August 2024
August 2024¶
August 28, 2024
This page provides announcements of newly released features available in DataRobot's SaaS single- and multi-tenant AI Platform, with links to additional resources. From the release center, you can also access:
In the spotlight¶
Custom feature lists in Workbench¶
Create custom feature lists from multiple areas in a Workbench Use Case, including a model's Feature Impact insight, and Cluster insights for time series experiments.
Video: Custom feature lists in Workbench
August features¶
The following table lists each new feature:
Features grouped by capability
*Premium
GA¶
Azure OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo LLM now available¶
With this deployment, the Azure OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo LLM is available from the playground, expanding the offerings of out-of-the-box LLMs you can choose to build your generative AI experiments. The ongoing addition of LLMs is an indicator of DataRobot’s commitment to delivering newly released LLMs as they are made available. A list of available LLMs is maintained here.
Replace custom application sources¶
Now generally available, you can replace the application source for custom applications. Doing so carries over a number of qualities from the application, including the application's code, the underlying execution environment, and the runtime parameters. When a source is replaced, all users with access to the application and still use it.
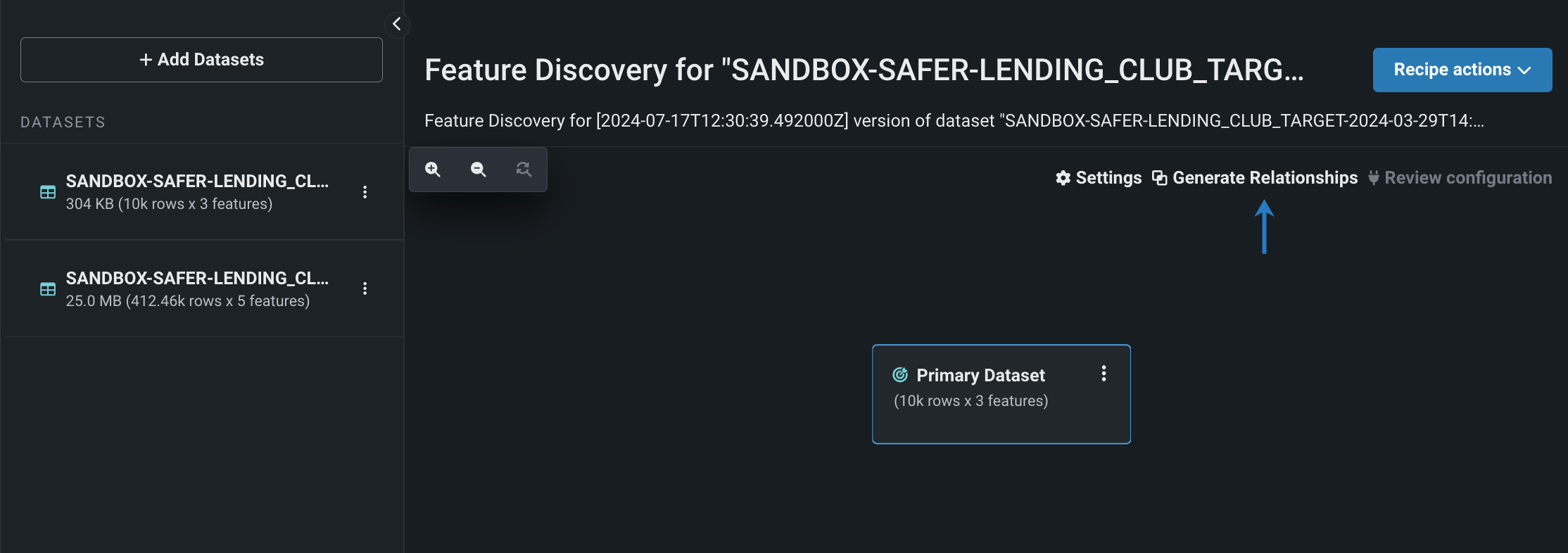
Automatically generate relationships for Feature Discovery in Workbench¶
Use automatic relationship detection (ARD) when performing Feature Discovery in Workbench. ARD analyzes the primary dataset and all secondary datasets added to the recipe to detect and generate relationships. After adding all secondary datasets to the recipe, click Generate Relationships—DataRobot then automatically adds secondary datasets to the canvas and configures relationships between the datasets.
