Managed SaaS releases¶
June SaaS feature announcements¶
June 2025
This page provides announcements of newly released features in June 2025, available in DataRobot's SaaS multi-tenant AI Platform, with links to additional resources. From the release center, you can also access past announcements and Self-Managed AI Platform release notes.
June features¶
The following table lists each new feature:
Features grouped by capability
Applications¶
Persistent storage added to applications¶
DataRobot now uses the key-value store API and file storage to provide persistent storage in applications—both custom applications and application templates. This can include user settings, preferences, and permissions to specific resources, as well as chat history, monitoring usage, and data caching for large data frames.
Control application access with API keys¶
You can now grant users the ability to access and use data from within a custom application using an application API key, which provides the application with access to the DataRobot public API. Sharing roles grants control over the application as an entity, while application API keys control the requests the application can make. For example, when a user accesses an application, the application requests the user's consent to generate an API key. That key has a configured level of access, controlled by the application source. Once authorized, the application API key is included in the header of the request made by the application. An application can take the API key from the web request header and, for example, look up what deployments the user has access to and use the API key to make predictions.
GenAI¶
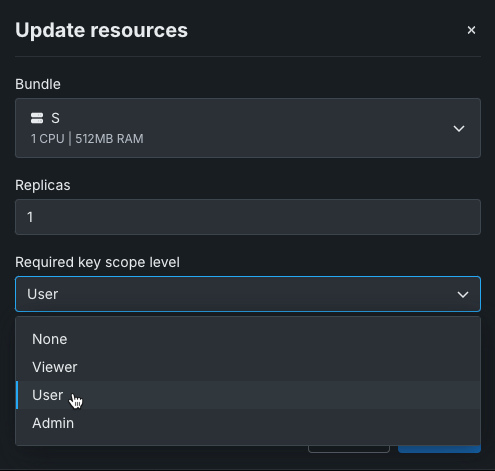
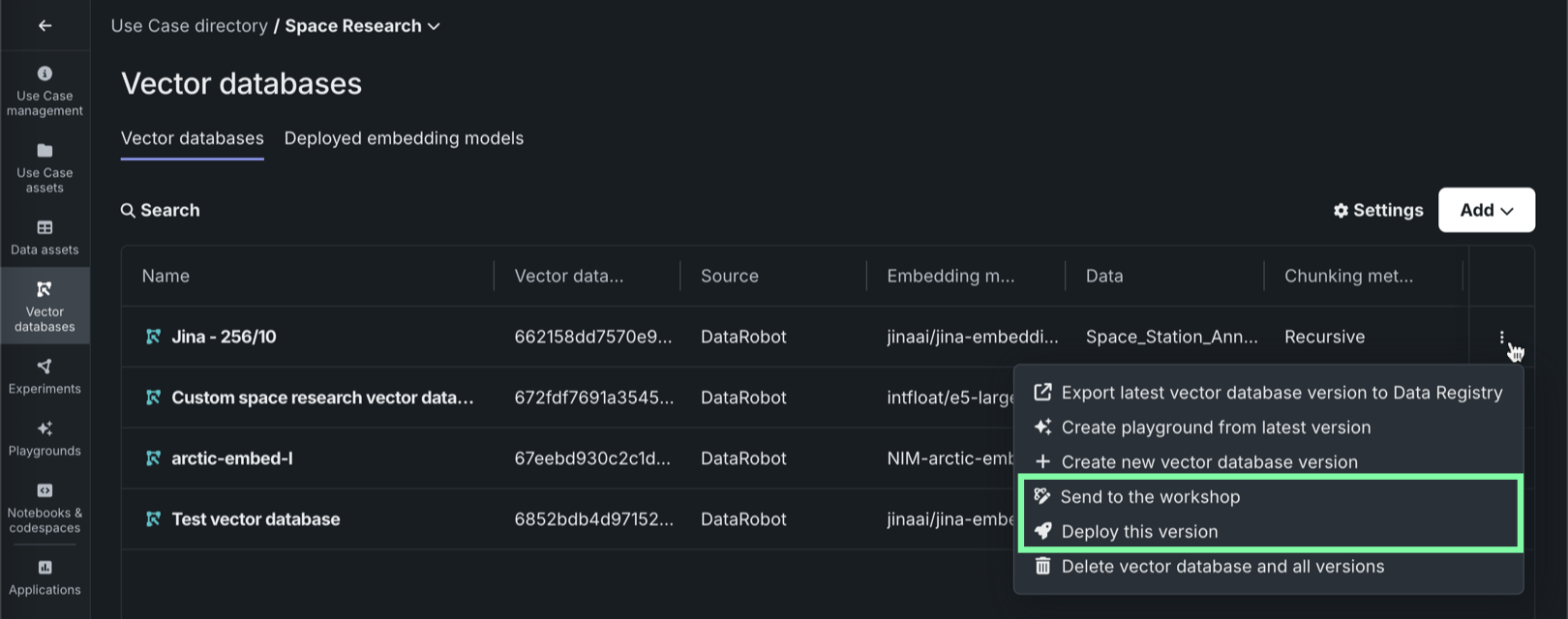
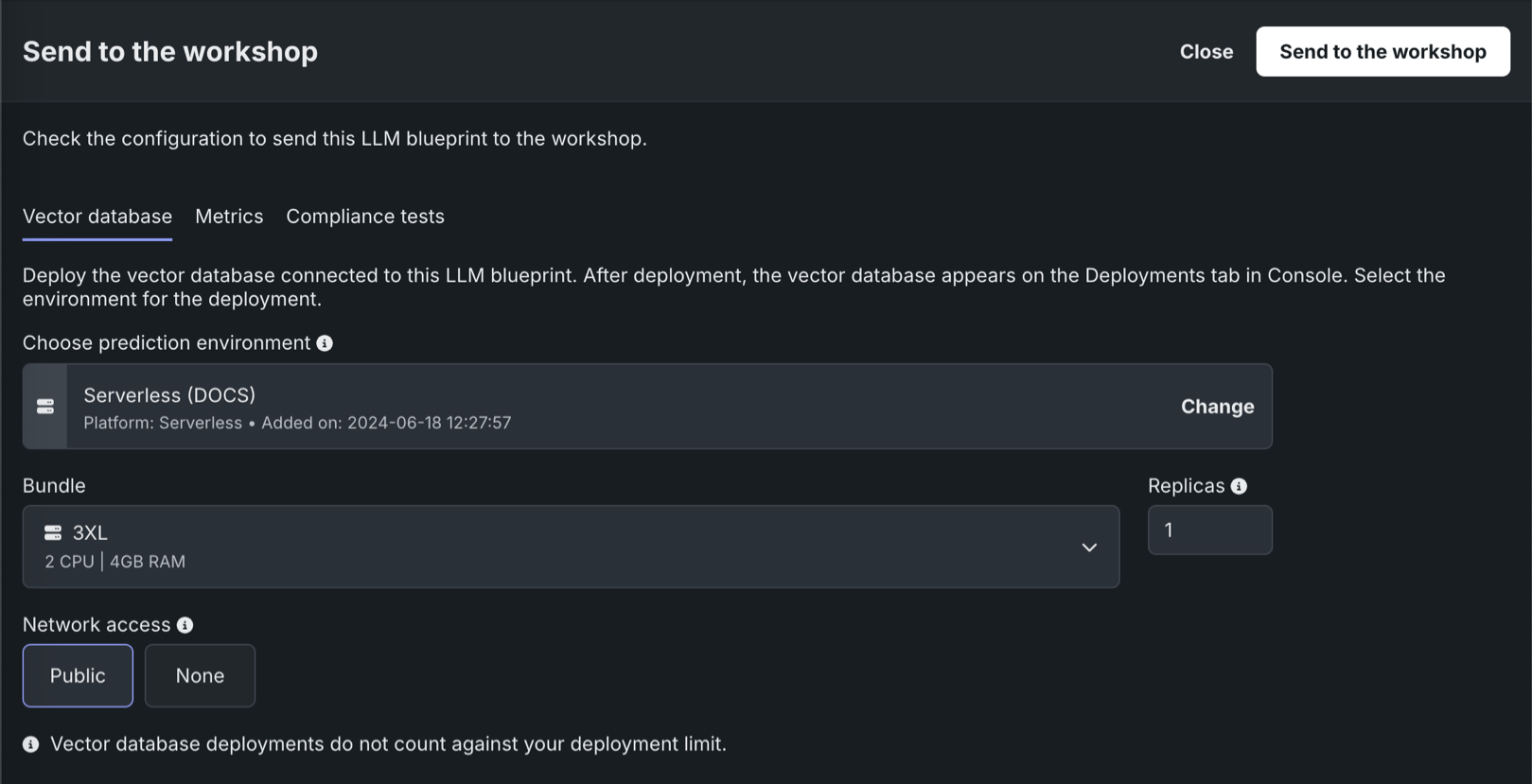
Register and deploy vector databases¶
With this release, you can now send vector databases to production from Workbench, in addition to creating and registering vector databases in Registry. DataRobot also supports monitoring vector database deployments, automatically generating custom metrics relevant to vector databases during the deployment process.
