Generative AI (V11.1)¶
July 17, 2025
DataRobot announces agentic AI Platform for scalable, governed AI application development¶
Premium
DataRobot's Generative AI capabilities are a premium feature; contact your DataRobot representative for enablement information. Try this functionality for yourself in a limited capacity in the DataRobot trial experience.
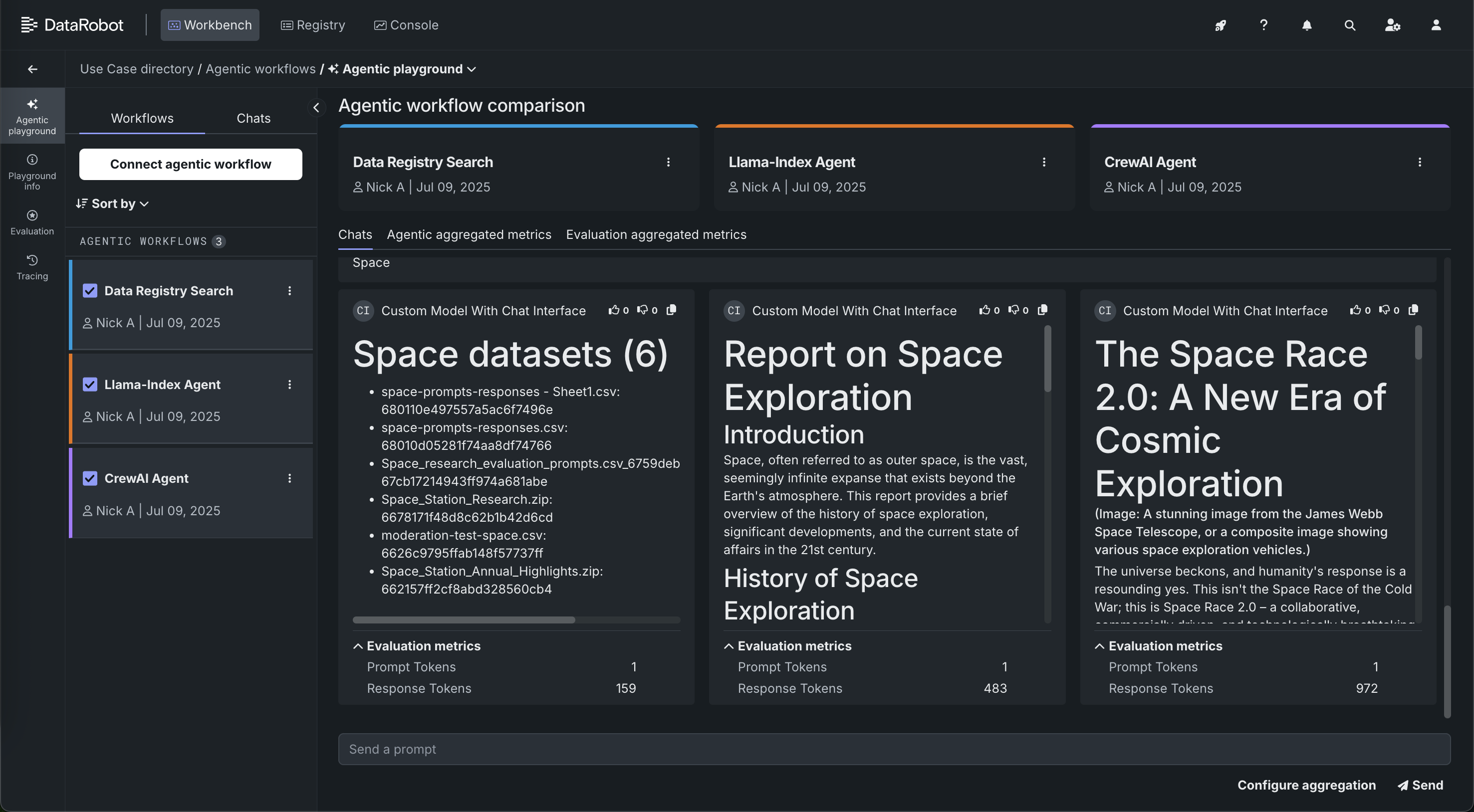
With the release of version 11.1.0, DataRobot is launching its new agentic AI Platform, designed to empower enterprises to build, operate, and govern scalable agentic AI applications. Because most app developers begin building agents in their local IDE, DataRobot is offering templates and a CLI to promote seamless local development, migration of code into DataRobot, and hooks into platform functionality. This allows you to prepare an agent prototype for production, which can include applying advanced agent debugging and experimentation tools—troubleshooting, evaluating, and testing guard models on agentic flows with individual compute instances via DataRobot codespaces. With agentic flows you get side-by-side flow comparison and granular error reporting for easy troubleshooting, and OTEL compliant tracing for observability in each component of the agent.
