API quickstart¶
The DataRobot API provides a programmatic alternative to the web interface for creating and managing DataRobot projects. The API can be used via REST, or DataRobot's Python or R clients in Windows, UNIX, and OS X environments. This guide walks you through setting up your environment and then you can follow a sample problem that outlines an end-to-end workflow for the API.
Note
The API quickstart guide uses methods for 3.x versions of DataRobot's Python client. If you are a Self-Managed AI Platform user, consult the Self-Managed AI Platform API resources page to verify which versions of DataRobot's clients are supported for your version of the DataRobot application.
Prerequisites¶
The DataRobot API requires the following prerequisites, depending on the coding language you choose to use.
Install the client¶
Before proceeding, access and install the DataRobot client package for Python or R (instructions are provided below). Review the API Reference documentation to familiarize yourself with the code-first resources available to you.
Note
Self-Managed AI Platform users may want to install a previous version of the client in order to match their installed version of the DataRobot application. Reference the available versions to map your installation to the correct version of the API client.
pip install datarobot datarobot-predict
(Optional) If you would like to build custom blueprints programmatically, install two additional packages: graphviz and blueprint-workshop.
For Windows users:
Download the graphviz installer
For Ubuntu users:
sudo apt-get install graphviz
For Mac users:
brew install graphviz
Once graphviz is installed, install the workshop:
pip install datarobot-bp-workshop
install.packages(“datarobot”)
Configure your environment¶
This section walks through how to execute a complete modeling workflow using the DataRobot API, from uploading a dataset to making predictions on a model deployed in a production environment.
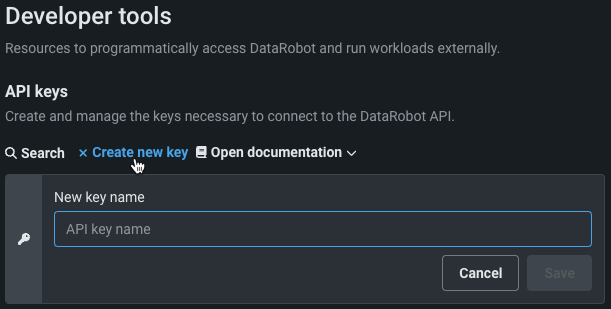
Create a DataRobot API key¶
-
From the DataRobot UI, click the user icon in the top right corner and select API keys and tools.
-
Click Create new key.
-
Name the new key, and click Create. The key is activated and ready for use.
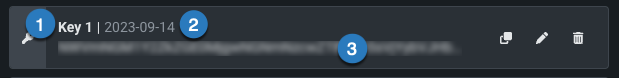
Once created, each individual key has three pieces of information:
| Label | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Name | The name of the key, which you can edit. |
| 2 | Key | The key value. |
| 3 | Date created | The date the key was created. Newly created and not yet used keys display “—”. |
| 4 | Last used | The date the key was last used. |
Retrieve the API endpoint¶
DataRobot provides several deployment options to meet your business requirements. Each deployment type has its own set of endpoints. Choose from the tabs below:
The AI Platform (US) offering is primarily accessed by US users. It can be accessed at https://app.datarobot.com.
API endpoint root: https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2
The AI Platform (EU) offering is primarily accessed by EMEA users. It can be accessed at https://app.eu.datarobot.com.
API endpoint root: https://app.eu.datarobot.com/api/v2
The AI Platform (JP) offering is primarily accessed by users in Japan. It can be accessed at https://app.jp.datarobot.com.
API endpoint root: https://app.jp.datarobot.com/api/v2
For Self-Managed AI Platform users, the API root will be the same as your DataRobot UI root. In the URL below, replace {datarobot.example.com} with your deployment endpoint.
API endpoint root: https://{datarobot.example.com}/api/v2
Configure API authentication¶
To authenticate with DataRobot's API, your code needs to have access to an endpoint and token from the previous steps. This can be done in three ways:
DataRobot's recommended authentication method is to use a drconfig.yaml file. This is a file that the DataRobot Python and R clients automatically look for. You can instruct the API clients to look for the file in a specific location, ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml by default, or under a unique name. Therefore, you can leverage this to have multiple config files. The example below demonstrates the format of the .yaml:
endpoint: 'https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2'
token: 'NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G'
Once created, you can test your access to the API.