In Registry, with the vector database target type in the model workshop, you can register and deploy vector databases, as you would any other custom model.
In Workbench, each vector database on the Vector databases tab can be sent to production in two ways:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Send to model workshop | Send the vector database to the model workshop for modification and deployment. |
| Deploy latest version | Deploy the latest version of the vector database to the selected prediction environment. |
In an LLM playground in Workbench, when you send an LLM associated with a vector database to production, you can also register and deploy the vector database.
Streaming support in the moderation framework¶
There is now improved moderation support for streaming LLM chat completions. Chat completions now include datarobot_moderations when a deployment meets two requirements: the execution environment image includes the moderation library and the custom model code contains moderation_config.yaml. For streaming responses with moderation enabled, the first chunk now provides information about configured prompt guards and response guards.
Improved workshop configuration for NeMo guard NIM¶
The Workshop now includes options to configure NVIDIA NeMo jailbreak and content safety guards. You only need to select the deployed LLM to configure these moderation metrics.
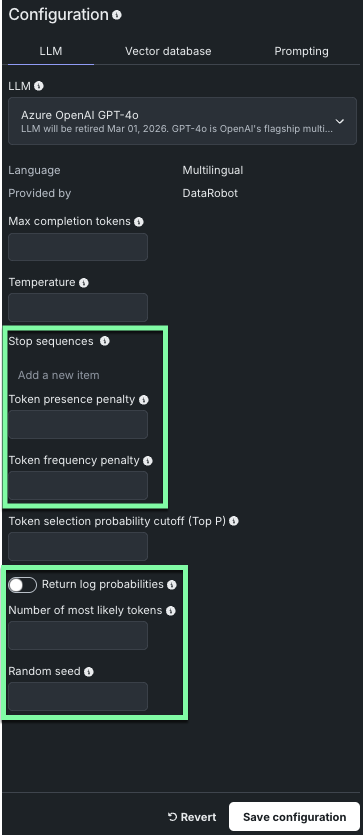
Expanded LLM model support¶
DataRobot has added support for many new LLM models when creating your LLM blueprint. Some of the new models implement additional model parameters, as indicated below.
Note
The parameters available will vary depending on the LLM model selected.
For steps on using the new models and parameters, refer to Build LLM blueprints.
Data¶
Connect to JDBC drivers in Workbench¶
In Workbench, you can connect to and add snapshotted data from supported JDBC drivers. When adding data to a Use Case, JDBC drivers are now listed under available data stores.
Note that only snapshotted data can be added from a JDBC driver.
Support for dynamic datasets in Workbench now GA¶
Support for dynamic datasets is now generally available in Workbench. Dynamic data is a “live” connection to the source data that DataRobot pulls upon request, for example, when creating a live sample for previews.
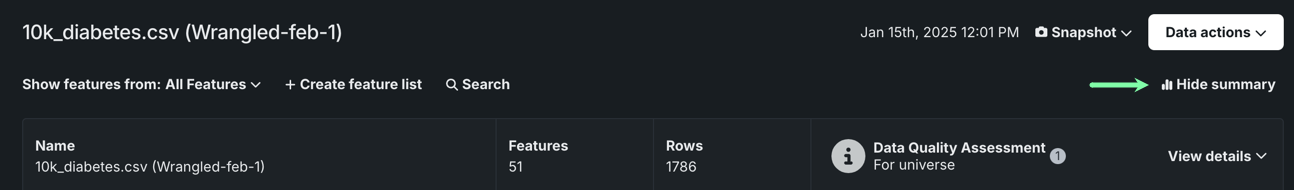
Additional data improvements added to Workbench¶
This release introduces the following updates to the data exploration experience in Workbench:
-
When exploring a dataset, click Show summary to view information, including feature and row count, as well as a Data Quality Assessment.