Global tools are accessible for common use cases along with tool-level authentication so you can bring your agents into production safely. DataRobot also offers "Batteries Included" integration with serverless LLMs from major providers like Azure OpenAI, Bedrock, and GCP, ensuring seamless experimentation, governance, and observability, all accessible via an LLM gateway. Finally, you can now connect to your own Pinecone or Elasticsearch vector databases during development and for use in production, allowing you to take advantage of scalable vector databases that give relevant context to LLMs.
All of this can be used alongside several other new features. DataRobot offers one-click deployment of NVIDIA Inference Microservices (NIMs) in air-gapped environments and sovereign clouds. A centralized AI Registry for all tools and models used in agentic Workflows provides robust approval workflows, RBAC, and custom alerts. Real-time LLM intervention and moderation are supported with out-of-the-box and custom guards, including integration with NVIDIA's NeMo for content safety and topical rails. GenAI compliance tests and documentation generate reports for PII, Prompt Injection, Toxicity, Bias, and Fairness to meet regulatory requirements.
Key capabilities of the 11.1 agentic release¶
The following are some of the major capabilities of the end-to-end agentic workflow experience, with more GenAI features described in the sections that follow:
-
BYO: Bring your agentic workflow, built with either the LangGraph, LangChain, or CrewAI frameworks, from the Registry workshop to the new agentic playground and test it.
-
Build and deploy agents from templates leveraging multi-agent frameworks. Build anywhere using Langchain, CrewAI, or Llamaindex, in Visual Studio Code, DataRobot, or your own notebooks. Using decorators, DataRobot auto-recognizes interrelations between tools, models, and more.
-
Single agent and multi-agent chat comparison functionality.
-
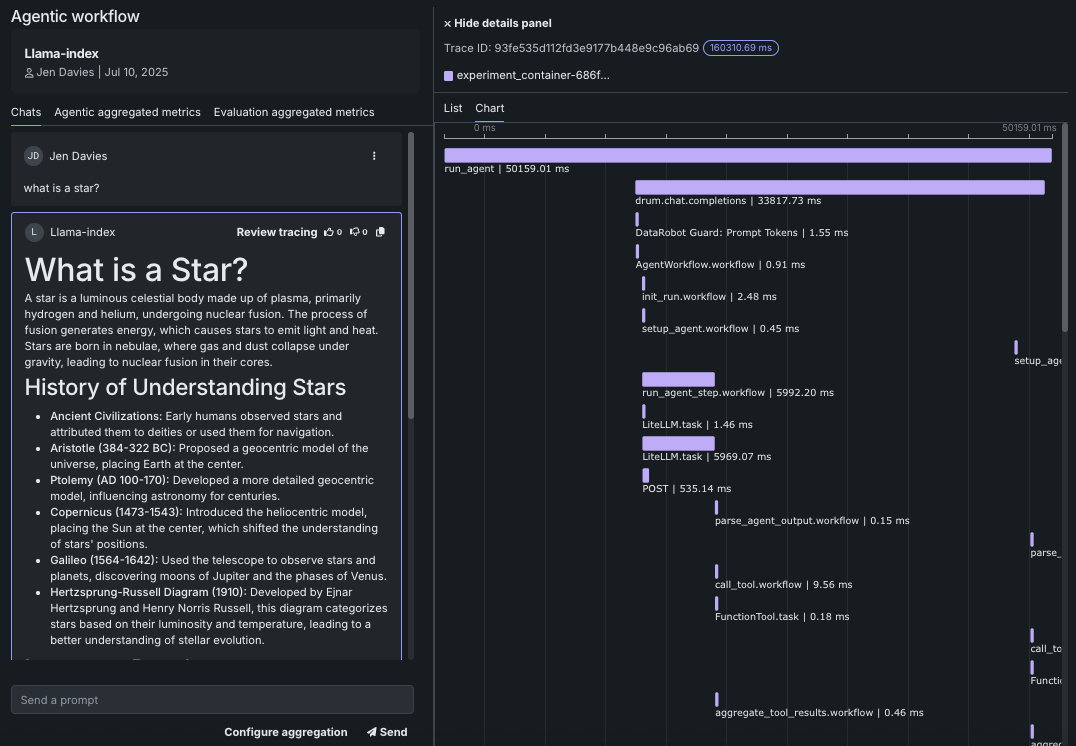
Detailed tracing for root cause analysis with metrics at both the agent and the tool level.