For Python:
If the config file is located at ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml, then all you need to do is import the library:
import datarobot as dr
Otherwise, use the following command:
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(config_path = "<file-path-to-drconfig.yaml>")
For R:
If the config file is located at ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml, then all you need to do is load the library:
library(datarobot)
Otherwise, use the following command:
ConnectToDataRobot(configPath = "<file-path-to-drconfig.yaml>"))
For cURL:
cURL doesn't natively support YAML files, but you can extract the values from your drconfig.yaml file and use them in your cURL commands. This sequence will read the values from your drconfig.yaml file and set them as environment variables:
# Extract values from drconfig.yaml and set as environment variables
export DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT=$(grep 'endpoint:' ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml | cut -d "'" -f2)
export DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN=$(grep 'token:' ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml | cut -d "'" -f2)
Once the environment variables are set, you can use them in your cURL commands:
curl --location -X GET "${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects" --header "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}"
For Windows:
For Windows users, open the Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator and set the following environment variables:
setx DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT "https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2"
setx DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN "your_api_token"
Once set, close and reopen the Command Prompt or PowerShell for the changes to take effect.
To configure persisting environment variables on Windows, search for "Environment Variables" in the Start menu and select Edit the system environment variables.
Then, click Environment Variables and, under System variables, click New to add the variables shown above.
For macOS and Linux:
For macOS and Linux users, open a terminal window and set the following environment variables:
export DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT="https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2"
export DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN="your_api_token"
To configure persisting environment variables on macOS or Linux, edit the shell configuration file (~/.bash_profile, ~/.bashrc, or ~/.zshrc) and add the environment variables shown above. Then, save the file and restart your terminal or run source ~/.bash_profile (or use any relevant file).
Once the environment variables are set, authenticate to connect to DataRobot.
For Python:
import datarobot as dr
dr.Project.list()
For cURL:
curl --location -X GET "${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects" --header "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}"
For R:
library(datarobot)
(Optional) Be cautious to never commit your credentials to Git.
For Python:
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(endpoint='https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2', token='NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G')
curl --location --request GET 'https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2/projects/' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>'
For R:
ConnectToDataRobot(endpoint =
"https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2",
token =
'NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G')
Use the API: Predicting fuel economy¶
Once the API credentials, endpoints, and environment are configured, use the DataRobot API to follow this example. The example uses the Python client and the REST API (using cURL), so a basic understanding of Python3 or cURL is required. It progresses through a simple problem: predicting the miles-per-gallon fuel economy from known automobile data (e.g., vehicle weight, number of cylinders, etc.). For additional code examples, reference DataRobot's AI accelerators.
Note
The following workflow uses methods introduced in version 3.0 of the Python client. Ensure that the client is up-to-date before executing the code included in this example.
The following sections provide sample code for Python and cURL that will:
- Upload a dataset.
- Train a model to learn from the dataset.
- Test prediction outcomes on the model with new data.
- Deploy the model.
- Predict outcomes on the deployed model using new data.
Upload a dataset¶
The first step to create a project is uploading a dataset. This example uses the dataset auto-mpg.csv and its supporting test dataset, auto-mpg-test.csv, both of which can be found in this .zip file.
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(config_path = "./drconfig.yaml")
# Set to the location of your auto-mpg.csv and auto-mpg-test.csv data files
# Example: dataset_file_path = '/Users/myuser/Downloads/auto-mpg.csv'
training_dataset_file_path = './auto-mpg.csv'
test_dataset_file_path = './auto-mpg-test.csv'
print("--- Starting DataRobot Model Training Script ---")
# Load dataset
training_dataset = dr.Dataset.create_from_file(training_dataset_file_path)
# Create a new project based on dataset
project = dr.Project.create_from_dataset(training_dataset.id, project_name='Auto MPG DR-Client')
DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN=${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}
DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT=${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}
DATASET_FILE_PATH="./auto-mpg.csv"
location=$(curl -Lsi \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-F 'projectName="Auto MPG"' \
-F "file=@${DATASET_FILE_PATH}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}"/projects/ | grep -i 'Location: .*$' | \
cut -d " " -f2 | tr -d '\r')
echo "Uploaded dataset. Checking status of project at: ${location}"
while true; do
project_id=$(curl -Ls \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" "${location}" \
| grep -Eo 'id":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
if [ "${project_id}" = "" ]
then
echo "Setting up project..."
sleep 10
else
echo "Project setup complete."
