Data ingestion from AWS S3¶
On-premise installations of DataRobot support ingestion of Amazon S3 objects from private buckets.
Once this is configured, users may click on the "URL" button at the "Create Project" screen and enter the full S3 URL. For example: s3://bucket-name/file-name.csv
After clicking the "Create New Project" button DataRobot starts the import by creating a signed URL for the S3 resource with a duration of 8 hours.
Required configuration¶
AWS Access¶
In order to ingest from private S3 buckets, the DataRobot installation needs access to the objects within those buckets.
This can be configured via IAM roles applied to Amazon EC2 instance(s) running the OpenShift/DataRobot application or by the inclusion of AWS credentials in the cluster's datarobot-modeling-envvars (see the Object Storage Configuration guide for more details on configuring AWS access for the cluster).
NOTE: it's not necessary to have the cluster utilizing S3 as the application backend in order to enable S3 Ingestion.
In this situation, follow the instructions in the Object Storage configuration section to configure access, but don't set the FILE_STORAGE_TYPE configuration variable to s3.
If the cluster is configured with S3 as the storage backend, the existing IAM role or AWS credentials applied to the cluster is also utilized for private bucket access.
NOTE: Unless using s3 signed URLs, S3 resources are not accessible when MinIO is used as an application backend.-
### s3 signed URLs are only valid for 12 hours ###
AWS S3 Access configuration¶
The DataRobot application needs only the AWS S3 GetObject permission in order to ingest data.
This permission should be applied as an additional AWS IAM Policy on the AWS user or role the cluster is using for access.
For example, to allow ingestion of data from a private bucket named examplebucket, the following policy could be applied:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Sid": "AllowReadOnlyAccessToS3Bucket",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::examplebucket/*"
}
}
Multiple policies can be applied to allow access to multiple private buckets.
AWS S3 Access via bucket policy¶
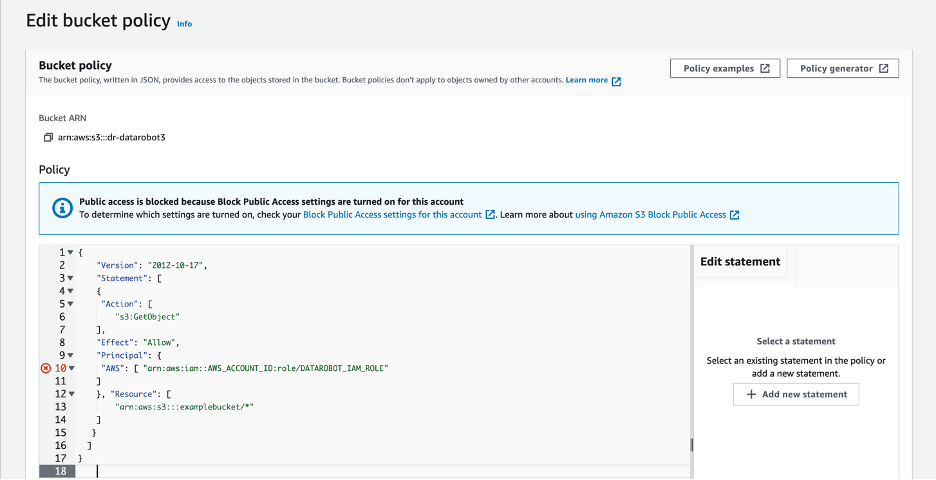
An alternative to granting GetObject via an IAM policy is to apply a bucket policy allowing this access. The following example bucket policy allows the AWS IAM Role the cluster utilizes read-only access to a private bucket:
Create S3 buckets¶
Ensure bucket is private¶
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"arn:aws:iam::AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/DATAROBOT_IAM_ROLE"
]
},
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::examplebucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Select the 'permissions' tab¶
Create bucket policy >> click 'EDIT'¶
DataRobot application configuration¶
To configure these options, refer to the Tuning DataRobot Environment Variables section of this guide.
With the AWS access and configuration in place, private bucket ingest is enabled via the ENABLE_S3_INGESTION configuration variable.
If the configuration variables S3_HOST and S3_REGION were not set as part of configuring AWS access, they must also be set at this time.
NOTE: DataRobot only supports ingestion from private S3 buckets in a single region.
