APIクイックスタート¶
DataRobot APIでは、DataRobotのプロジェクトを作成・管理するために、ウェブインターフェイスに代わるプログラム的な方法を提供します。 APIはREST経由、またはDataRobotのPythonやRクライアントを使って、Windows、UNIX、OS Xの環境で利用できます。 このガイドでは、環境を設定する手順について説明します。次に サンプル問題に従って、APIのエンドツーエンドのワークフローの概要を理解します。
備考
APIクイックスタートガイドでは、DataRobotのPythonクライアントバージョン3.x用のメソッドを使用しています。 If you are a Self-Managed AI Platform user, consult the Self-Managed AI Platform API resources page to verify which versions of DataRobot's clients are supported for your version of the DataRobot application.
前提条件¶
DataRobot APIには、使用を選択したコーディング言語に応じて、以下の前提条件があります。
クライアントのインストール¶
先に進む前に、PythonまたはR用のDataRobotクライアントパッケージにアクセスし、インストールしてください(手順は以下に記載されています)。 APIリファレンスのドキュメントを参照することで、使用可能なコードファーストのリソースについて理解を深めることができます。
備考
セルフマネージドAIプラットフォーム環境をお使いの場合、インストールされているDataRobotアプリケーションのバージョンに合わせて、以前のバージョンのクライアントをインストールすることをお勧めします。 利用可能なバージョンを参照して、インストールをAPIクライアントの正しいバージョンにマッピングします。
pip install datarobot datarobot-predict
(オプション)カスタムブループリントをプログラム的に構築したい場合は、graphvizとblueprint-workshopの2つのパッケージを追加でインストールします。
Windows
Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install graphviz
Mac
brew install graphviz
graphvizをインストールしたら、ワークショップをインストールします。
pip install datarobot-bp-workshop
install.packages(“datarobot”)
環境設定¶
このセクションでは、DataRobotのAPIを使用して、データセットのアップロードから、本番環境にデプロイされたモデルでの予測まで、完全なモデリングワークフローを実行する方法を説明します。
DataRobot APIキーの作成¶
-
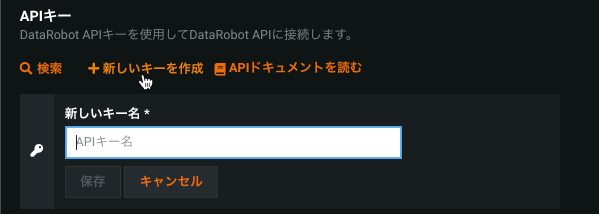
DataRobotのUIで、右上隅にあるユーザーアイコンをクリックし、APIのキーとツールを選択します。
-
新しいキーを作成をクリックします。
-
新しいキーに名前を付けて、作成をクリックします。 キーがアクティブ化され、使用できるようになります。
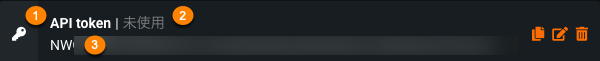
作成された個々のキーは、3つの情報を持っています。
| ラベル | 要素 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 名前 | 編集可能なキーの名前。 |
| 2 | キー | 新しいキー値 |
| 3 | 作成日 | キーが作成された日付。 新しく作成され、まだ使用されていないキーには「—」が表示されます。 |
| 4 | 最後の使用 | キーが最後に使用された日付。 |
APIエンドポイントの取得¶
DataRobotでは、お客様のビジネス要件に合わせて、複数のデプロイオプションを提供しています。 デプロイのタイプごとに、独自のエンドポイントのセットが用意されています。 以下のタブよりお選びください。
AIプラットフォーム(US)サービスは、主に米国のユーザーが利用します。 https://app.datarobot.comからアクセスできます。
APIエンドポイントのルート:https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2
マネージドAIプラットフォーム(EU)は、主にEMEA地域のユーザーが利用しています。 https://app.eu.datarobot.comからアクセスできます。
APIエンドポイントのルート:https://app.eu.datarobot.com/api/v2
AIプラットフォーム(JP)サービスは、主に日本のユーザーが利用します。 https://app.jp.datarobot.comからアクセスできます。
APIエンドポイントのルート:https://app.jp.datarobot.com/api/v2
セルフマネージドAIプラットフォーム環境の場合、APIルートはDataRobot UIのルートと同じになります。 以下のURLで、{datarobot.example.com}をデプロイのエンドポイントに置き換えてください。
APIエンドポイントのルート:https://{datarobot.example.com}/api/v2
APIの認証設定¶
DataRobotのAPIで認証を行うには、前のステップで取得したエンドポイントとトークンにアクセスできるコードが必要です。 これには、3つの方法があります。
DataRobotが推奨する認証方法は、drconfig.yamlファイルを使用することです。 これは、DataRobotのPythonおよびRクライアントが自動的に検索するファイルです。 APIクライアントに対して、特定の場所(デフォルトでは~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml)、または一意な名前でファイルを探すように指示することができます。 したがって、これを利用して複数の設定ファイルを持つことが可能です。 以下の例は .yamlの形式を示したものです。
endpoint: 'https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2'
token: 'NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G'
作成後、APIへのアクセスをテストすることができます。
Pythonの場合:
設定ファイルが~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yamlにあれば、あとはライブラリをインポートするだけです。
import datarobot as dr
そうでない場合は、以下のコマンドを使用します。