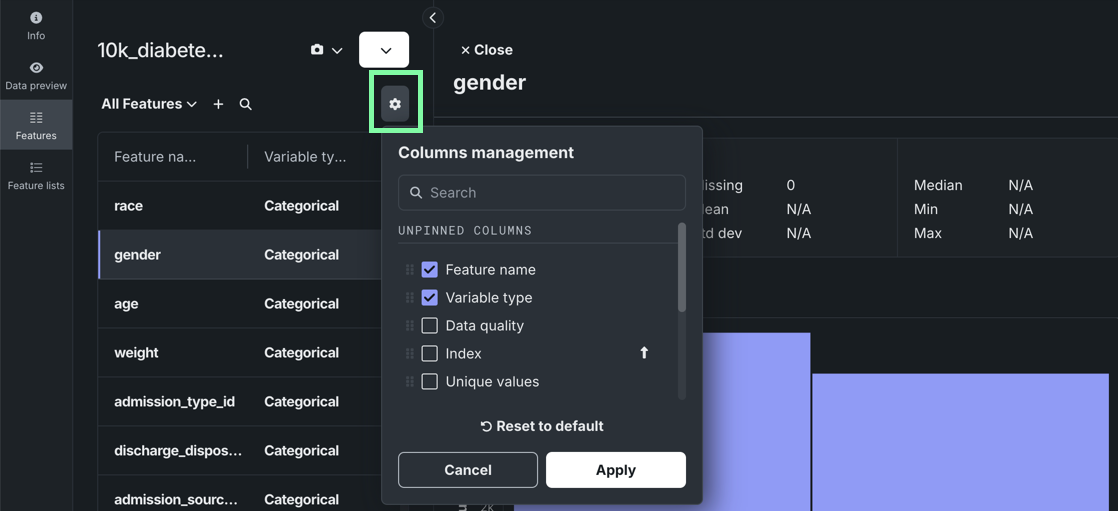
-
Manage which columns are visible when viewing individual features.
Modeling¶
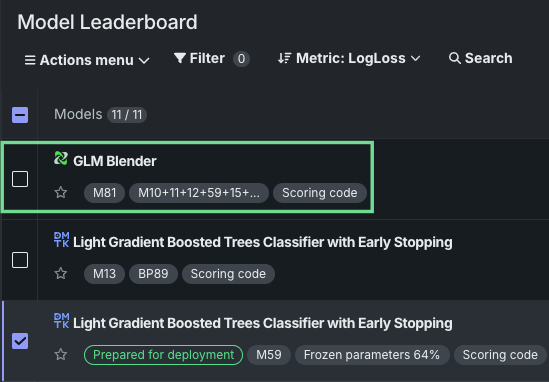
Blenders now available in Workbench¶
Blenders, also known as ensemble models, are now available as a post-modeling operation in Workbench. By combining the base predictions of multiple models and training them on predictions from the validation set of those models, blenders can potentially increase accuracy and reduce overfitting. With multiple blending methods available, blenders can be created for both time-aware and non-time-aware experiments.
Select from two to eight models from the Leaderboard’s Actions menu, select a blend method, and train the new model. When training is complete, the new blended model displays in the list on the Leaderboard.
Incremental learning improvements speed experiment start¶
Incremental learning (IL) is a model training method specifically tailored for supervised experiments leveraging datasets between 10GB and 100GB. By chunking data and creating training iterations, you can identify the most appropriate model for making predictions. This deployment brings two substantial improvements to incremental learning:
-
For static (or snapshotted) datasets, you can now begin experiment setup once EDA1 completes; the experiment summary populates almost immediately. Previously, because the first chunk was used as the data to start the project, depending on the size of the dataset it could take a long time to create the first chunk. The EDA sample is a good representation of the full dataset and using it allows moving forward with setup, speeding experimentation. It also provides more efficiency and flexibility in iterating to find the most appropriate configuration before committing to applying settings to the full dataset.
-
Support for experiments creating time-aware predictions is now available.