echo "Project ID: ${project_id}"
break
fi
done
# Set to the location of your auto-mpg.csv and auto-mpg-test.csv data files
# Example: dataset_file_path = '/Users/myuser/Downloads/auto-mpg.csv'
training_dataset_file_path <- "./auto-mpg.csv"
test_dataset_file_path <- "./auto-mpg-test.csv"
# Load dataset using modern DataRobot R client
training_dataset <- UploadDataset(training_dataset_file_path)
test_dataset <- utils::read.csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Create a new project based on dataset
project <- CreateProject(training_dataset, projectName = "Auto MPG DR-Client")
Train models¶
Now that DataRobot has data, it can use the data to train and build models with Autopilot. Autopilot is DataRobot's "survival of the fittest" modeling mode that automatically selects the best predictive models for the specified target feature and runs them at increasing sample sizes. The outcome of Autopilot is not only a selection of best-suited models, but also identification of a recommended model—the model that best understands how to predict the target feature "mpg". Choosing the best model is a balance of accuracy, metric performance, and model simplicity. You can read more about the model recommendation process in the UI documentation.
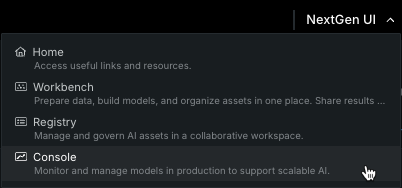
Note
This code opens a browser window to display progress in the DataRobot classic UI. Once the window has opened, click the NextGen UI dropdown and select Console to view the deployment once it is complete.
# Use training data to build models
from datarobot import AUTOPILOT_MODE
# Set the project's target and initiate Autopilot (runs in Quick mode unless a different mode is specified)
project.analyze_and_model(target='mpg', worker_count=-1, mode=AUTOPILOT_MODE.QUICK)
print("\nAutopilot is running. This may take some time...")
project.wait_for_autopilot()
print("Autopilot has completed!")
# Open the project in a web browser to view progress
print("Opening the project in your default web browser to view real-time events...")
project.open_in_browser()
# Get the recommended model (the best model for deployment)
print("\nRetrieving the best model from the Leaderboard...")
best_model = project.recommended_model()
print(f"Best Model Found:")
print(f" - Model Type: {best_model.model_type}")
print(f" - Blueprint ID: {best_model.blueprint_id}")
response=$(curl -Lsi \
-X PATCH \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"target": "mpg", "mode": "quick"}' \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/aim" | grep 'location: .*$' \
| cut -d " " | tr -d '\r')
echo "AI training initiated. Checking status of training at: ${response}"
while true; do
initial_project_status=$(curl -Ls \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" "${response}" \
| grep -Eo 'stage":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
if [ "${initial_project_status}" = "" ]
then
echo "Setting up AI training..."
sleep 10
else
echo "Training AI."
echo "Grab a coffee or catch up on email."
break
fi
done
echo "Polling for Autopilot completion..."
while true; do
autopilot_done=$(curl -s \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"autopilotDone":\s*(true|false)' | cut -d ':' -f2 | tr -d ' ')
if [ "${autopilot_done}" = "true" ]; then
echo "Autopilot training complete. Model ready to deploy."
break
else
echo "Autopilot training in progress... checking again in 60 seconds."
sleep 60
fi
done
# Get the recommended model ID
recommended_model_id=$(curl -s \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/recommendedModels/recommendedModel/" \
| grep -Eo 'modelId":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
echo "Recommended model ID: ${recommended_model_id}"
# Set the project target and initiate Autopilot in Quick mode
SetTarget(project, target = "mpg")
# Start Autopilot in Quick mode (equivalent to Python's AUTOPILOT_MODE.QUICK)
StartAutopilot(project, mode = "quick")
# Block execution until Autopilot is complete
WaitForAutopilot(project)
# Open the project in a web browser to view progress
OpenProject(project)
# Get the recommended model (the best model for deployment)
model <- GetRecommendedModel(project, type = RecommendedModelType$RecommendedForDeployment)
Deploy the model¶
Deployment is the method by which you integrate a machine learning model into an existing production environment to make predictions with live data and generate insights. See the deployment overview for more information.
# Deploy the model to a serverless prediction environment
print("\nDeploying the model to a serverless prediction environment...")
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
serverless_env = None
for env in dr.PredictionEnvironment.list():
if env.platform == 'datarobotServerless':
serverless_env = env
break
if serverless_env is None:
print("Creating a new serverless prediction environment...")
serverless_env = dr.PredictionEnvironment.create(
name="Auto MPG Serverless Environment",
platform='datarobotServerless'
)
# First, register the model to create a registered model version
print("Registering the model...")
