July 2023¶
July 26, 2023
With the latest deployment, DataRobot's AI Platform delivered the new GA and preview features listed below. From the release center you can also access:
July release¶
The following table lists each new feature:
Features grouped by capability
Data enhancements¶
Preview¶
BigQuery support added to Workbench¶
Support for Google BigQuery has been added to Workbench, allowing you to:
- Create and configure data connections.
- Add BigQuery datasets to a Use Case.
- Wrangle BigQuery datasets, and then publish recipes to BigQuery to materialize the output in the Data Registry.
Feature flag: Enable Native BigQuery Driver
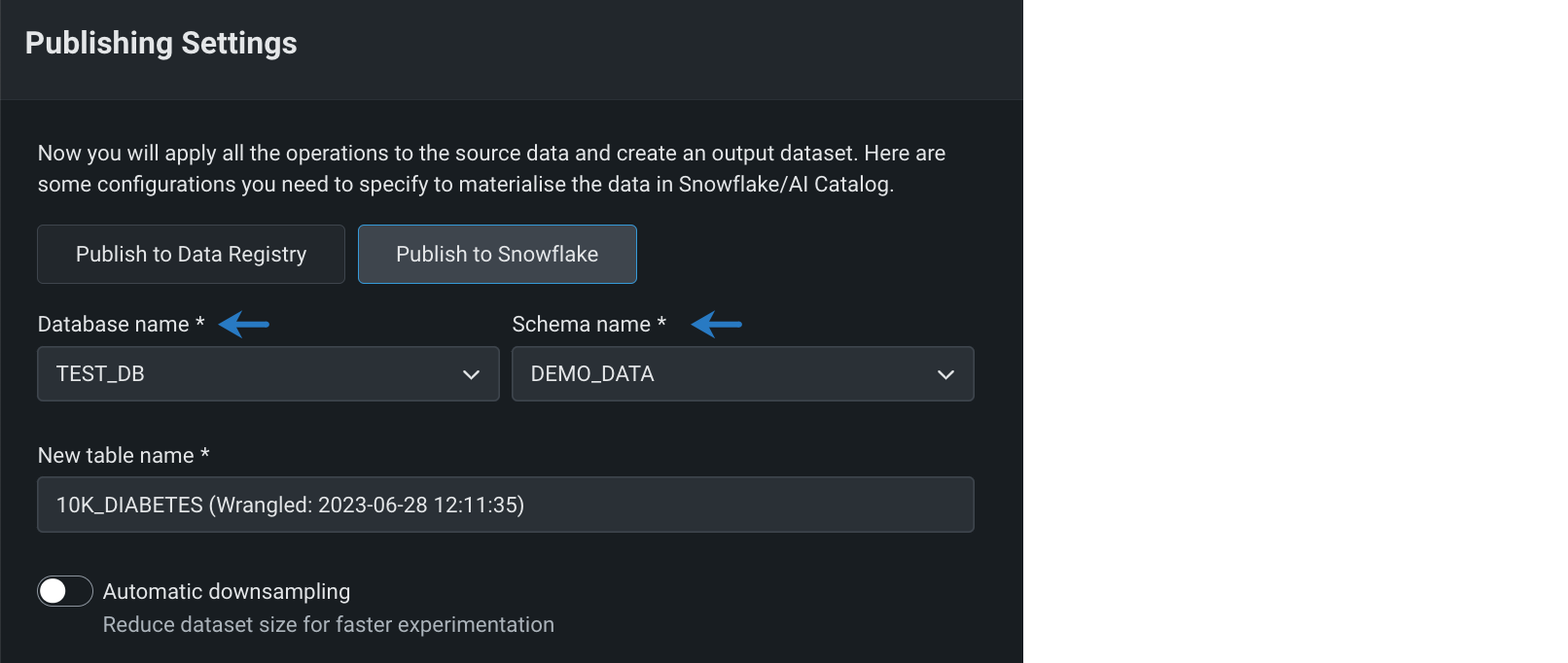
Materialize wrangled datasets in Snowflake¶
You can now publish wrangling recipes to materialize data in DataRobot’s Data Registry or Snowflake. When you publish a wrangling recipe, operations are pushed down into a Snowflake virtual warehouse, allowing you to leverage the security, compliance, and financial controls of Snowflake. By default, the output dataset is materialized in DataRobot's Data Registry. Now you can materialize the wrangled dataset in Snowflake databases and schemas for which you have write access.
Preview documentation.
Feature flags: Enable Snowflake In-Source Materialization in Workbench, Enable Dynamic Datasets in Workbench
Perform joins and aggregations on your data in Workbench¶
You can now add Join and Aggregation operations to your wrangling recipe in Workbench. Use the Join operation to combine datasets that are accessible via the same connection instance, and the Aggregation operation to apply aggregation functions like sum, average, counting, minimum/maximum values, standard deviation, and estimation, as well as some non-mathematical operations to features in your dataset.