The format for S3_HOST follows the pattern s3.<REGION>.amazonaws.com.
Example configuration to enable S3 ingest in the us-east-1 region:
# helm chart values snippet
core:
config_env_vars:
ENABLE_S3_INGESTION: True
S3_HOST: s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
S3_REGION: us-east-1
User-specific IAM role usage¶
With the above configuration in place, all access to AWS S3 resources occurs using the credentials configured as indicated above. Customers wishing for a more granular level of permissions may configure DataRobot to assume AWS IAM roles associated with a particular DataRobot user prior to accessing the data. In this way, different application users can be granted access to different private S3 buckets when ingesting data.
To enable this functionality, the cluster must be connected to an LDAP system (see the ldap configuration guide).
The following configuration options are present for this functionality:
ENABLE_S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION- Bool value to enable S3 role assumption (default: false).USER_AUTH_LDAP_ATTR_S3_ROLE_ARNS- The name of the ldap attribute containing zero or more Amazon Resource Name(s) (ARN) that should be utilized when ingesting data for the DataRobot user. When multiple ARNs are specified for a user, they're tried iteratively until one with access to the object is located.S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION_DEFAULT- An optional ARN to add to the user specific list of ARNs supplied via ldap.S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION_SESSION_PREFIX- String prefix to add to AWS session names when assuming roles for ingest; see Assumed Session Names for more details (default: DataRobot-APP).
Changes to AWS configuration¶
Instead of granting direct bucket access to the user/role DataRobot is utilizing for AWS access, a policy should be applied allowing these credentials to AssumeRole:
IAM policy creation¶
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Sid": "AllowRoleAssumptionForIngest",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "*"
}
}
NOTE: The policy above applies a blanket Allow permission to assume roles.
With this in place DataRobot would be able to attempt to assume any role provided via ldap for a user (or set as a cluster default via S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION_DEFAULT).
Whether or not this assumption is successful would depend on if the role was configured to allow this assumption to occur. Customer wishing to apply a more restrictive policy on what DataRobot is allowed to attempt to assume could do so by modifying the policy above with a more specific resource list.
For example, to limit DataRobot to assumptions where the role is named finance-dataaccess from the local AWS account or starts with DRAPP followed by anything from any AWS account, the following policy could be applied:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowRoleAssumptionForIngest",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/DRAPP*",
"arn:aws:iam::AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/finance-dataaccess"
]
}
]
}
Next, any number of roles can be created and configured with access to the desired buckets. These roles should be created with a trust policy that allows assumption by the credentials utilized for DataRobot.
For example, one would apply the following trust policy to a role that should be assumable by a DataRobot installation running in AWS account 123456789012 with a IAM instance role named dr-app:
IAM policy for s3 ingestion¶
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/dr-app"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
These data access roles should then be configured with policies defining the appropriate GetObject access, as described previously.
Finally, the Maximum CLI/API session duration configuration value for the role should be increased to at least 8 hours.
When ingesting from S3, DataRobot generates a temporary secure URL with an 8 hour lifetime by default to allow ingest support of large files. AssumeRole calls are made with this same lifetime, and fails if the role has a maximum session lifetime lower than this value.
If necessary, this can be modified via the configuration variable S3_LINK_EXPIRATION_DEFAULT, expressed as a number of seconds.
Example config with assumption¶
# helm chart values snippet
core:
config_env_vars:
ENABLE_S3_INGESTION: True
ENABLE_S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION: True
S3_HOST: s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
S3_REGION: us-east-1
USER_AUTH_LDAP_ATTR_S3_ROLE_ARNS: s3_arns # LDAP attribute `s3_arns` contains the information for each user
S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION_DEFAULT: arn:aws:iam::AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/DEFAULT_ACCESS_ROLE # appended to ARN(s) supplied via LDAP for all users
Assumed session names¶
When ingesting data with an assumed role, that role is assumed with a unique name that allows access to be associated with a particular DataRobot application user. Sessions are assumed with a name of <PREFIX>-<USER ID>, where PREFIX is the value of the configuration option S3_ROLE_ASSUMPTION_SESSION_PREFIX and USER ID is the requesting users' unique identifier in the DataRobot application.