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(config_path = "<file-path-to-drconfig.yaml>")
Rの場合:
設定ファイルが~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yamlにあれば、あとはライブラリを読み込むだけです。
library(datarobot)
そうでない場合は、以下のコマンドを使用します。
ConnectToDataRobot(configPath = "<file-path-to-drconfig.yaml>"))
cURLの場合:
cURLはYAMLファイルをネイティブにサポートしていませんが、drconfig.yamlファイルから値を抽出し、cURLコマンドで使用できます。 このシーケンスは、drconfig.yamlファイルから値を読み取り、環境変数として設定します。
# Extract values from drconfig.yaml and set as environment variables
export DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT=$(grep 'endpoint:' ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml | cut -d "'" -f2)
export DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN=$(grep 'token:' ~/.config/datarobot/drconfig.yaml | cut -d "'" -f2)
環境変数が設定されたら、cURLコマンドで使用できます。
curl --location -X GET "${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects" --header "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}"
Windows
Windowsを使用している場合は、管理者としてコマンドプロンプトまたはPowerShellを開き、以下の環境変数を設定します。
setx DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT "https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2"
setx DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN "your_api_token"
設定したら、コマンドプロンプトまたはPowerShellを閉じて再度開き、変更を有効にします。
Windowsで永続的な環境変数を設定するには、スタートメニューで「環境変数」を検索し、システム環境変数の編集を選択します。
次に、環境変数をクリックし、システム変数の下にある新規をクリックして、上に示した変数を追加します。
macOSとLinuxの場合:
macOSおよびLinux環境では、ターミナルウィンドウを開いて、以下の環境変数を設定します。
export DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT="https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2"
export DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN="your_api_token"
macOSやLinuxで永続的な環境変数を設定するには、シェル設定ファイル(~/.bash_profile、~/.bashrc、または~/.zshrc)を編集し、上に示した環境変数を追加します。 次に、ファイルを保存してターミナルを再起動するか、source ~/.bash_profileを実行します(または関連するファイルを使用します)。
環境変数が設定されたら、DataRobotに接続するための認証を行います。
Pythonの場合:
import datarobot as dr
dr.Project.list()
cURLの場合:
curl --location -X GET "${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects" --header "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}"
Rの場合:
library(datarobot)
(オプション)資格情報をGitにコミットしないように注意してください。
Pythonの場合:
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(endpoint='https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2', token='NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G')
cURLの場合
curl --location --request GET 'https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2/projects/' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>'
Rの場合:
ConnectToDataRobot(endpoint =
"https://app.datarobot.com/api/v2",
token =
'NjE3ZjA3Mzk0MmY0MDFmZGFiYjQ0MztergsgsQwOk9G')
APIの使用:燃費を予測する¶
API資格情報、エンドポイント、環境の各設定が完了したら、DataRobot APIを使用して、この例に従います。 この例では、PythonクライアントとREST API(cURLを使用)を使用しているため、Python3またはcURLの基礎知識が必要です。 既知の自動車データ(車両重量、気筒数など)から燃費(燃料1ガロン当たりの走行マイル数)を予測するという簡単な問題から進んでいきます。 追加のコード例については、DataRobotの AIアクセラレーターを参照してください。
備考
以下のワークフローでは、Pythonクライアントのバージョン3.0で導入されたメソッドを使用します。 この例に含まれるコードを実行する前に、クライアントが最新であることを確認してください。
以降のセクションでは、次のことを行うためのPythonおよびcURLのサンプルコードを提供します。
- データセットをアップロードする
- モデルをトレーニングして、データセットから学習する
- 新しいデータを使って、モデルの予測結果をテストする
- モデルをデプロイする