Preview documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Additional Wrangler Operations
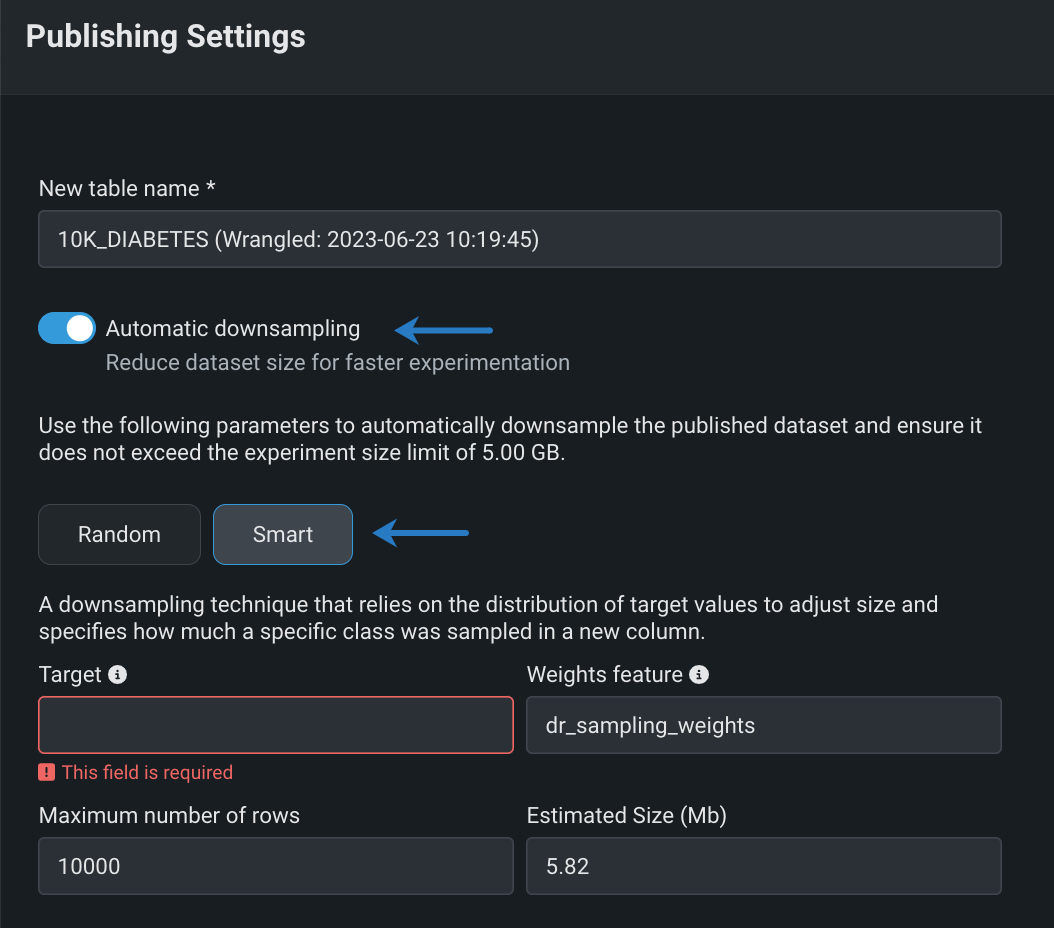
Publish recipes with smart downsampling¶
When publishing a wrangling recipe in Workbench, use smart downsampling to reduce the size of your output dataset and optimize model training. Smart downsampling is a data science technique to reduce the time it takes to fit a model without sacrificing accuracy. This downsampling technique accounts for class imbalance by stratifying the sample by class. In most cases, the entire minority class is preserved and sampling only applies to the majority class, which is particularly useful for imbalanced data. Because accuracy is typically more important on the minority class, this technique greatly reduces the size of the training dataset, reducing modeling time and cost while preserving model accuracy.
Feature flag: Enable Smart Downsampling in Wrangle Publishing Settings
Improvements to data preparation in Workbench¶
This release introduces several improvements to the data preparation experience in Workbench.
Workbench now supports dynamic datasets.
- Datasets added via a data connection will be registered as dynamic datasets in the Data Registry and Use Case.
- Dynamic datasets added via a connection will be available for selection in the Data Registry.
- DataRobot will pull a new live sample when viewing Exploratory Data Insights for dynamic datasets.
Feature flag: Enable Dynamic Datasets in Workbench
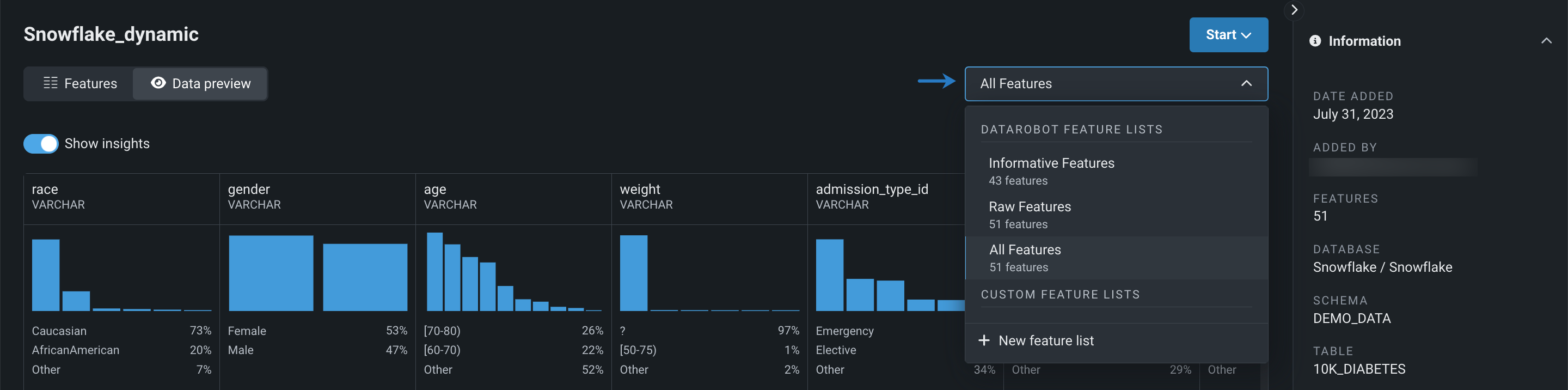
You can now view and create custom feature lists while exploring datasets registered in a Workbench Use Case.