-
Iterative experimentation using DataRobot codespaces to develop agentic workflows alongside testing in an agentic playground.
-
A test suite to assess RAG lookup, LLM response quality, and user-defined guardrail efficacy. Synthetically generate or define evaluation data and then use LLMs and built-in NLP metrics to judge response quality (e.g. correctness, faithfulness, and hallucinations). A configurable "LLM as a Judge" assesses responses based on prompt and context. Synthetic examples are generated automatically based on content within the grounding data.
-
Monitor and govern in Registry and Console, including:
-
End-to-end monitoring to trace execution flow visually with functional and operational metrics at both the tool and agent levels. These detailed traces for each execution flow include tool usage and LLM input and output.
-
Register and deploy agents and tools in Registry and Console to enable production-ready governance, monitoring, mitigation, and moderation capabilities.
-
Deploy OSS and proprietary evaluation and moderation guards for agentic flows (for example, PII, relevance, jailbreak, hate speech).
-
Connect custom metrics for agentic cost, prompt tokens, and completion tokens to deployed agentic workflows in Console.
-
GenAI general enhancements¶
The following lists other new GenAI functionality. See also other new features of V11.1.
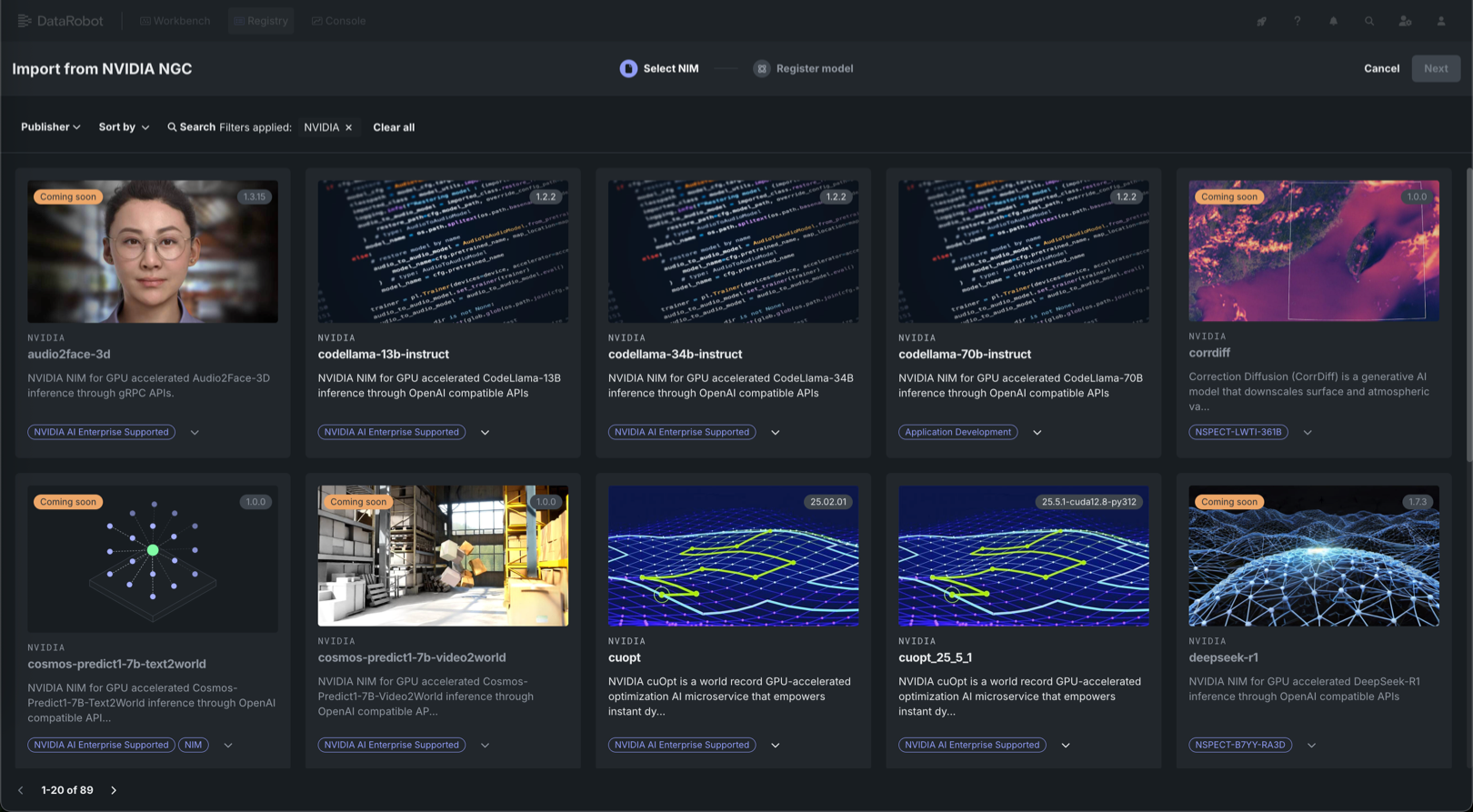
Explore 60+ GPU-optimized containers in the NIM Gallery¶
NVIDIA AI Enterprise and DataRobot provide a pre-built AI stack solution, designed to integrate with your organization's existing DataRobot infrastructure, which gives access to robust evaluation, governance, and monitoring features. This integration includes a comprehensive array of tools for end-to-end AI orchestration, accelerating your organization's data science pipelines to rapidly deploy production-grade AI applications on NVIDIA GPUs in DataRobot Serverless Compute.