Simplified login process for applications¶
Applications now use an API key for authentication, so after creating an app in Workbench or DataRobot Classic, you no longer need to click through the OAuth authentication prompts. Note that when you create an app or access one that was shared with you, a new key (AiApp<app_id>) will appear in your list of API Keys.
Time series now generally available; support for partial and new series blueprints added¶
In this deployment, time series functionality in Workbench becomes generally available. As part of the update, the forecasting capabilities now include support for new and partial history data. Some blueprints return suboptimal predictions on new series with only partial history available. When this option is selected, DataRobot will also train models that can make predictions on incomplete historical data—series that were not seen in the training data (“cold start”) and prediction datasets with series history that is only partially known (historical rows are partially available within the feature derivation window).

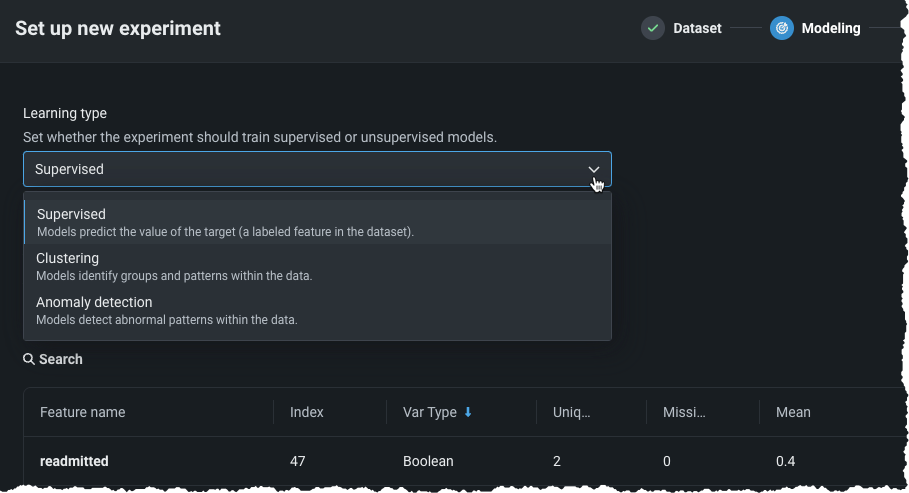
Unsupervised modeling now available in Workbench¶
Now, Workbench offers unsupervised learning, where no target is specified and data is unlabeled. Instead of generating predictions, unsupervised learning surfaces insights about patterns in your data. Available for both predictive and time-aware experiments, unsupervised learning brings clustering and anomaly detection, answering questions like "Are there anomalies in my data?" and "Are there natural clusters?" To create an unsupervised experiment, specify a learning type and complete the corresponding fields.
After model building completes, unsupervised-specific insights surface the identified patterns.