Preview documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Feature Lists in Workbench Preview
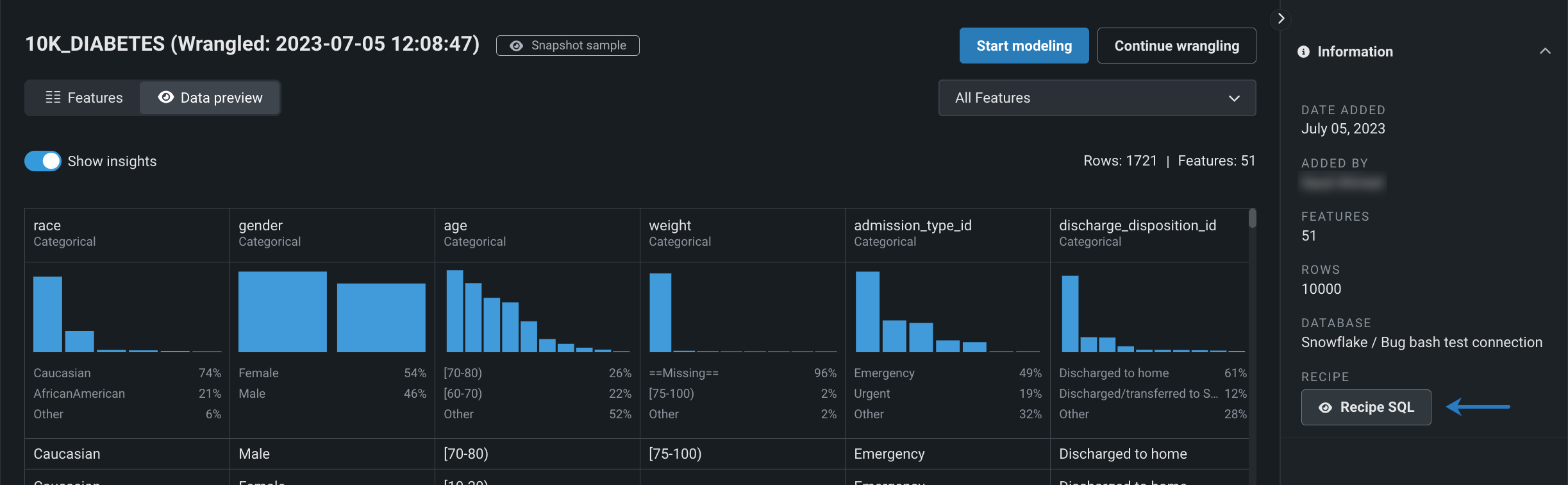
Additionally, for wrangled datasets added to a Use Case, you can now view the SQL recipe used to generate the output.
BigQuery connection enhancements¶
A new BigQuery connector is now available for preview, providing several performance and compatibility enhancements, as well as support for authentication using Service Account credentials.
Preview documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Native BigQuery Driver
Modeling enhancements¶
GA¶
Sklearn library upgrades¶
In this release, the sklearn library was upgraded from 0.15.1 to 0.24.2. The impacts are summarized as follows:
-
Feature association insights: Updated the spectral clustering logic. This only affects the cluster ID (a numeric identifier for each cluster, e.g., 0, 1, 2, 3). The values of feature association insights are not affected.
-
AUC/ROC insights: Due to the improvement in sklearn ROC curve calculation, the precision of AUC/ROC values are slightly affected.
Preview¶
Tune hyperparameters for custom tasks¶
You can now tune hyperparameters for custom tasks. You can provide two values for each hyperparameter: the name and type. The type can be one of int, float, string, select, or multi, and all types support a default value. See Model metadata and validation schema for more details and example configuration of hyperparameters.
Preview documentation.
No-Code AI App enhancements¶
Preview¶
Improvements to the new app experience in Workbench¶
This release introduces the following improvements to the new application experience (available for preview) in Workbench:
- The Overview folder now displays the blueprint of the model used to create the application.
- Alpine Light has been added to the available app themes.
Preview documentation.