# Check if the registered model already exists
registered_model_name = "Auto MPG Registered Model"
existing_models = [m for m in dr.RegisteredModel.list() if m.name == registered_model_name]
if existing_models:
print(f"Using existing registered model: {registered_model_name}")
registered_model = existing_models[0]
# Create a new version of the existing model
registered_model_version = dr.RegisteredModelVersion.create_for_leaderboard_item(
best_model.id,
name="Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id=registered_model.id
)
else:
print(f"Creating new registered model: {registered_model_name}")
# Create a new registered model
registered_model_version = dr.RegisteredModelVersion.create_for_leaderboard_item(
best_model.id,
name="Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_name=registered_model_name
)
# Retrieve the newly created registered model object by ID
registered_model = dr.RegisteredModel.get(registered_model_version.registered_model_id)
# Wait for the model build to complete
print("Waiting for model build to complete...")
while True:
current_version = registered_model.get_version(registered_model_version.id)
if current_version.build_status in ('READY', 'complete'):
print("Model build completed successfully!")
registered_model_version = current_version # Update our reference
break
elif current_version.build_status == 'FAILED':
raise Exception("Model build failed. Please check the model registration.")
else:
print(f"Build status: {current_version.build_status}. Waiting...")
import time
time.sleep(30) # Wait 30 seconds before checking again
# Deploy the model to the serverless environment using the registered model version
deployment = dr.Deployment.create_from_registered_model_version(
registered_model_version.id,
label="Auto MPG Predictions",
description="Deployed with DataRobot client for Auto MPG predictions",
prediction_environment_id=serverless_env.id
)
print(f"Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID: {deployment.id}")
# Use the recommended model ID from training section
echo "Using recommended model ID: ${recommended_model_id}"
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
echo "Looking for serverless prediction environment..."
serverless_env_id=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/predictionEnvironments/" \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*".*"platform":"datarobotServerless"' \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4 | head -1)
if [ -z "${serverless_env_id}" ]; then
echo "Creating new serverless prediction environment..."
serverless_env_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"name":"Auto MPG Serverless Environment","platform":"datarobotServerless"}' \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/predictionEnvironments/")
serverless_env_id=$(echo "$serverless_env_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Created serverless environment ID: ${serverless_env_id}"
else
echo "Using existing serverless environment ID: ${serverless_env_id}"
fi
# Check if registered model already exists
registered_model_name="Auto MPG Registered Model"
existing_model_id=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/" \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*".*"'${registered_model_name}'"' \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4 | head -1)
if [ -n "${existing_model_id}" ]; then
echo "Using existing registered model: ${registered_model_name}"
# Create new version of existing model
model_version_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"Auto MPG Model\",\"registeredModelId\":\"${existing_model_id}\",\"leaderboardItemId\":\"${recommended_model_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/")
else
echo "Creating new registered model: ${registered_model_name}"
# Create new registered model
model_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"${registered_model_name}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/")
existing_model_id=$(echo "$model_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
# Create first version
model_version_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"Auto MPG Model\",\"registeredModelId\":\"${existing_model_id}\",\"leaderboardItemId\":\"${recommended_model_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/")
fi
model_version_id=$(echo "$model_version_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Model version ID: ${model_version_id}"
# Wait for model build to complete
echo "Waiting for model build to complete..."
while true; do
build_status=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/${model_version_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"buildStatus":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
if [ "${build_status}" = "READY" ] || [ "${build_status}" = "complete" ]; then
echo "Model build completed successfully!"
break
elif [ "${build_status}" = "FAILED" ]; then
echo "Model build failed. Please check the model registration."
exit 1
else
echo "Build status: ${build_status}. Waiting..."
sleep 30
fi
done
# Deploy the model using the registered model version
echo "Deploying the model to the serverless environment..."
deployment_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"label\":\"Auto MPG Predictions\",\"description\":\"Deployed with cURL for Auto MPG predictions\",\"predictionEnvironmentId\":\"${serverless_env_id}\",\"registeredModelVersionId\":\"${model_version_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/deployments/fromRegisteredModelVersion/")
deployment_id=$(echo "$deployment_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID: ${deployment_id}"
# Get the prediction URL for the deployment
echo "Retrieving prediction URL for deployment..."