In DataRobot, create custom AI applications tailored to your organization's needs by selecting NVIDIA Inference Microservices (NVIDIA NIM) from a gallery of AI applications and agents. NVIDIA NIM provides pre-built and pre-configured microservices within NVIDIA AI Enterprise, designed to accelerate the deployment of generative AI across enterprises.
With the release of version 11.1, DataRobot added new GPU-optimized containers to the NIM Gallery, including:
-
Document processing: PaddleOCR and the NemoRetriever suite for OCR, document parsing, and intelligent data extraction from PDFs and forms.
-
Language models: DeepSeek R1 Distill (14B/32B) and Nemotron (Nano-8B/Super-49B) for reasoning, content generation, and conversational AI.
-
Specialized tools: CuOpt for decision optimization, StarCoder2-7B for code generation, and OpenFold2 for protein folding.
Use the DataRobot LLM gateway¶
Now available as a premium feature, the DataRobot LLM gateway service provides a DataRobot API endpoint to interface with LLMs hosted by external LLM providers. To request LLM responses from the DataRobot LLM gateway, you can use any API client that supports OpenAI-compatible chat completion API, such as the OpenAI Python API library.
To use this service, learn how to make requests to the DataRobot LLM gateway in your code. Or, in a text generation custom model from the playground, provide the ENABLE_LLM_GATEWAY_INFERENCE runtime parameter set to True to use the gateway for that model.
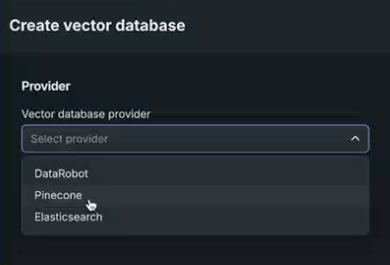
Vector database as a service¶