Predictions and MLOps¶
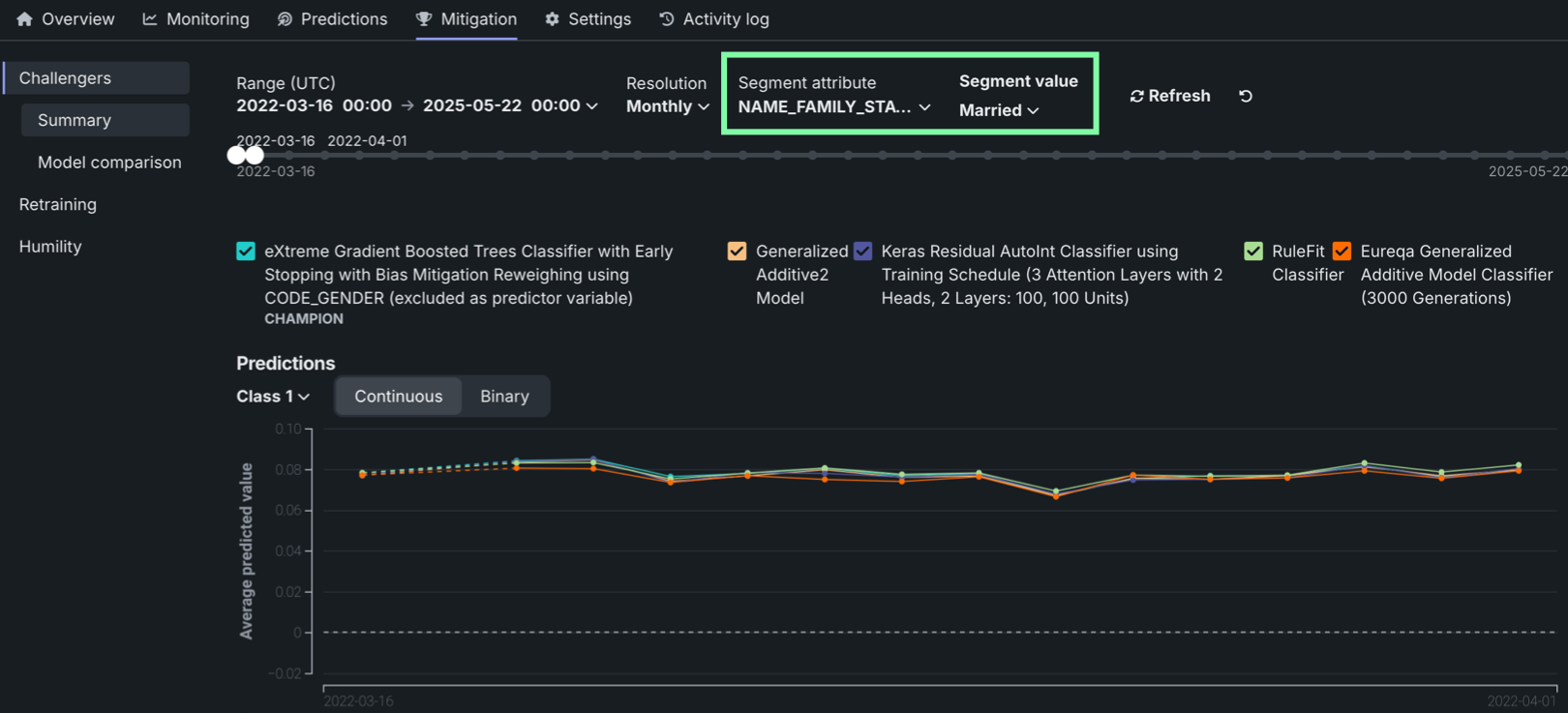
Segmented analysis on the Challengers tab¶
On a deployment’s Challengers tab, you can now select a segment attribute and segment value to filter the challenger performance metrics charts.