- デプロイされたモデルで新しいデータを使って、結果を予測する
データセットのアップロード¶
プロジェクトを作成するには、まずデータセットをアップロードします。 この例では、データセットauto-mpg.csvとそれに付随するテストデータセットauto-mpg-test.csvを使用します。どちらもこの.zipファイルにあります。
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(config_path = "./drconfig.yaml")
# Set to the location of your auto-mpg.csv and auto-mpg-test.csv data files
# Example: dataset_file_path = '/Users/myuser/Downloads/auto-mpg.csv'
training_dataset_file_path = './auto-mpg.csv'
test_dataset_file_path = './auto-mpg-test.csv'
print("--- Starting DataRobot Model Training Script ---")
# Load dataset
training_dataset = dr.Dataset.create_from_file(training_dataset_file_path)
# Create a new project based on dataset
project = dr.Project.create_from_dataset(training_dataset.id, project_name='Auto MPG DR-Client')
DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN=${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}
DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT=${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}
DATASET_FILE_PATH="./auto-mpg.csv"
location=$(curl -Lsi \
-X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-F 'projectName="Auto MPG"' \
-F "file=@${DATASET_FILE_PATH}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}"/projects/ | grep -i 'Location: .*$' | \
cut -d " " -f2 | tr -d '\r')
echo "Uploaded dataset. Checking status of project at: ${location}"
while true; do
project_id=$(curl -Ls \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" "${location}" \
| grep -Eo 'id":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
if [ "${project_id}" = "" ]
then
echo "Setting up project..."
sleep 10
else
echo "Project setup complete."
echo "Project ID: ${project_id}"
break
fi
done
# Set to the location of your auto-mpg.csv and auto-mpg-test.csv data files
# Example: dataset_file_path = '/Users/myuser/Downloads/auto-mpg.csv'
training_dataset_file_path <- "./auto-mpg.csv"
test_dataset_file_path <- "./auto-mpg-test.csv"
# Load dataset using modern DataRobot R client
training_dataset <- UploadDataset(training_dataset_file_path)
test_dataset <- utils::read.csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Create a new project based on dataset
project <- CreateProject(training_dataset, projectName = "Auto MPG DR-Client")
モデルのトレーニング¶
DataRobotにデータが取り込まれたので、そのデータを使ってオートパイロットでモデルのトレーニングと構築が可能になりました。 オートパイロットは、DataRobotの「適者生存」モデリングモードです。このモードでは、指定したターゲット特徴量に最適な予測モデルが自動的に選択され、サンプルサイズを増やしながら実行されます。 オートパイロットの成果は、最適なモデルの選択だけでなく、推奨されるモデル、つまりターゲット特徴量「mpg」の予測方法を最もよく理解しているモデルの特定でもあります。 最適なモデルの選択では、精度、指標が示すパフォーマンス、モデルのシンプルさのバランスが考慮されます。 モデルの推奨プロセスについては、UIドキュメントで詳しく説明されています。
備考
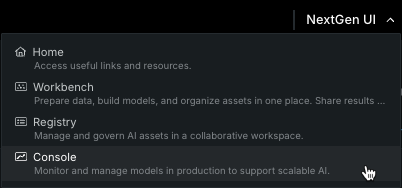
このコードはブラウザーウィンドウを開き、DataRobot Classic UIでの進捗状況を表示します。 ウィンドウが開いたら、NextGen UIドロップダウンをクリックし、コンソールを選択して、完了したデプロイを表示します。
# Use training data to build models
from datarobot import AUTOPILOT_MODE
# Set the project's target and initiate Autopilot (runs in Quick mode unless a different mode is specified)
project.analyze_and_model(target='mpg', worker_count=-1, mode=AUTOPILOT_MODE.QUICK)
print("\nAutopilot is running. This may take some time...")
project.wait_for_autopilot()
print("Autopilot has completed!")