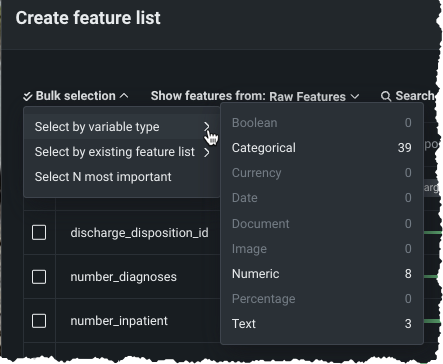
Data tab and custom feature list functionality now GA¶
The ability to add new, custom feature lists to an existing predictive or forecasting experiment through the UI was introduced in April as a preview feature. Now generally available, you can create your own lists from the Feature Lists or Data tabs (also both now GA) in the Experiment information window accessed from the Leaderboard. Use bulk selections to choose multiple features with a single click:
Data tracing for deployments¶
Available as a premium feature, on the Data exploration tab of a Generative AI deployment, click Tracing to explore prompts, responses, user ratings, and custom metrics matched by association ID. This view can provide insight into the quality of the Generative AI model's responses, as rated by users or based on any Generative AI custom metrics you implement. Prompts, responses, and any available metrics are matched by association ID:
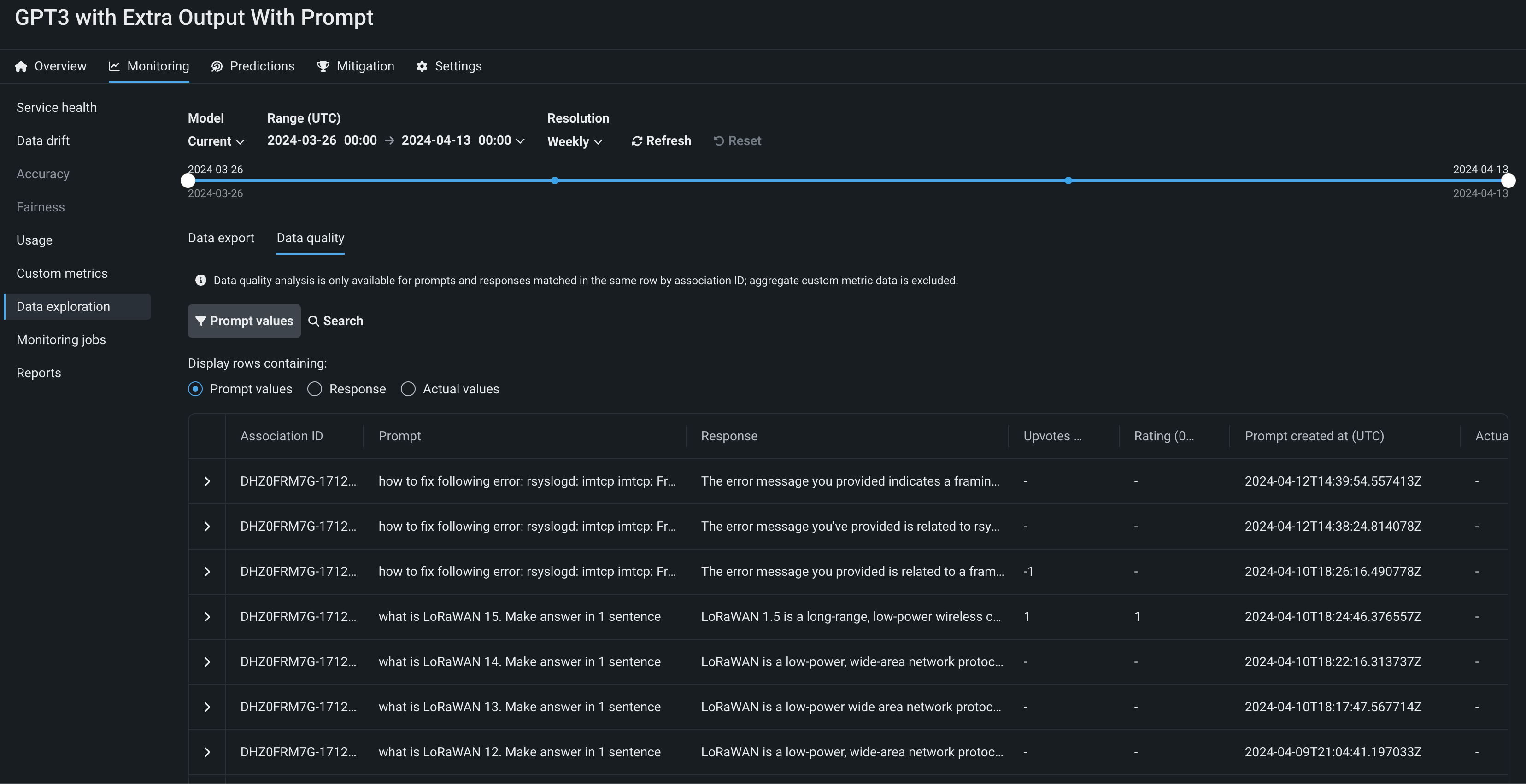