When creating a vector database in a Use Case, you can now select DataRobot or a direct connection to either Pinecone or Elasticsearch external data sources. These connections support up to 100GB file sizes. When you connect, the data source is stored locally in the Data Registry, configuration settings are applied, and the created vector database is written back to the provider. When selecting Pinecone or Elasticsearch, you will provide credential and connection information. Otherwise, the flow is the same as the DataRobot-resident Facebook AI Similarity Search (FAISS) vector database, with the exception of these considerations.
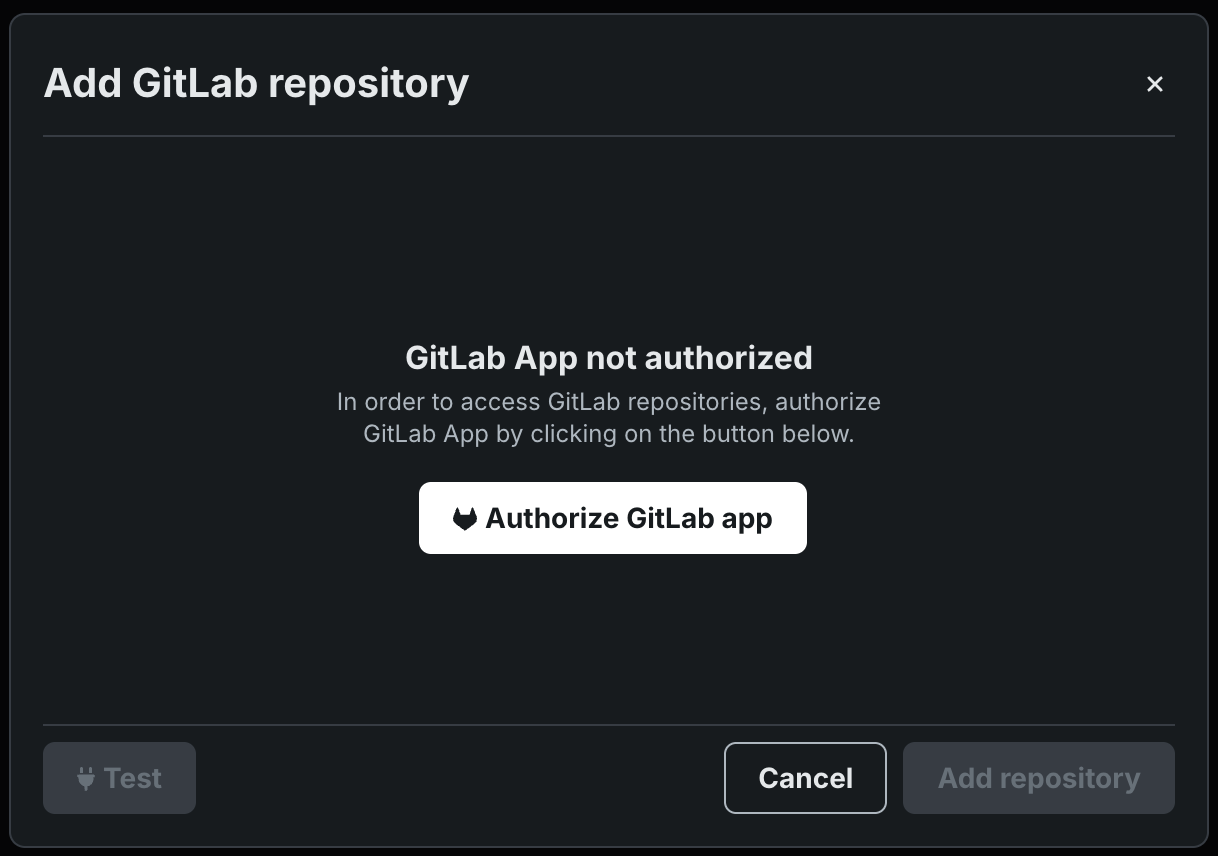
GitLab repository integration¶
Connect to GitLab and GitLab Enterprise repositories to pull custom model files into Workshop, accelerating the development and assembly of custom models and custom agentic workflows.
Attach metadata for filtering prompt queries¶
You can select an additional file to define the metadata to attach to the chunks in the vector database. Select whether to replace duplicates or retain.
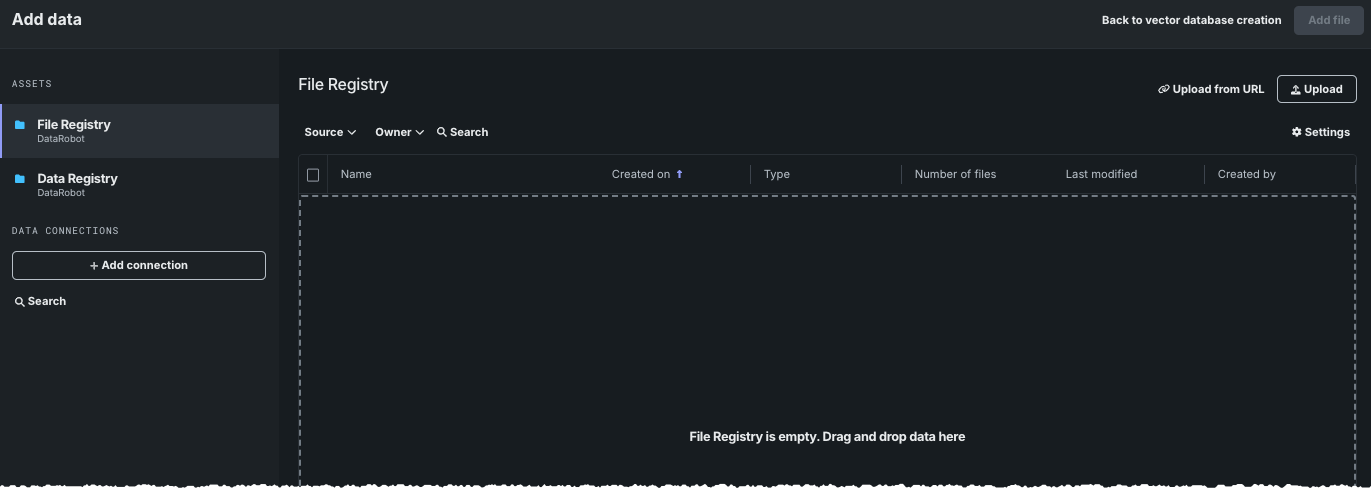
File Registry for vector databases¶
The File Registry is a "general purpose" storage system that can store any type of data. In contrast to the Data Registry, the File Registry does not do CSV conversion on files uploaded to it. In the UI, vector database creation is the only place where the File Registry is applicable, and it is only accessible via the Add data modal. While any file type can be stored there, the same file types are supported for vector database creation regardless of registry type.