# Open the project in a web browser to view progress
print("Opening the project in your default web browser to view real-time events...")
project.open_in_browser()
# Get the recommended model (the best model for deployment)
print("\nRetrieving the best model from the Leaderboard...")
best_model = project.recommended_model()
print(f"Best Model Found:")
print(f" - Model Type: {best_model.model_type}")
print(f" - Blueprint ID: {best_model.blueprint_id}")
response=$(curl -Lsi \
-X PATCH \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"target": "mpg", "mode": "quick"}' \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/aim" | grep 'location: .*$' \
| cut -d " " | tr -d '\r')
echo "AI training initiated. Checking status of training at: ${response}"
while true; do
initial_project_status=$(curl -Ls \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" "${response}" \
| grep -Eo 'stage":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
if [ "${initial_project_status}" = "" ]
then
echo "Setting up AI training..."
sleep 10
else
echo "Training AI."
echo "Grab a coffee or catch up on email."
break
fi
done
echo "Polling for Autopilot completion..."
while true; do
autopilot_done=$(curl -s \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"autopilotDone":\s*(true|false)' | cut -d ':' -f2 | tr -d ' ')
if [ "${autopilot_done}" = "true" ]; then
echo "Autopilot training complete. Model ready to deploy."
break
else
echo "Autopilot training in progress... checking again in 60 seconds."
sleep 60
fi
done
# Get the recommended model ID
recommended_model_id=$(curl -s \
-X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/projects/${project_id}/recommendedModels/recommendedModel/" \
| grep -Eo 'modelId":\s"\w+' | cut -d '"' -f3 | tr -d '\r')
echo "Recommended model ID: ${recommended_model_id}"
# Set the project target and initiate Autopilot in Quick mode
SetTarget(project, target = "mpg")
# Start Autopilot in Quick mode (equivalent to Python's AUTOPILOT_MODE.QUICK)
StartAutopilot(project, mode = "quick")
# Block execution until Autopilot is complete
WaitForAutopilot(project)
# Open the project in a web browser to view progress
OpenProject(project)
# Get the recommended model (the best model for deployment)
model <- GetRecommendedModel(project, type = RecommendedModelType$RecommendedForDeployment)
モデルのデプロイ¶
デプロイとは、実際のデータでの予測およびインサイトの生成を目的として、機械学習モデルを既存の本番環境に統合する方法のことです。 詳細については、デプロイの概要を参照してください。
# Deploy the model to a serverless prediction environment
print("\nDeploying the model to a serverless prediction environment...")
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
serverless_env = None
for env in dr.PredictionEnvironment.list():
if env.platform == 'datarobotServerless':
serverless_env = env
break
if serverless_env is None:
print("Creating a new serverless prediction environment...")
serverless_env = dr.PredictionEnvironment.create(
name="Auto MPG Serverless Environment",
platform='datarobotServerless'
)
# First, register the model to create a registered model version
print("Registering the model...")
# Check if the registered model already exists
registered_model_name = "Auto MPG Registered Model"
existing_models = [m for m in dr.RegisteredModel.list() if m.name == registered_model_name]
if existing_models:
print(f"Using existing registered model: {registered_model_name}")
registered_model = existing_models[0]
# Create a new version of the existing model
registered_model_version = dr.RegisteredModelVersion.create_for_leaderboard_item(
best_model.id,
name="Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id=registered_model.id
)
else:
print(f"Creating new registered model: {registered_model_name}")
# Create a new registered model
registered_model_version = dr.RegisteredModelVersion.create_for_leaderboard_item(
best_model.id,
name="Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_name=registered_model_name
)
# Retrieve the newly created registered model object by ID
registered_model = dr.RegisteredModel.get(registered_model_version.registered_model_id)
# Wait for the model build to complete
print("Waiting for model build to complete...")
while True:
current_version = registered_model.get_version(registered_model_version.id)
if current_version.build_status in ('READY', 'complete'):
print("Model build completed successfully!")
registered_model_version = current_version # Update our reference
break
elif current_version.build_status == 'FAILED':
raise Exception("Model build failed. Please check the model registration.")
else:
print(f"Build status: {current_version.build_status}. Waiting...")