Feature flags OFF by default: Enable Data Quality Table for Text Generation Target Types (Premium feature), Enable Actuals Storage for Generative Models (Premium feature)
Wrangler recipes in batch predictions¶
Use a deployment's Predictions > Make predictions tab to efficiently score Wrangler datasets with a deployed model by making batch predictions. Batch predictions are a method of making predictions with large datasets, in which you pass input data and get predictions for each row. In the Prediction dataset box, click Choose file > Wrangler to make predictions with a Wrangler dataset:
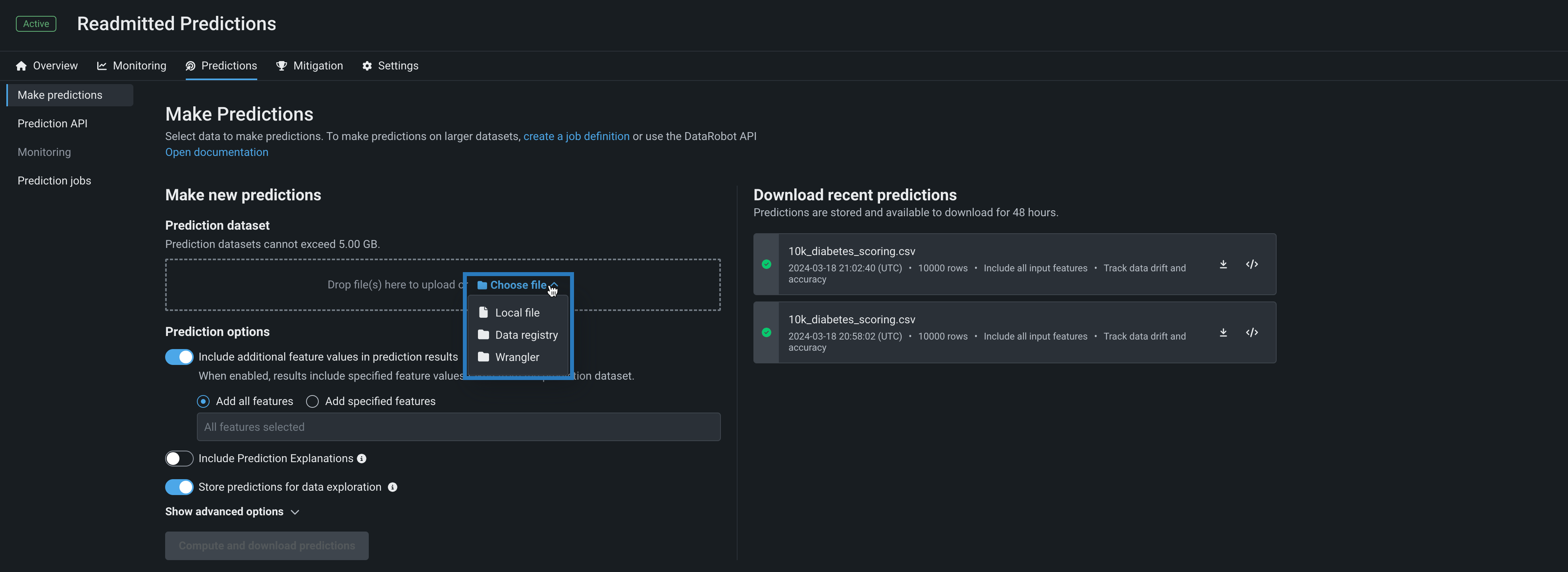
Predictions in Workbench
Wrangler is also available as a prediction dataset source in Workbench. To make predictions with a model before deployment, select the model from the Models list in an experiment and then click Model actions > Make predictions.
You can also schedule batch prediction jobs by specifying the prediction data source and destination and determining when DataRobot runs the predictions.