Feature flag: Enable New No-Code AI Apps Edit Mode
MLOps enhancements¶
GA¶
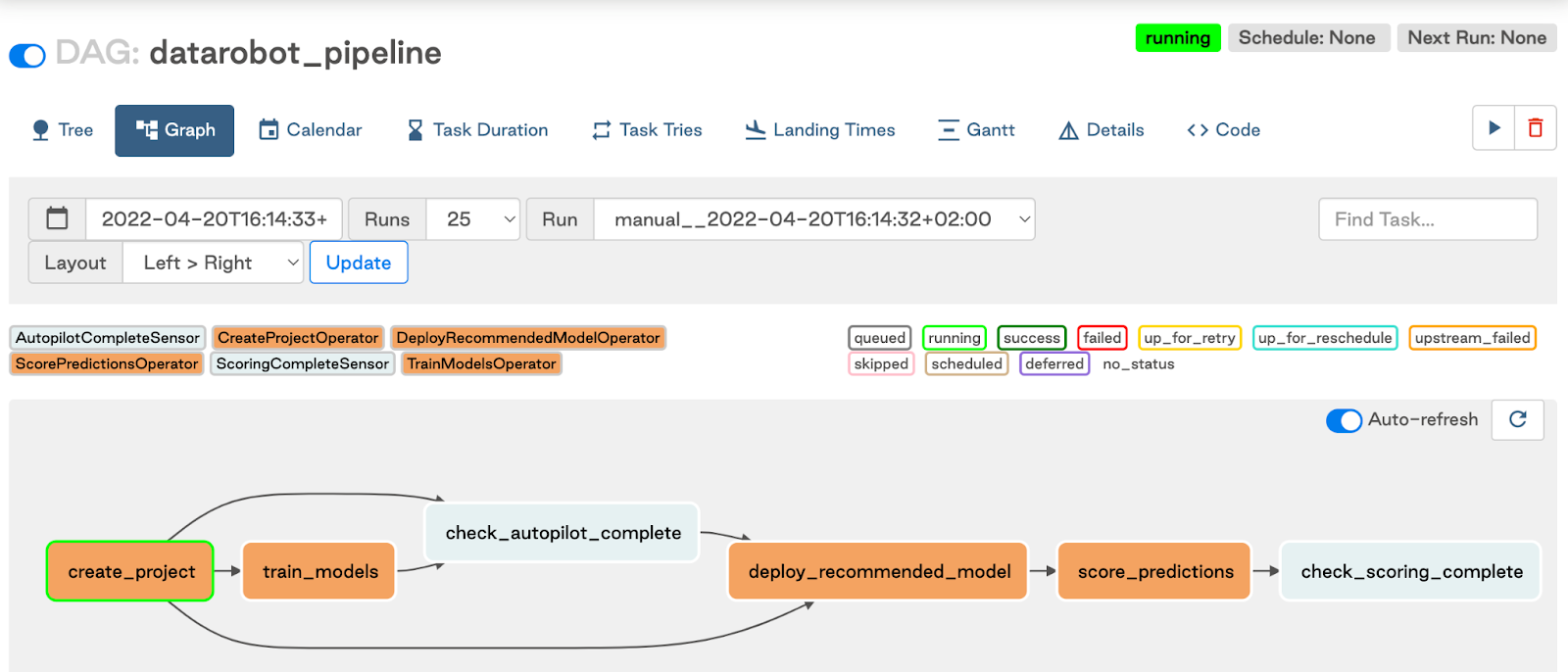
DataRobot provider for Apache Airflow¶
Now generally available, you can combine the capabilities of DataRobot MLOps and Apache Airflow to implement a reliable solution for retraining and redeploying your models; for example, you can retrain and redeploy your models on a schedule, on model performance degradation, or using a sensor that triggers the pipeline in the presence of new data. The DataRobot provider for Apache Airflow is a Python package built from source code available in a public GitHub repository and published in PyPI (The Python Package Index). It is also listed in the Astronomer Registry. The integration uses the DataRobot Python API Client, which communicates with DataRobot instances via REST API.
For more information, see the DataRobot provider for Apache Airflow quickstart guide.
Preview¶
MLflow integration for the DataRobot Model Registry¶
The preview release of the MLflow integration for DataRobot allows you to export a model from MLflow and import it into the DataRobot Model Registry, creating key values from the training parameters, metrics, tags, and artifacts in the MLflow model. You can use the integration's command line interface to carry out the export and import processes:
DR_MODEL_ID="<MODEL_PACKAGE_ID>"
env PYTHONPATH=./ \
python datarobot_mlflow/drflow_cli.py \
--mlflow-url http://localhost:8080 \
--mlflow-model cost-model \
--mlflow-model-version 2 \
--dr-model $DR_MODEL_ID \
--dr-url https://app.datarobot.com \
--with-artifacts \
--verbose \
--action sync
Preview documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Extended Compliance Documentation
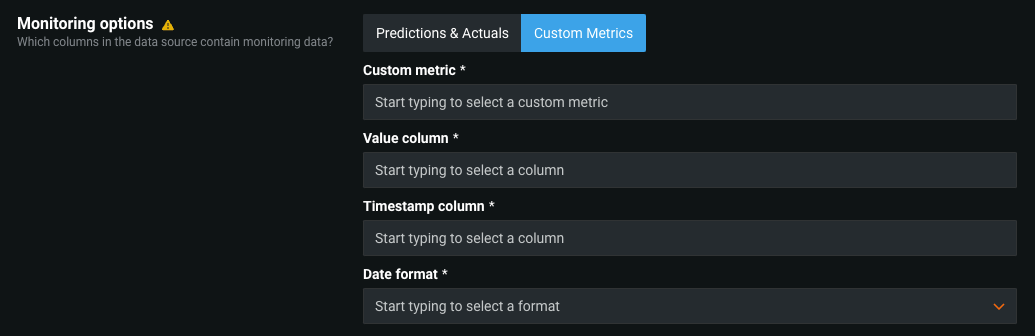
Monitoring jobs for custom metrics¶
Now available for preview, monitoring job definitions allow DataRobot to pull calculated custom metric values from outside of DataRobot into the custom metric defined on the Custom Metrics tab, supporting custom metrics with external data sources. For example, you can create a monitoring job to connect to Snowflake, fetch custom metric data from the relevant Snowflake table, and send the data to DataRobot:
For more information, see the documentation.