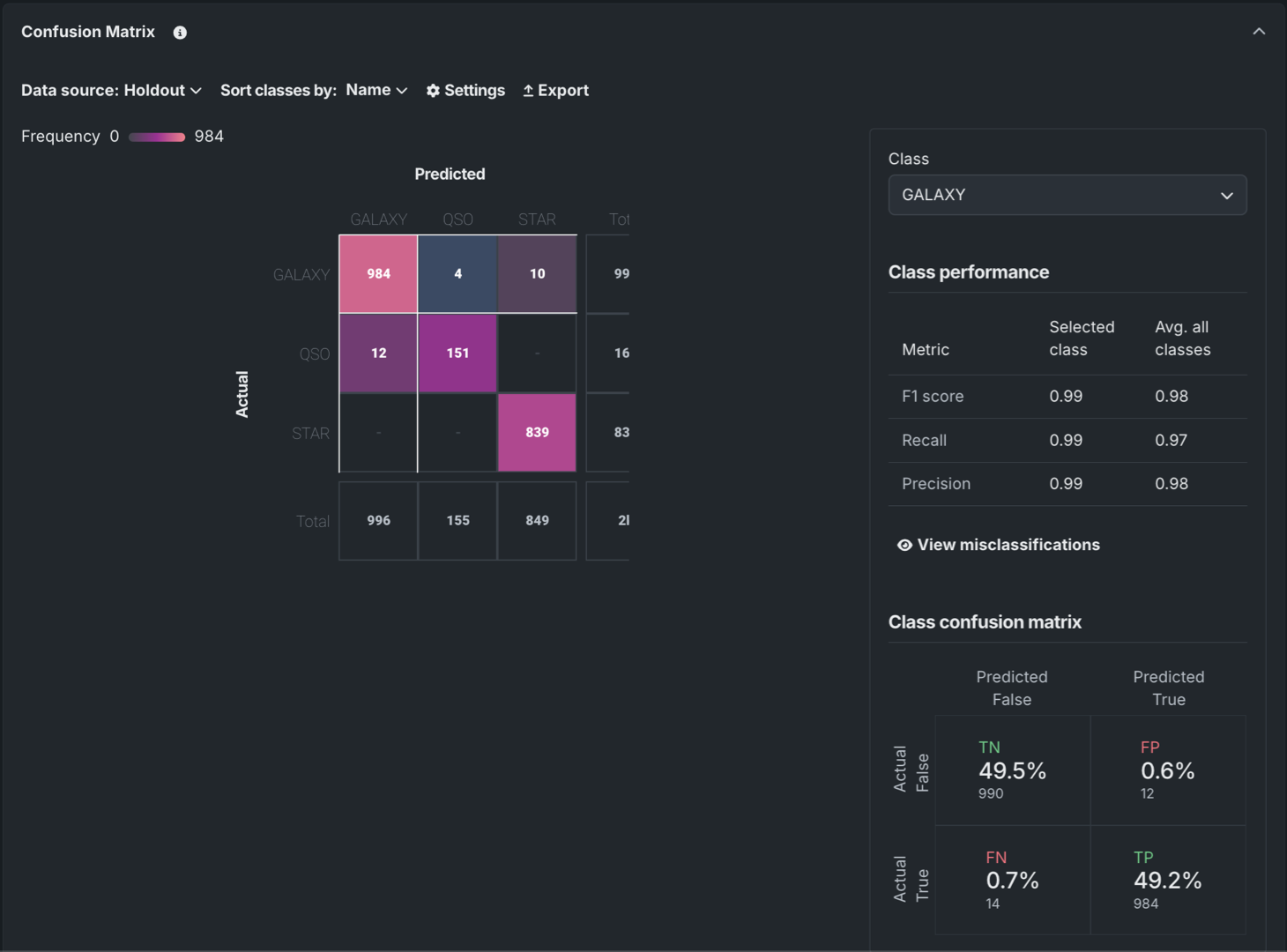
View the Confusion Matrix in the Registry¶
For DataRobot and custom models in the Registry, the Insights tab can now include the Confusion Matrix insight. For more information, see the registered model insights documentation.
List models support for custom models¶
Custom models now support the OpenAI client .models.list() method, which returns available models in a deployment along with basic information such as the owner and availability. This functionality is available out-of-the-box for managed RAGs, NIMs, and hosted LLMs. For custom models, you can customize the response by implementing the get_supported_llm_models() hook in custom.py.