Multipart upload for batch prediction API¶
Multipart upload for the batch prediction API allows you to upload scoring data through multiple files to improve file intake for large datasets. The multipart upload process calls for multiple PUT requests followed by a POST request (finalizeMultipart) to finalize the upload manually. The multipart upload process can be helpful when you want to upload large datasets over a slow connection or if you experience frequent network instability.
This feature adds two endpoints to the batch prediction API and two new intake settings for the local file adapter.
Batch predictions for TTS and LSTM models¶
Traditional Time Series (TTS) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models— sequence models that use autoregressive (AR) and moving average (MA) methods—are common in time series forecasting. Both AR and MA models typically require a complete history of past forecasts to make predictions. In contrast, other time series models only require a single row after feature derivation to make predictions. Previously, batch predictions couldn't accept historical data beyond the effective feature derivation window (FDW) if the history exceeded the maximum size of each batch, while sequence models required complete historical data beyond the FDW. These requirements made sequence models incompatible with batch predictions. This feature removes those limitations to allow batch predictions for TTS and LSTM models.

Create custom environments for notebooks¶
Now generally available, DataRobot Notebooks integrates with DataRobot custom environments, allowing you to define reusable custom Docker images for running notebook sessions. Custom environments provide full control over the environment configuration and the ability to leverage reproducible dependencies beyond those available in the built-in images. After creating a custom environment, you can share it with other users, or update its components to create a new version of the environment.
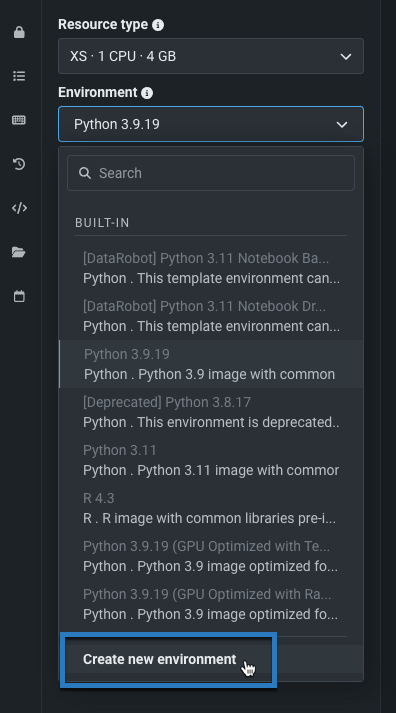
Preview¶
Support for SAP Datasphere connector in DataRobot¶
DataRobot now supports the SAP Datasphere connector, available for preview, in both NextGen and DataRobot Classic.
Feature flag OFF by default: Enable SAP Datasphere Connector
Preview documentation.
Additional EDA insights and UI improvements added to the data explore page¶
The following EDA insights and improvements have been added to the data explore page in Workbench:
- On the data explore page, navigate between views for Features, Feature lists, Data preview, and Info using icons the left panel.
- The new Info view displays summary information about the dataset.
- An updated footer for the Features and Data preview views.
- Wrangled datasets display recipe operations in the right panel.
- In the Features view, click specific features to view insights. The available insights depend on the feature type.
- When viewing insights for a summarized categorical feature, you can show a histogram for a selected key.
Feature flag ON by default: Enable EDA insights in Workbench
Preview documentation.
New Incremental Learning insight for comparing iterations¶
The Model Iterations insight for incremental learning allows you to compare trained iterations and, optionally, assign a different active iteration or continue training. Now, the insight adds a learning curve as an aid in data visualization. With the information gained from viewing the chart, you can, for example continue your experimentation by changing your active iteration or training new iterations.