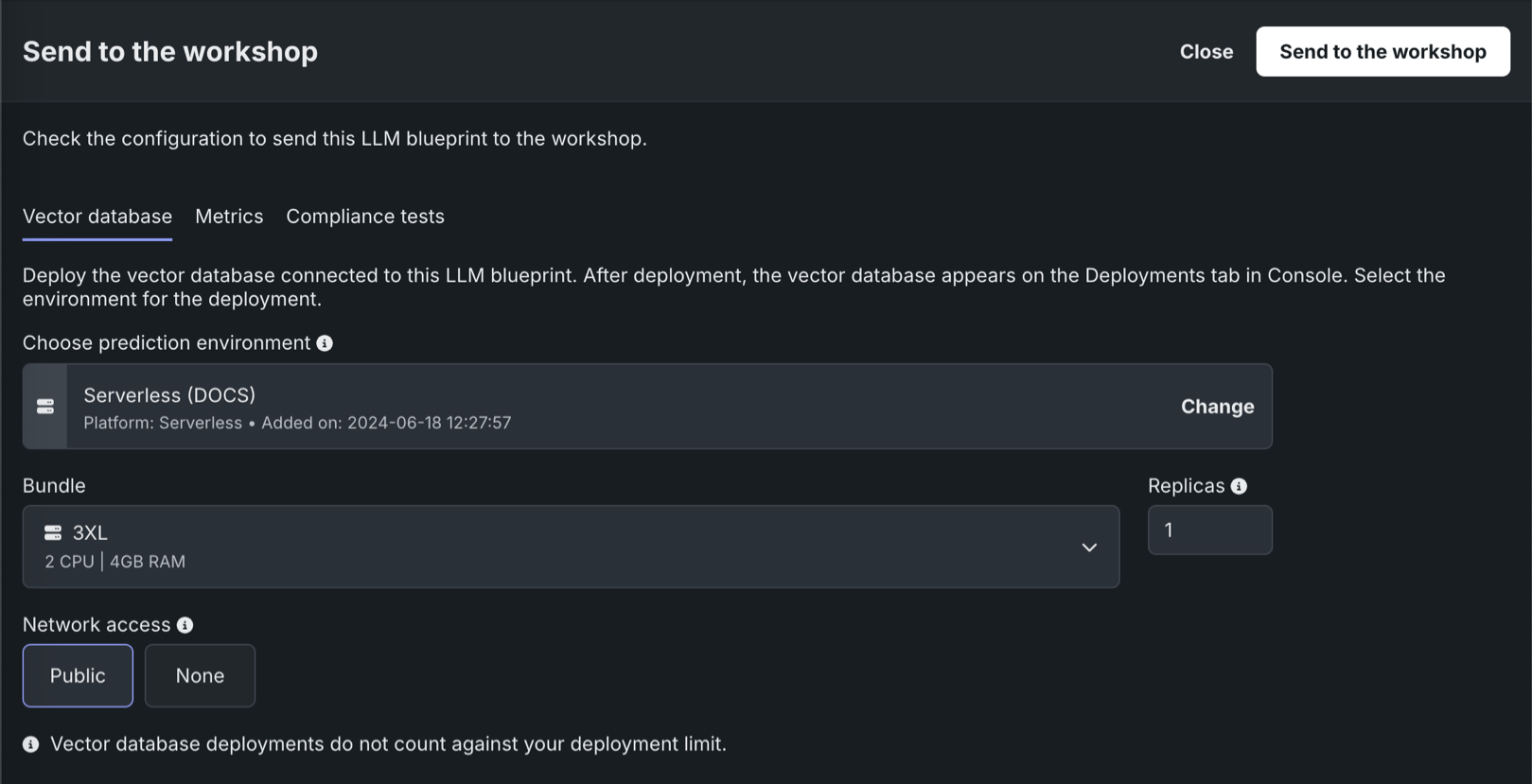
Register and deploy vector databases¶
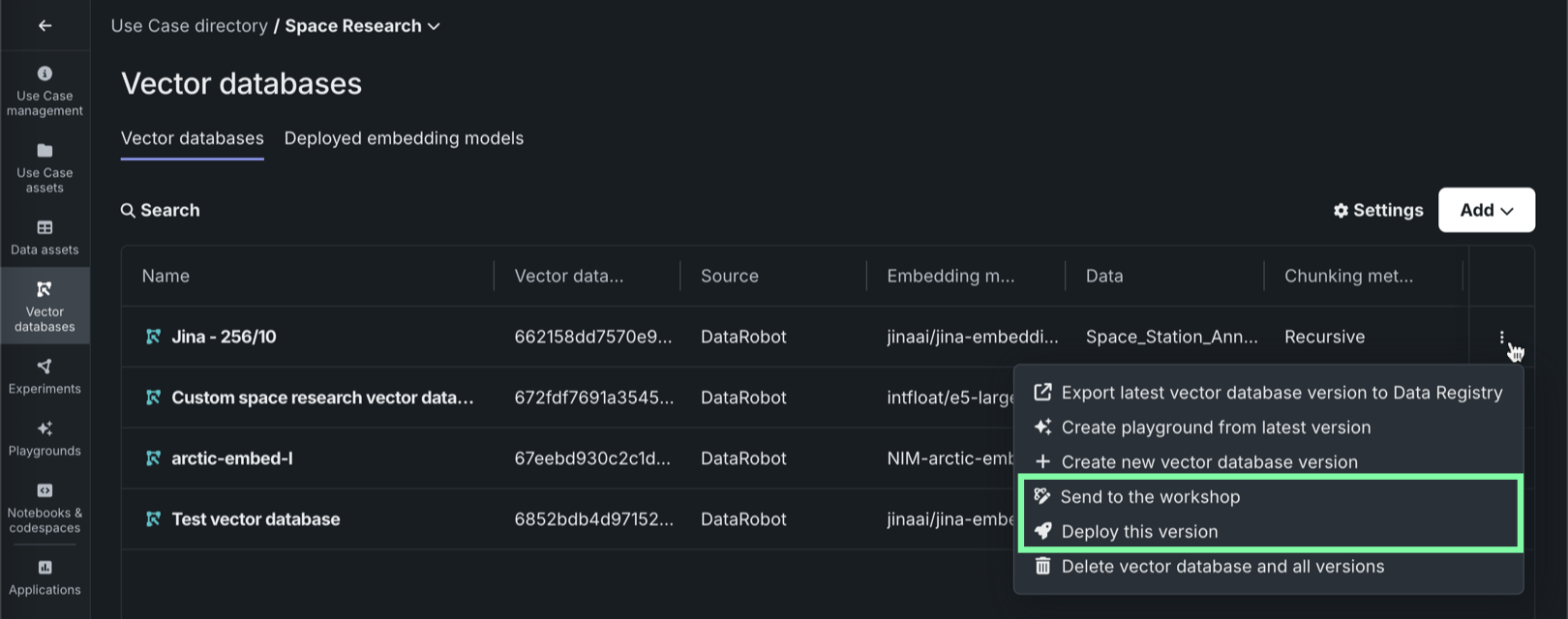
With this release, you can now send vector databases to production from Workbench, in addition to creating and registering vector databases in Registry. DataRobot also supports monitoring vector database deployments, automatically generating custom metrics relevant to vector databases during the deployment process.
In Registry, with the vector database target type in the workshop, you can register and deploy vector databases, as you would any other custom model.
In Workbench, each vector database on the Vector databases tab can be sent to production in two ways:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Send to the workshop | Send the vector database to the Registry workshop for modification and deployment. |
| Deploy this version | Deploy this version of the vector database to the selected prediction environment. |
In an LLM playground in Workbench, when you send an LLM associated with a vector database to production, you can also register and deploy the vector database.
Improved workshop configuration for NeMo guard NIM¶
The Workshop now includes options to configure NVIDIA NeMo jailbreak and content safety guards. You only need to select the deployed LLM to configure these moderation metrics.
New versions of Gemini released; Bison retired¶
On May 24, 2025, Gemini 1.5 Pro v001 and Gemini 1.5 Flash v001 will be replaced with v002. On-premise users must upgrade to DataRobot release 11.0.1 to continue using these embedding models. On September 24, 2025 both Gemini 1.5 Pro v002 and Gemini 1.5 Flash v002 will be retired. Once upgraded, any LLM blueprint in the playground will be automatically switched to v002. If you have a registered model or deployment that uses v001, you must send the LLM blueprint to the Registry’s workshop again and redeploy it to start using v002. Alternatively, if using the Bolt-on Governance API for inference, specify gemini-1.5-flash-002 / gemini-1.5-pro-002 as the model ID in the inference request without redeploying the LLM blueprint.
Additionally, Google Bison has been retired. See the full list of LLM availability in DataRobot, with links to creator documentation, for assistance in choosing a replacement embedding model.