Platform¶
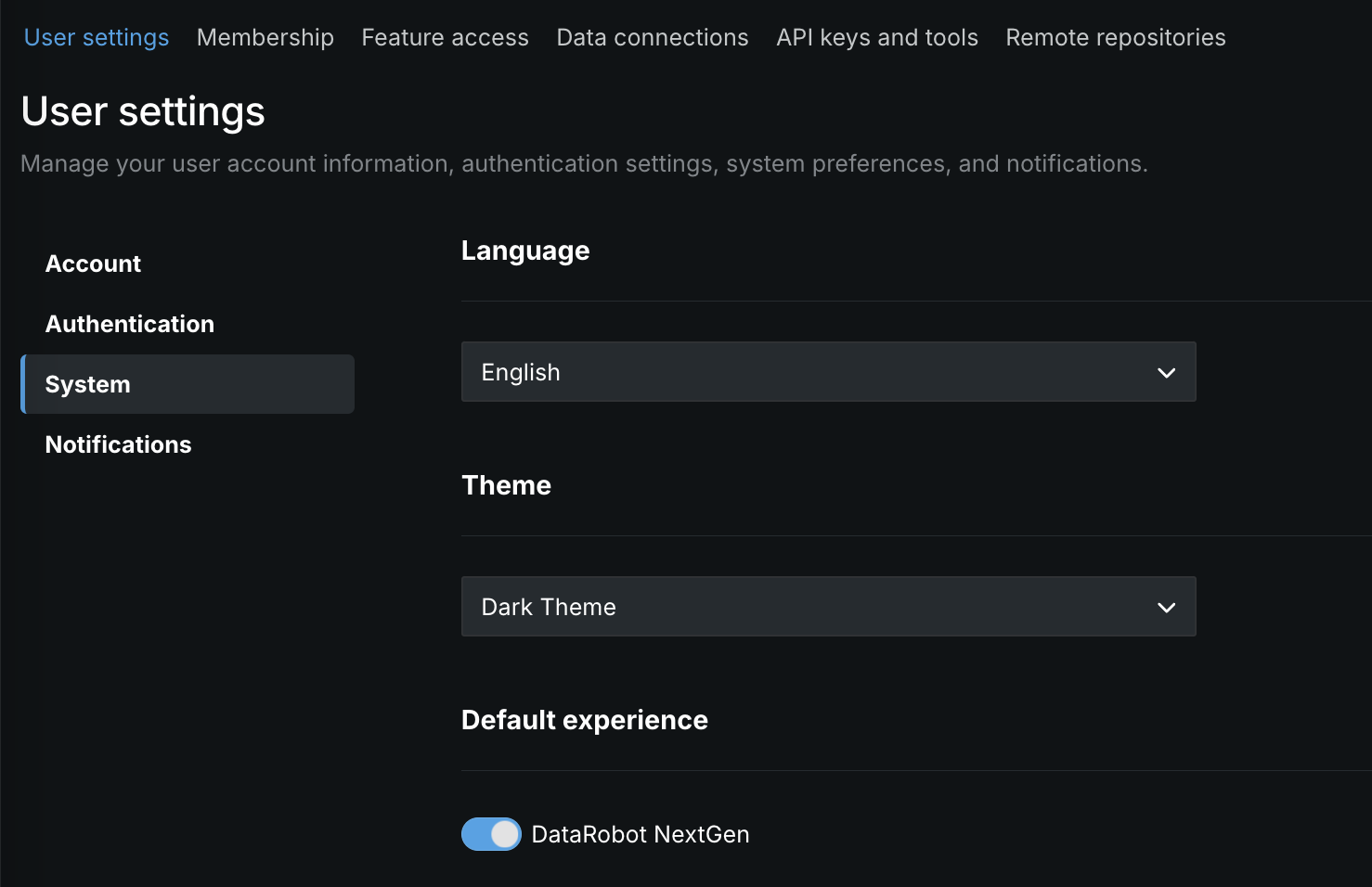
NextGen is now the default landing page¶
The NextGen homepage is now the default landing page when accessing app.datarobot.com. However, when you request a specific page, for example app.datarobot.com/projects/123abc/models, you will be brought to the requested page. You can make DataRobot Classic the default page instead of NextGen by selecting User settings > System and disabling the toggle.