import time
time.sleep(30) # Wait 30 seconds before checking again
# Deploy the model to the serverless environment using the registered model version
deployment = dr.Deployment.create_from_registered_model_version(
registered_model_version.id,
label="Auto MPG Predictions",
description="Deployed with DataRobot client for Auto MPG predictions",
prediction_environment_id=serverless_env.id
)
print(f"Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID: {deployment.id}")
# Use the recommended model ID from training section
echo "Using recommended model ID: ${recommended_model_id}"
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
echo "Looking for serverless prediction environment..."
serverless_env_id=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/predictionEnvironments/" \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*".*"platform":"datarobotServerless"' \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4 | head -1)
if [ -z "${serverless_env_id}" ]; then
echo "Creating new serverless prediction environment..."
serverless_env_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"name":"Auto MPG Serverless Environment","platform":"datarobotServerless"}' \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/predictionEnvironments/")
serverless_env_id=$(echo "$serverless_env_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Created serverless environment ID: ${serverless_env_id}"
else
echo "Using existing serverless environment ID: ${serverless_env_id}"
fi
# Check if registered model already exists
registered_model_name="Auto MPG Registered Model"
existing_model_id=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/" \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*".*"'${registered_model_name}'"' \
| grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4 | head -1)
if [ -n "${existing_model_id}" ]; then
echo "Using existing registered model: ${registered_model_name}"
# Create new version of existing model
model_version_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"Auto MPG Model\",\"registeredModelId\":\"${existing_model_id}\",\"leaderboardItemId\":\"${recommended_model_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/")
else
echo "Creating new registered model: ${registered_model_name}"
# Create new registered model
model_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"${registered_model_name}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/")
existing_model_id=$(echo "$model_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
# Create first version
model_version_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"name\":\"Auto MPG Model\",\"registeredModelId\":\"${existing_model_id}\",\"leaderboardItemId\":\"${recommended_model_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/")
fi
model_version_id=$(echo "$model_version_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Model version ID: ${model_version_id}"
# Wait for model build to complete
echo "Waiting for model build to complete..."
while true; do
build_status=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/registeredModels/${existing_model_id}/versions/${model_version_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"buildStatus":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
if [ "${build_status}" = "READY" ] || [ "${build_status}" = "complete" ]; then
echo "Model build completed successfully!"
break
elif [ "${build_status}" = "FAILED" ]; then
echo "Model build failed. Please check the model registration."
exit 1
else
echo "Build status: ${build_status}. Waiting..."
sleep 30
fi
done
# Deploy the model using the registered model version
echo "Deploying the model to the serverless environment..."
deployment_response=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{\"label\":\"Auto MPG Predictions\",\"description\":\"Deployed with cURL for Auto MPG predictions\",\"predictionEnvironmentId\":\"${serverless_env_id}\",\"registeredModelVersionId\":\"${model_version_id}\"}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/deployments/fromRegisteredModelVersion/")
deployment_id=$(echo "$deployment_response" | grep -Eo '"id":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID: ${deployment_id}"
# Get the prediction URL for the deployment
echo "Retrieving prediction URL for deployment..."
prediction_url=$(curl -s -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
"${DATAROBOT_ENDPOINT}/deployments/${deployment_id}/" \
| grep -Eo '"predictionUrl":"[^"]*"' | cut -d '"' -f4)
echo "Prediction URL: ${prediction_url}"
# Deploy the model to a serverless prediction environment
cat("Deploying the model to a serverless prediction environment...\n")
# Find or create a serverless prediction environment
prediction_environments <- ListPredictionEnvironments()
serverless_env <- NULL
for (env in prediction_environments) {
if (env$platform == "datarobotServerless") {
serverless_env <- env
break
}
}
if (is.null(serverless_env)) {
cat("Creating a new serverless prediction environment...\n")
serverless_env <- CreatePredictionEnvironment(
name = "Auto MPG Serverless Environment",
platform = "datarobotServerless"
)
}
# Register the model to create a registered model version
cat("Registering the model...\n")
registered_model_name <- "Auto MPG Registered Model"
# Check if registered model already exists
existing_models <- ListRegisteredModels()
existing_model <- NULL
for (m in existing_models) {
if (m$name == registered_model_name) {
existing_model <- m
break
}
}
if (!is.null(existing_model)) {
cat("Using existing registered model:", registered_model_name, "\n")
# Create a new version of the existing model
registered_model_version <- CreateRegisteredModelVersion(
model_id = model$modelId,
name = "Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id = existing_model$id
)
} else {
cat("Creating new registered model:", registered_model_name, "\n")
# Create a new registered model
registered_model <- CreateRegisteredModel(name = registered_model_name)
# Create first version
registered_model_version <- CreateRegisteredModelVersion(
model_id = model$modelId,
name = "Auto MPG Model",
registered_model_id = registered_model$id
)
}
# Wait for the model build to complete
cat("Waiting for model build to complete...\n")
while (TRUE) {
current_version <- GetRegisteredModelVersion(registered_model_version$id)
if (current_version$buildStatus %in% c("READY", "complete")) {
cat("Model build completed successfully!\n")
break
} else if (current_version$buildStatus == "FAILED") {
stop("Model build failed. Please check the model registration.")
