit¶
Modeling worker allocations are set by your administrator. Each worker processes a modeling job. This job count applies across all projects in the cluster, that is, multiple browser windows building models are all a part of your personal worker count—more windows does not provide more workers.
Pooled workers¶
If you are in an organization, it may implement a shared pool of workers. In this case, workers are allocated across all jobs for all users in the organization on a first-in, first-out basis. While you may not have to wait for jobs of other users in your organization to complete, your (and their) jobs will be seeded in the queue and processed as they were received.
Workers in use¶
If you believe you should be able to increase the worker count but you cannot, for example, "using X of Y workers," there are two values to consider for debugging. When Y is lower than you expect, check your worker limit and the org limit. When X is less than you expect, check whether workers are being allocated to other projects or users in your organization.
To check worker use in your projects, navigate to the Manage Projects inventory and look for queued jobs. You can identify them by:
-
An icon and count in the inventory.
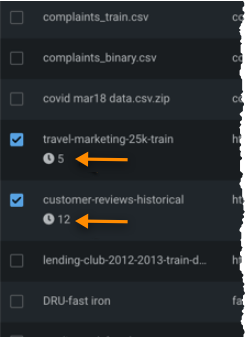
-
The list that results from using Filter Projects and selecting Running or queued.
If you find a project with queued jobs, you can stop Worker Queue processing.
- Click on the project in the inventory to make it the active project.
-
In the Worker Queue, click the X icon (
 ) to remove all tasks. This removes all in-progress or queued models.
) to remove all tasks. This removes all in-progress or queued models.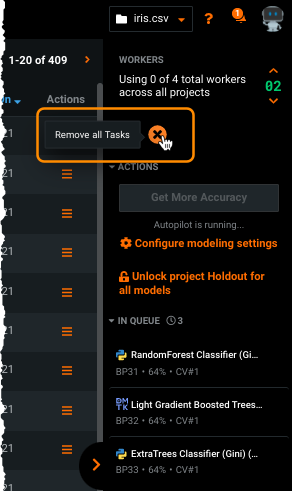 You can also pause the project. As workers complete active jobs, they will become available to pick up jobs from other projects.
You can also pause the project. As workers complete active jobs, they will become available to pick up jobs from other projects.