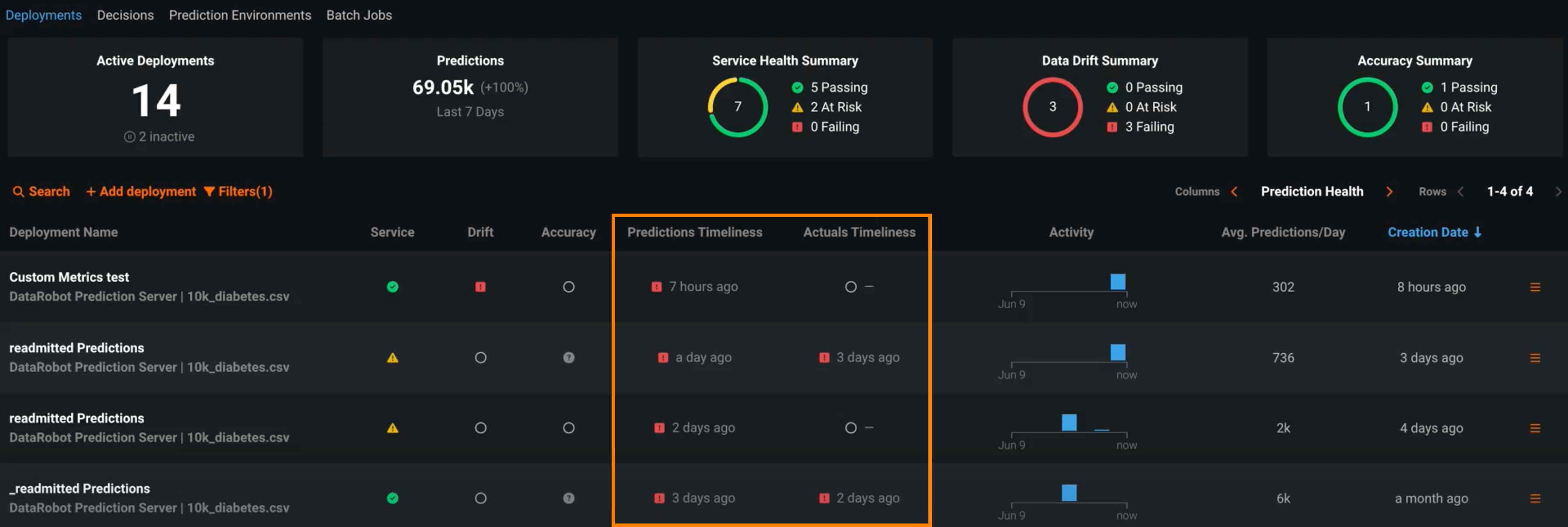
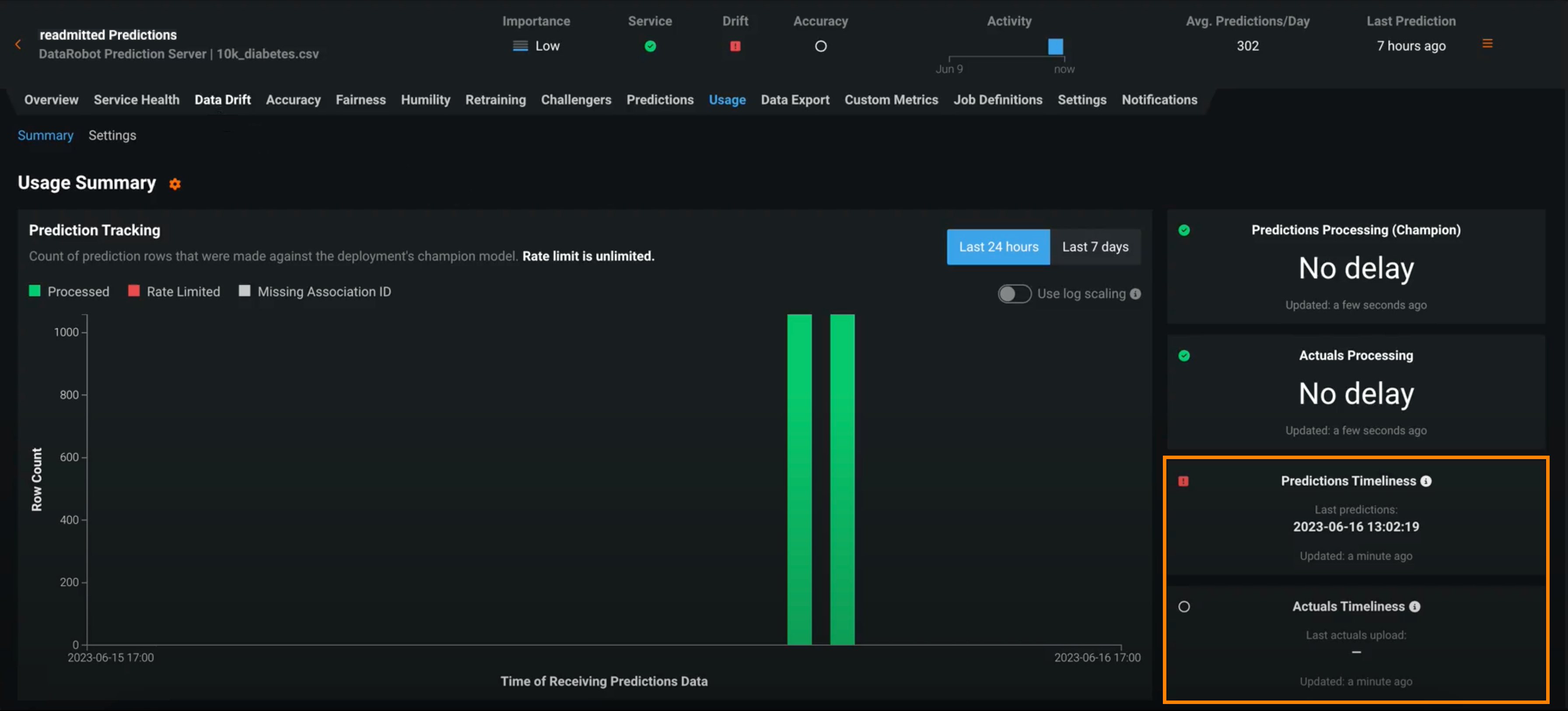
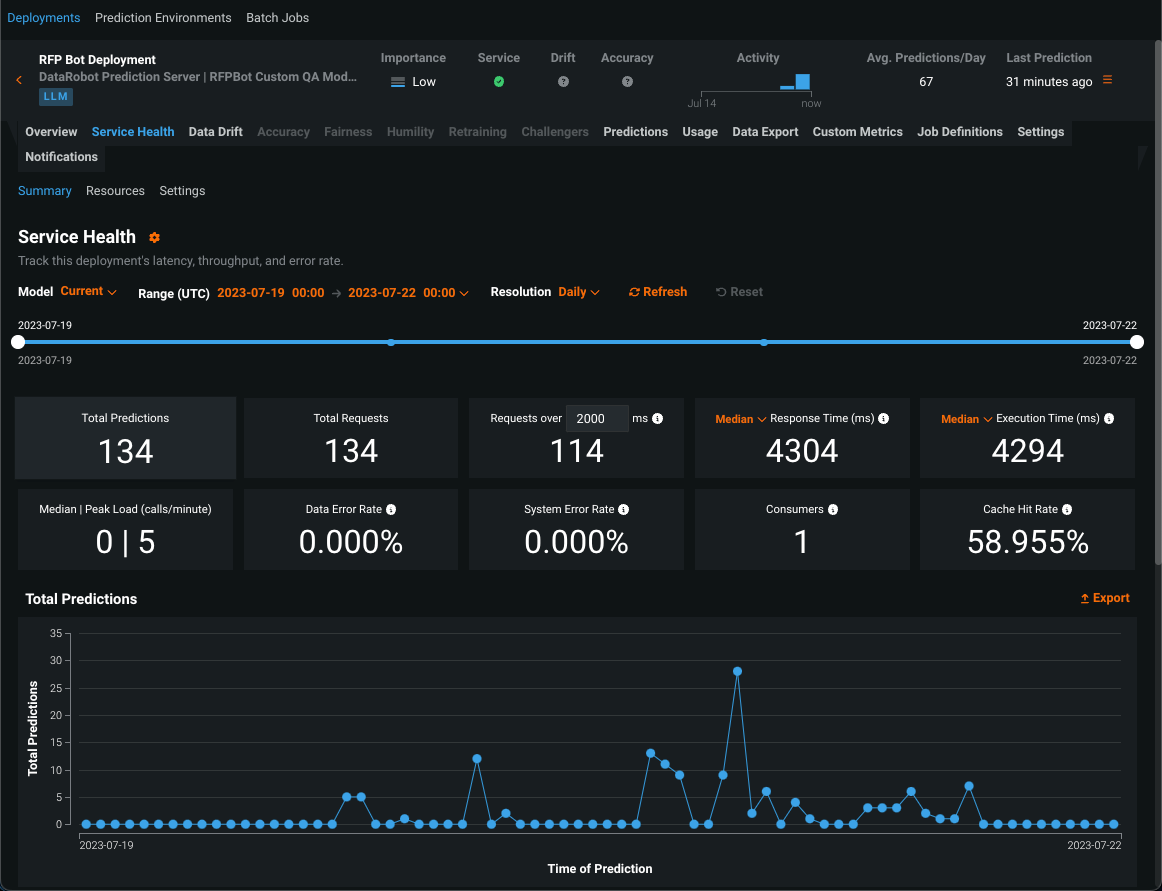
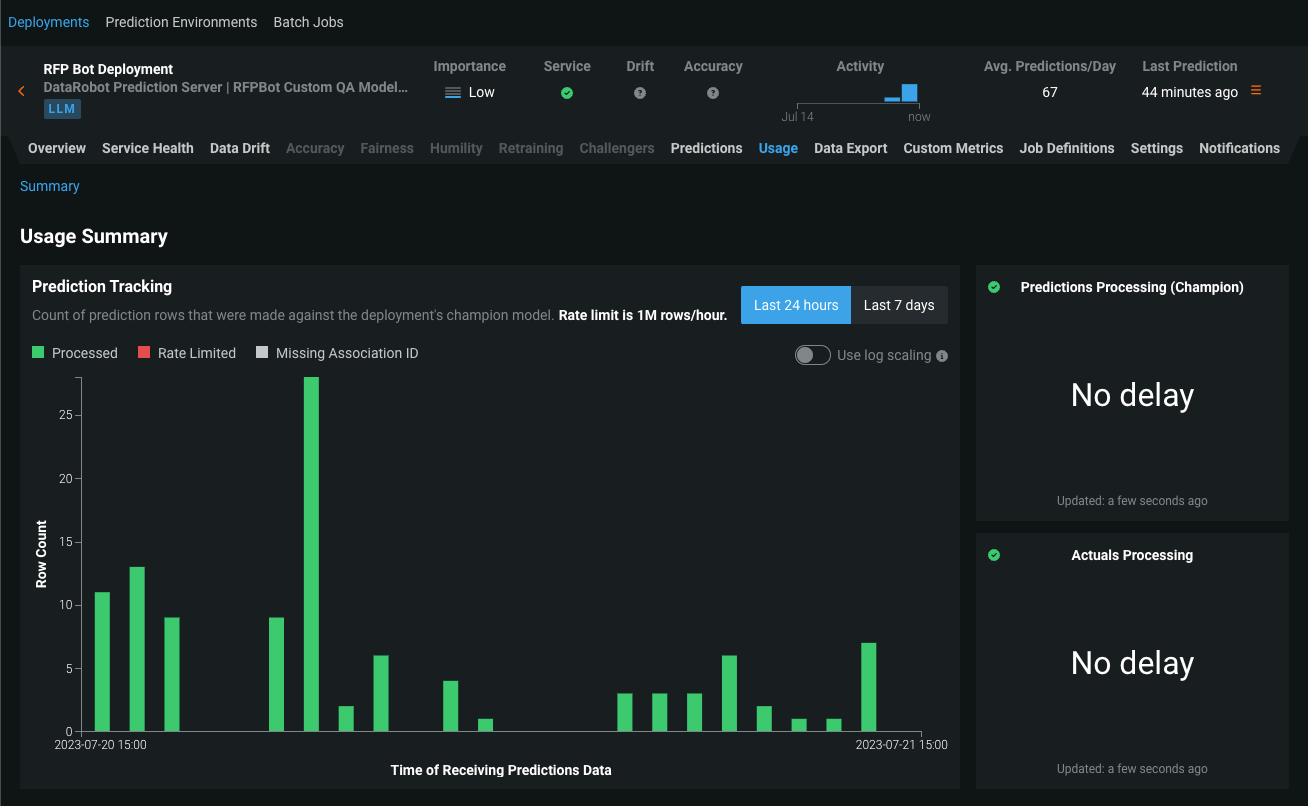
Timeliness indicators for predictions and actuals¶
Deployments have several statuses to define the general health of a deployment, including Service Health, Data Drift, and Accuracy. These statuses are calculated based on the most recent available data. For deployments relying on batch predictions made in intervals greater than 24 hours, this method can result in an unknown status value on the Prediction Health indicators in the deployment inventory. Now available for preview, those deployment health indicators can retain the most recently calculated health status, presented along with timeliness status indicators to