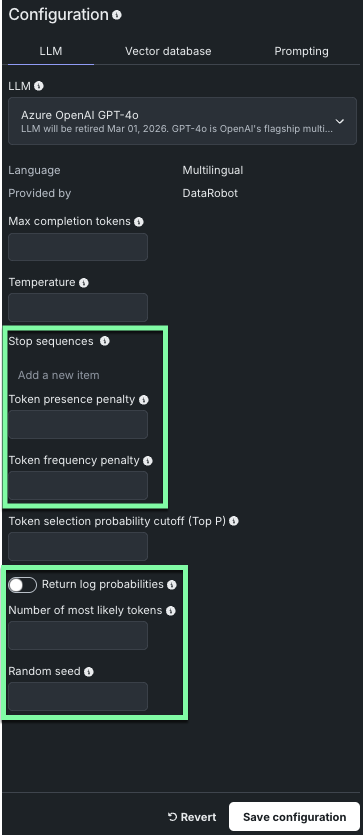
Expanded LLM model support¶
DataRobot has added support for many new LLM models when creating your LLM blueprint. Some of the new models implement additional model parameters, as indicated below.
Note
The parameters available will vary depending on the LLM model selected.
For steps on using the new models and parameters, refer to Build LLM blueprints.
Streaming support in the moderation framework¶
There is now improved moderation support for streaming LLM chat completions. Chat completions now include datarobot_moderations when a deployment meets two requirements: the execution environment image includes the moderation library and the custom model code contains moderation_config.yaml. For streaming responses with moderation enabled, the first chunk now provides information about configured prompt and response guards.
List models support for custom models¶
Custom models now support the OpenAI client .models.list() method, which returns available models in a deployment along with basic information such as the owner and availability. This functionality is available out-of-the-box for managed RAGs, NIMs, and hosted LLMs. For custom models, you can customize the response by implementing the get_supported_llm_models() hook in custom.py.
Platform enhancements¶
The following new capabilities provide further support for the DataRobot GenAI experience.
Support for unstructured data¶
This release brings connectors for S3 and ADLS to support unstructured data, enabling consistent read access to files, documents, media, and other non-tabular formats. The new endpoints support efficient, chunked transfer of unstructured data, enabling scalable ingestion and serving of large files, ultimately creating a scalable, maintainable, and unified approach to data connectivity that complements existing structured data support.
Support for dynamic datasets in Workbench now GA¶
Support for dynamic datasets is now generally available in Workbench. Dynamic data is a “live” connection to the source data that DataRobot pulls upon request, for example, when creating a live sample for previews.
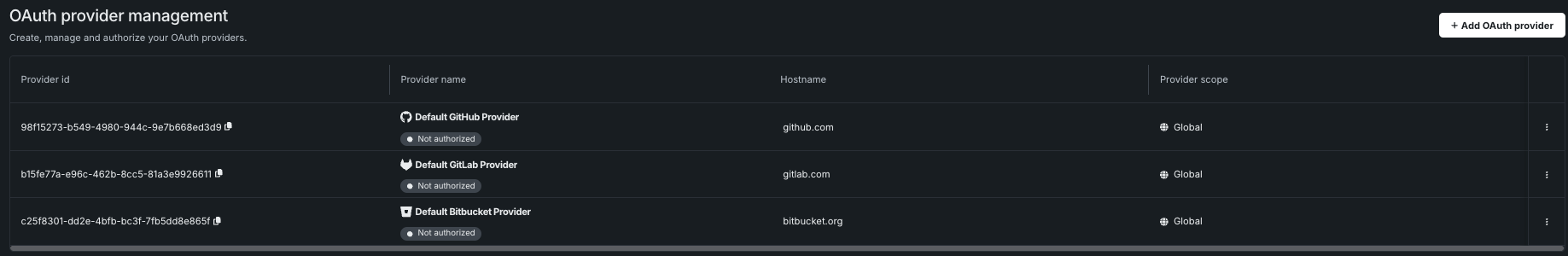
Support for external OAuth server configuration¶
This release adds a new Manage OAuth providers page that allows you to configure, add, remove, or modify OAuth providers for your cluster.
Additionally, support has been added for two new OAuth providers: Google and Box. Refer to the documentation for more details.
Updated FIPS password requirements for Snowflake connections¶
Due to updates in FIPS credential requirements, DataRobot now requires that credentials adhere to Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS), a government standard that ensures cryptographic modules meet specific security requirements validation. All credentials used in DataRobot, particularly Snowflake basic credentials and key pairs, must adhere to FIPS-compliant formats as indicated below:
- RSA keys must be at least 2048 bits in length, and their passphrases must be at least 14 characters long.
- Snowflake key pair credentials must use a FIPS-approved algorithm and have a salt length of at least 16 bytes (128 bits).
For additional details, refer to the FIPS validation FAQ.
All product and company names are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Use of them does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.