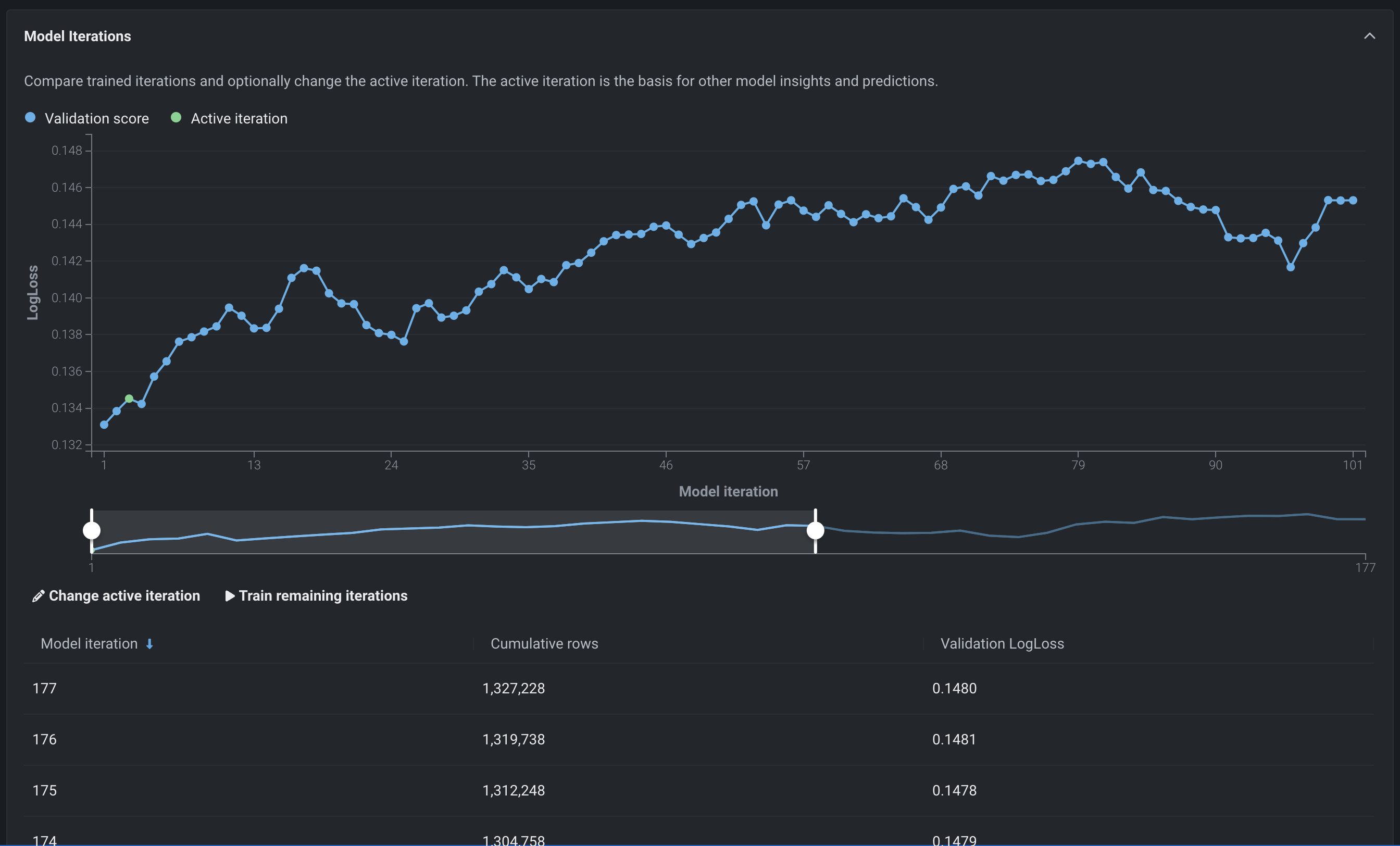
Feature flag ON by default: Enable Incremental Learning
Preview documentation.