reveal when they are based on old data. You can determine the appropriate timeliness intervals for your deployments on a case-by-case basis. Once you've enabled timeliness tracking on a deployment's Usage > Settings tab, you can view timeliness indicators on the Usage tab and in the Deployments inventory:
Note
In addition to the indicators on the Usage tab and the Deployments inventory, when a timeliness status changes to Red / Failing, a notification is sent through email or the channel configured in your notification policies.
For more information, see the documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Timeliness Stats Indicator for Deployments
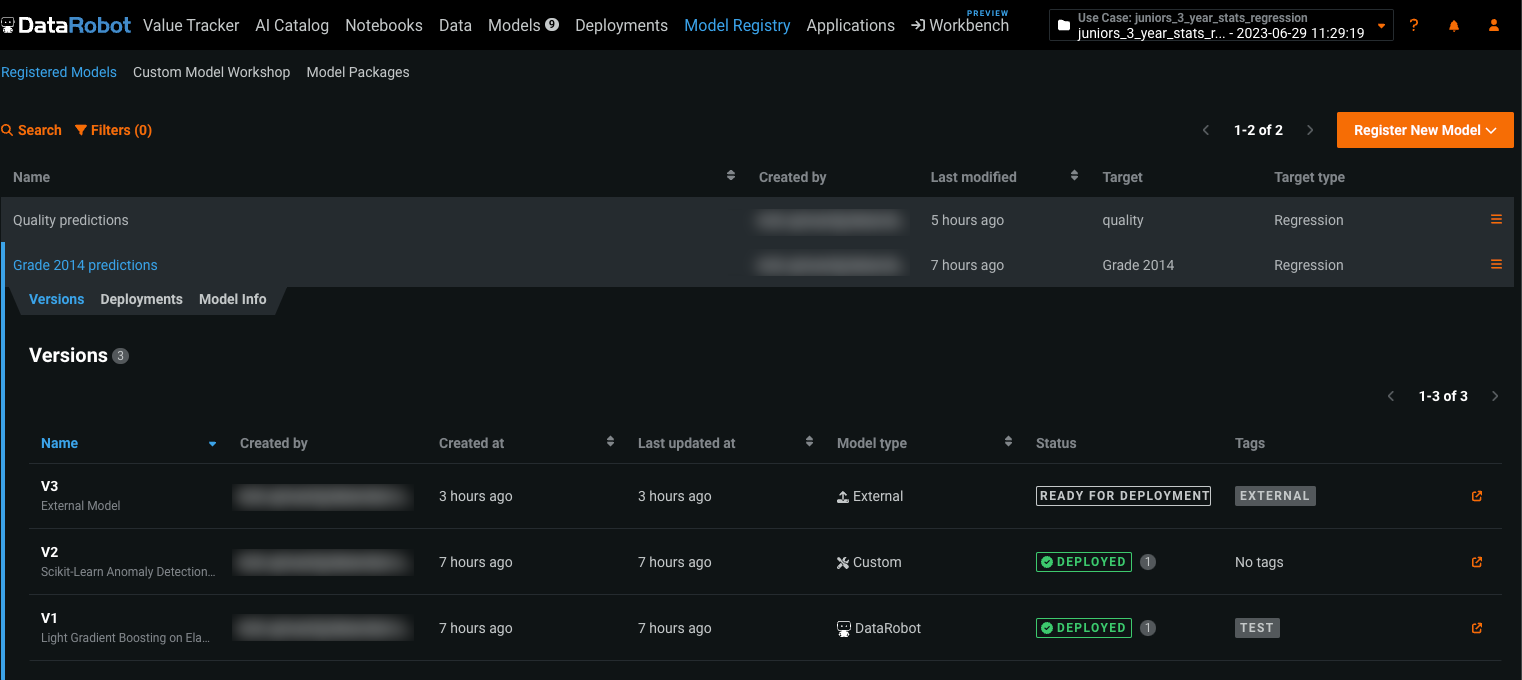
Versioning support in the Model Registry¶