} else {
cat("Build status:", current_version$buildStatus, ". Waiting...\n")
Sys.sleep(30) # Wait 30 seconds before checking again
}
}
# Deploy the model to the serverless environment using the registered model version
deployment <- CreateDeploymentFromRegisteredModelVersion(
registered_model_version_id = registered_model_version$id,
label = "Auto MPG Predictions",
description = "Deployed with DataRobot R client for Auto MPG predictions",
prediction_environment_id = serverless_env$id
)
cat("Model deployed successfully! Deployment ID:", deployment$id, "\n")
デプロイされたモデルを使った予測¶
モデルが正常にデプロイされたら、DataRobotの予測APIを使用して、新しいデータに対して予測を行うことで、モデルをさらにテストできます。 これにより、データドリフト、精度、サービス正常性統計などの高度なモデル管理 機能にアクセスできます。
DataRobotでは、新しいデータで予測を行うための方法が複数用意されています。 予測方法については、UIドキュメントで詳しく説明されています。 また、UIからPythonの予測スニペットを参照することも可能です。 予測を行うためのスニペットを参照するには、デプロイページでデプロイを選択して、予測 > 予測APIに移動します。
このコードでは、データをアップロードした際に、最初のステップで特定したテストセット(test_dataset_file_path)を用いて、モデルの予測を行います。
# Make predictions on test data
print("\nMaking predictions on test data...")
# Read the test data directly
import pandas as pd
from datarobot_predict.deployment import predict
test_data = pd.read_csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Use datarobot-predict for deployment predictions
predictions, response_headers = predict(deployment, test_data)
# Display the results
print("\nPrediction Results:")
print(predictions.head())
print(f"\nTotal predictions made: {len(predictions)}")
このコードでは、データをアップロードした際に、最初のステップで特定したテストセット(test_dataset_file_path)を用いて、デプロイモデルの予測を行います。
# Use the prediction URL from deployment section
TEST_DATASET_FILE_PATH="./auto-mpg-test.csv"
# Make predictions by sending the CSV data directly
predictions=$(curl -s -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATAROBOT_API_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: text/csv; charset=UTF-8" \
--data-binary "@${TEST_DATASET_FILE_PATH}" \
"${prediction_url}")
echo "Prediction Results:"
echo "$predictions" | jq '.'
prediction_count=$(echo "$predictions" | jq '.data | length')
echo "Total predictions made: ${prediction_count}"
このコードでは、データをアップロードした際に、最初のステップで特定したテストセット(test_dataset_file_path)を用いて、デプロイモデルの予測を行います。
# Make predictions on test data
cat("Making predictions on test data...\n")
# Read the test data directly
test_data <- read.csv(test_dataset_file_path)
# Use the deployment for predictions (modern approach)
predictions <- PredictDeployment(deployment, test_data)
# Display the results
cat("Prediction Results:\n")
print(head(predictions))
cat("Total predictions made:", nrow(predictions), "\n")
学習リソース¶
After getting started with DataRobot's APIs, browse the developer learning section for overviews, Jupyter notebooks, and task-based tutorials that help you find complete examples of common data science and machine learning workflows. AIアクセラレーターを参照して、反復可能なコードファーストのワークフローとモジュール化された構築ブロックをお試しください。 また、REST APIおよびPython APIクライアントで利用できるリファレンスドキュメントも併せてお読みください。