Automated deployment and replacement of Scoring Code in SAP AI Core¶
Create a DataRobot-managed SAP AI Core prediction environment to deploy DataRobot Scoring Code in SAP AI Core. With DataRobot management enabled, the model deployed externally to SAP AI Core has access to MLOps features, including automatic Scoring Code replacement. Once you've created an SAP AI Core prediction environment, you can deploy a Scoring Code-enabled model to that environment from the Registry:
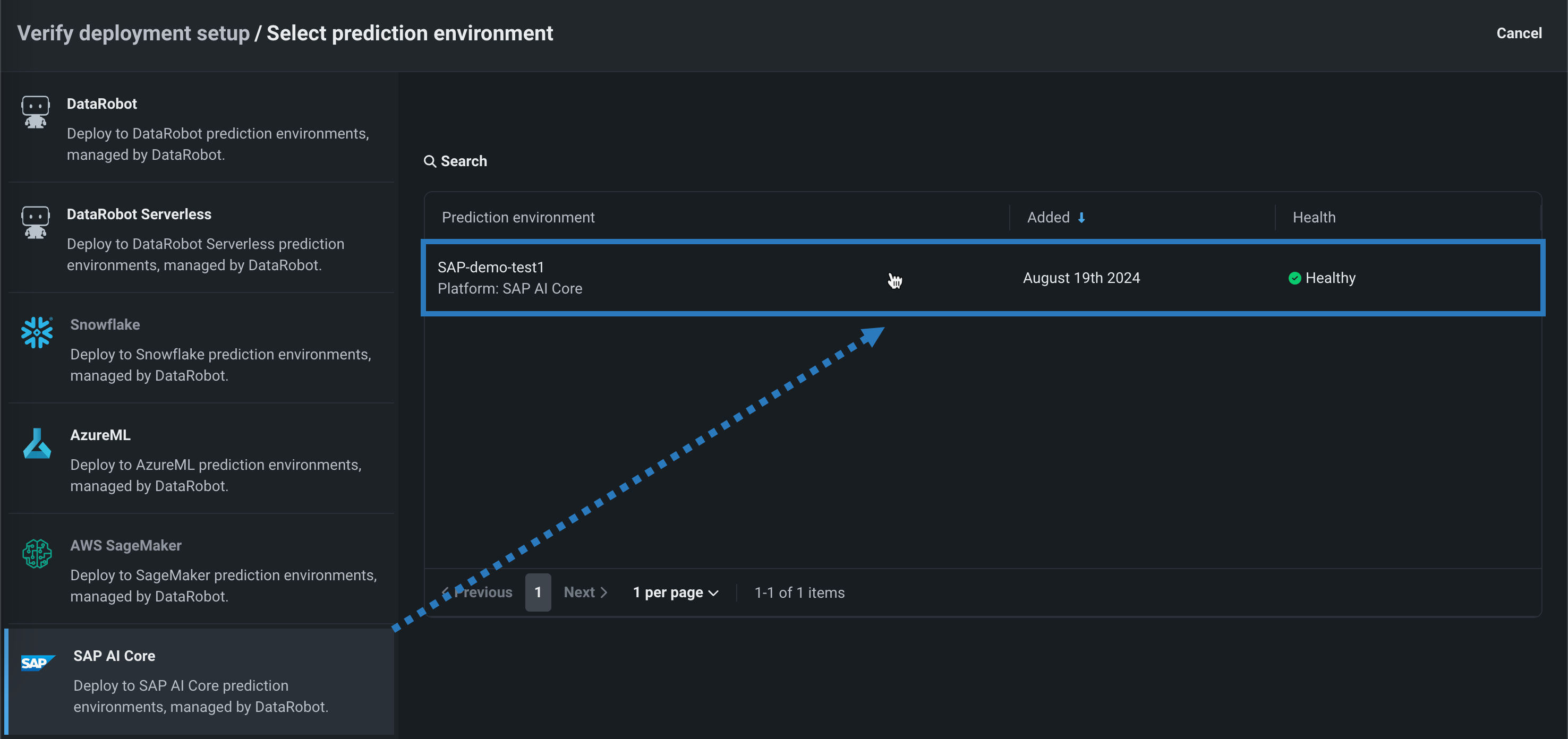
Feature OFF flag by default: Enable the Automated Deployment and Replacement of Scoring Code in SAP AI Core
Preview documentation.
Manage network policies to control access to public resources within DataRobot¶
By default, some DataRobot capabilities, including Notebooks, have full public internet access from within DataRobot. To limit the public resources users can access within DataRobot, multi-tenant SaaS administrators can set network access controls for all users within an organization.