prediction_url=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/deployments/${deployment_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"predictionUrl":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Prediction URL: ${prediction_url}"
# Deploy the model to a serverless prediction environment
cat("Deploying the model to a serverless prediction environment...\n")
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
prediction_environments <- ListPredictionEnvironments()
serverless_env <- NULL
for (env in prediction_environments) {
if (env$platform == "datarobotServerless") {
serverless_env <- env
break
}
}
if (is.null(serverless_env)) {
cat("Creating a new serverless prediction environment...\n")
serverless_env <- CreatePredictionEnvironment(
name = "Auto MPG Serverless Environment",
platform = "datarobotServerless"
)
}
# Register the model to create a registered model version
cat("Registering the model...\n")
registered_model_name <- "Auto MPG Registered Model"
# Check if registered model already exists
existing_models <- ListRegisteredModels()
existing_model <- NULL
for (m in existing_models) {
if (m$name == registered_model_name) {
existing_model <- m
break
}
}
if (!is.null(existing_model)) {
cat("Using existing registered model:", registered_model_name, "\n")
# Create a new version of the existing model
registered_model_version <- CreateRegisteredModelVersion(
model_id = model$modelId,
name = "Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id = existing_model$id
)
} else {
cat("Creating new registered model:", registered_model_name, "\n")
# Create a new registered model
registered_model <- CreateRegisteredModel(name = registered_model_name)
# Create first version
registered_model_version <- CreateRegisteredModelVersion(
model_id = model$modelId,
name = "Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id = registered_model$id
)
}
# Wait for the model build to complete
cat("Waiting for model build to complete...\n")
while (TRUE) {
current_version <- GetRegisteredModelVersion(registered_model_version$id)
if (current_version$buildStatus %in% c("READY", "complete")) {
cat("Model build completed successfully!\n")
break
} else if (current_version$buildStatus == "FAILED") {
stop("Model build failed. Please check the model registration.")
} else {
cat("Build status:", current_version$buildStatus, ". Waiting...\n")
Sys.sleep(30) # Wait 30 seconds before checking again
}
}
# Deploy the model to the serverless environment using the registered model version
deployment <- CreateDeploymentFromRegisteredModelVersion(
registered_model_version_id = registered_model_version$id,
label = "Auto MPG Predictions",
description = "Deployed with DataRobot R client for Auto MPG predictions",
prediction_environment_id = serverless_env$id
)
cat("Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID:", deployment$id, "\n")
Make predictions against the deployed model¶
When you have successfully deployed a model, you can use the DataRobot Prediction API to further test the model by making predictions on new data. This allows you to access advanced model management features such as data drift, accuracy, and service health statistics.
DataRobot offers several methods for making predictions on new data. You can read more about prediction methods in the UI documentation. You can also reference a Python prediction snippet from the UI. Navigate to the Deployments page, select your deployment, and go to Predictions > Prediction API to reference the snippet for making predictions.
This code makes predictions on the model using the test set you identified in the first step (test_dataset_file_path), when you uploaded data.
# Make predictions on test data
print("\nMaking predictions on test data...")
# Read the test data directly
import pandas as pd
from datarobot_predict.deployment import predict
test_data = pd.read_csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Use datarobot-predict for deployment predictions
predictions, response_headers = predict(deployment, test_data)
# Display the results
print("\nPrediction Results:")
print(predictions.head())
print(f"\nTotal predictions made: {len(predictions)}")
This code makes predictions on the deployed model using the test set identified in the first step (test_dataset_file_path), when you uploaded data.
# Use the prediction URL from deployment section
TEST_DATASET_FILE_PATH="./auto-mpg-test.csv"
# Make predictions by sending the CSV data directly
predictions=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: text/csv; charset=UTF-8" \
--data-binary "@${TEST_DATASET_FILE_PATH}" \
"${prediction_url}")
echo "Prediction Results:"
echo "$predictions" | jq '.'
prediction_count=$(echo "$predictions" | jq '.data | length')
echo "Total predictions made: ${prediction_count}"
This code makes predictions on the deployed model using the test set you identified in the first step (test_dataset_file_path), when you uploaded data.
# Make predictions on test data
cat("Making predictions on test data...\n")
# Read the test data directly
test_data <- read.csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Use the deployment for predictions (modern approach)
predictions <- PredictDeployment(deployment, test_data)
# Display the results
cat("Prediction Results:\n")
print(head(predictions))
cat("Total predictions made:", nrow(predictions), "\n")
Learn more¶
After getting started with DataRobot's APIs, browse the developer learning section for overviews, Jupyter notebooks, and task-based tutorials that help you find complete examples of common data science and machine learning workflows. Browse AI accelerators to try out repeatable, code-first workflows and modular building blocks. You can also read the reference documentation available for the REST API and Python API client.