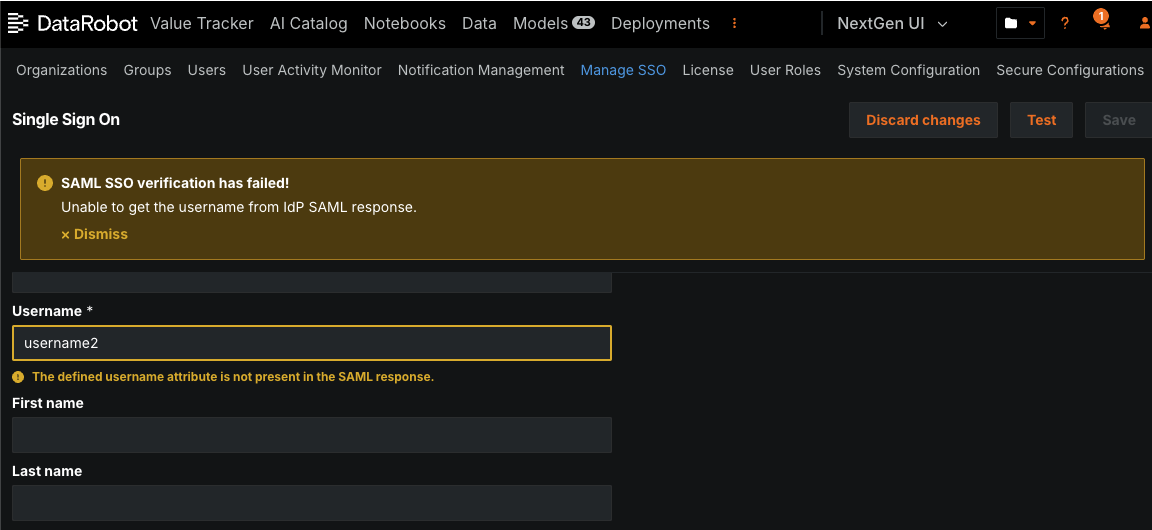
Automated SAML SSO testing¶
You can conduct automated testing for a SAML SSO connection after configuring it from the SSO management page. When you conduct a test, administrators provide the user credentials and perform the login process on the IdP side. When testing completes, you receive either a success message or a warning message about what went wrong, with fields highlighting the incorrect values.
Updated FIPS password requirements for Snowflake connections¶
Due to updates in FIPS credential requirements, DataRobot now requires that credentials adhere to Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS), a government standard that ensures cryptographic modules meet specific security requirements validation. All credentials used in DataRobot, particularly Snowflake basic credentials and key pairs, must adhere to FIPS-compliant formats as indicated below:
- RSA keys must be at least 2048 bits in length, and their passphrases must be at least 14 characters long.
- Snowflake key pair credentials must use a FIPS-approved algorithm and have a salt length of at least 16 bytes (128 bits).
For additional details, refer to the FIPS validation FAQ.
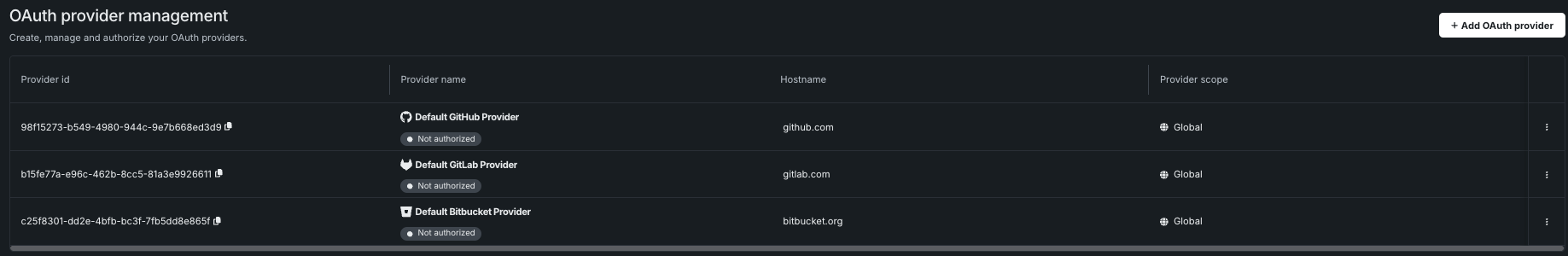
Support for external OAuth server configuration¶
This release adds a new Manage OAuth providers page that allows you to configure, add, remove, or modify OAuth providers for your cluster.
Additionally, support has been added for two new OAuth providers: Google and Box. Refer to the documentation for more details.
All product and company names are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Use of them does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.