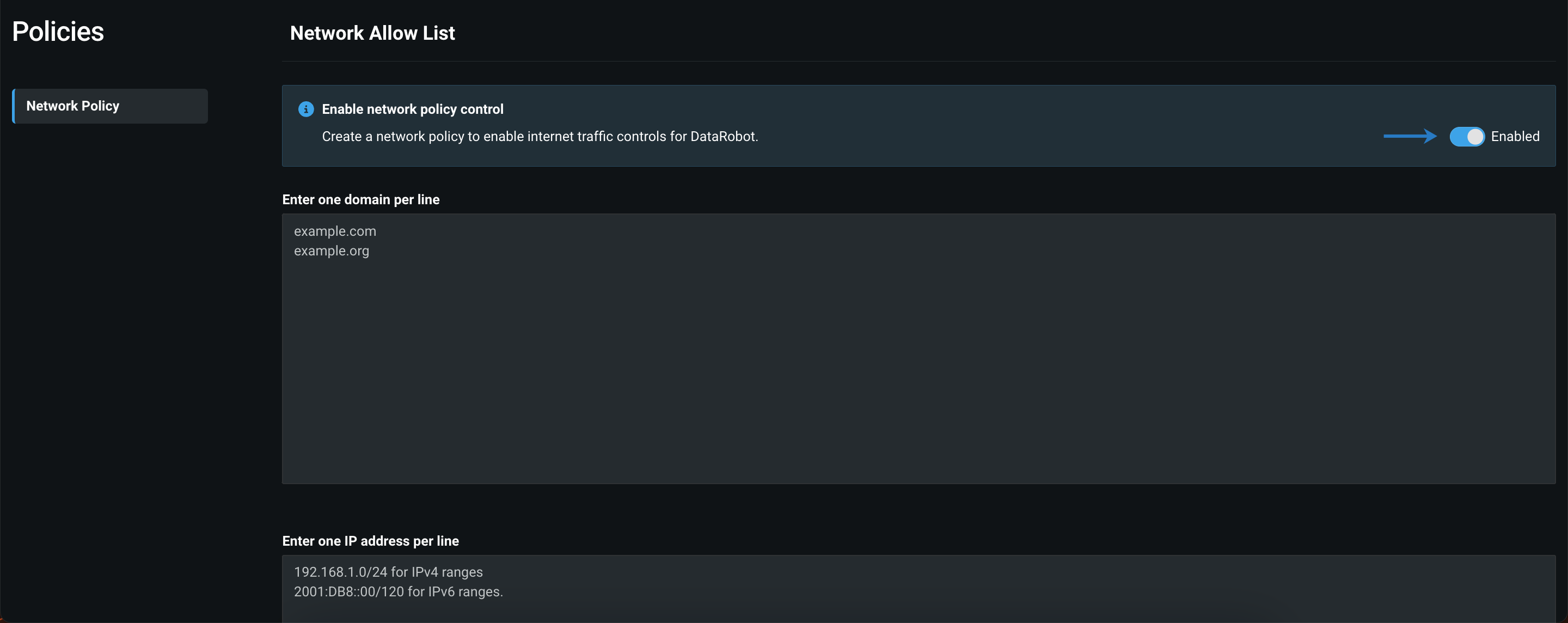
Feature flag ON by default: Enable Network policy Enforcement.
Preview documentation.
Deprecations and migrations¶
ADLS Gen2 and S3 connectors versions¶
The ADLS Gen 2 ( versions 2021.2.1634676262008 and 2020.3.1605726437949) and Amazon S3 (version 2020.3.1603724051432) have been deprecated. It is recommended that you recreate any existing data connections using the new connector versions to benefit from additional authentication mechanisms, bug fixes, and the ability to use these connections in NextGen.
The following preview feature flags will also be disabled:
- Enable DataRobot Connector
- Enable OAuth 2.0 for ADLS Gen2
The existing connections created using older versions will continue to work. Moving forward, DataRobot won't make any enhancements or bug fixes to these older versions.
All product and company names are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Use of them does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.