The Model Registry is an organizational hub for various models used in DataRobot, where you can access models as deployment-ready model packages. Now available as a preview feature, the Model Registry > Registered Models page provides an additional layer of organization to your models.
On this page, you can group model packages into registered models, allowing you to categorize them based on the business problem they solve. Registered models can contain:
-
DataRobot, custom, and external models
-
Challenger models (alongside the champion)
-
Automatically retrained models.
Once you add registered models, you can search, filter, and sort them. You can also share your registered models (and the versions they contain) with other users.
For more information, see the Model Registry documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Versioning Support in the Model Registry
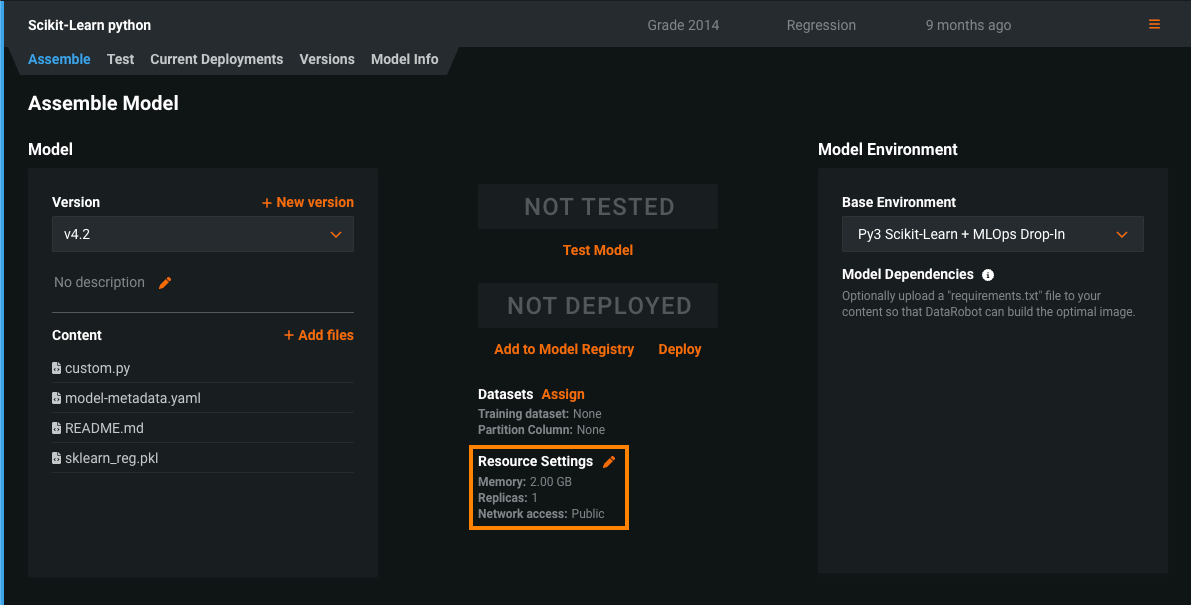
Public network access for custom models¶
Now available as a preview feature, you can enable full network access for any custom model. When you create a custom model, you can access any fully qualified domain name (FQDN) in a public network so that the model can leverage third-party services. Alternatively, you can disable public network access if you want to isolate a model from the network and block outgoing traffic to enhance the security of the model. To review this access setting for your custom models, on the Assemble tab, under Resource Settings, check the Network access:
For more information, see the documentation.
Feature flag: Enable Public Network Access for all Custom Models
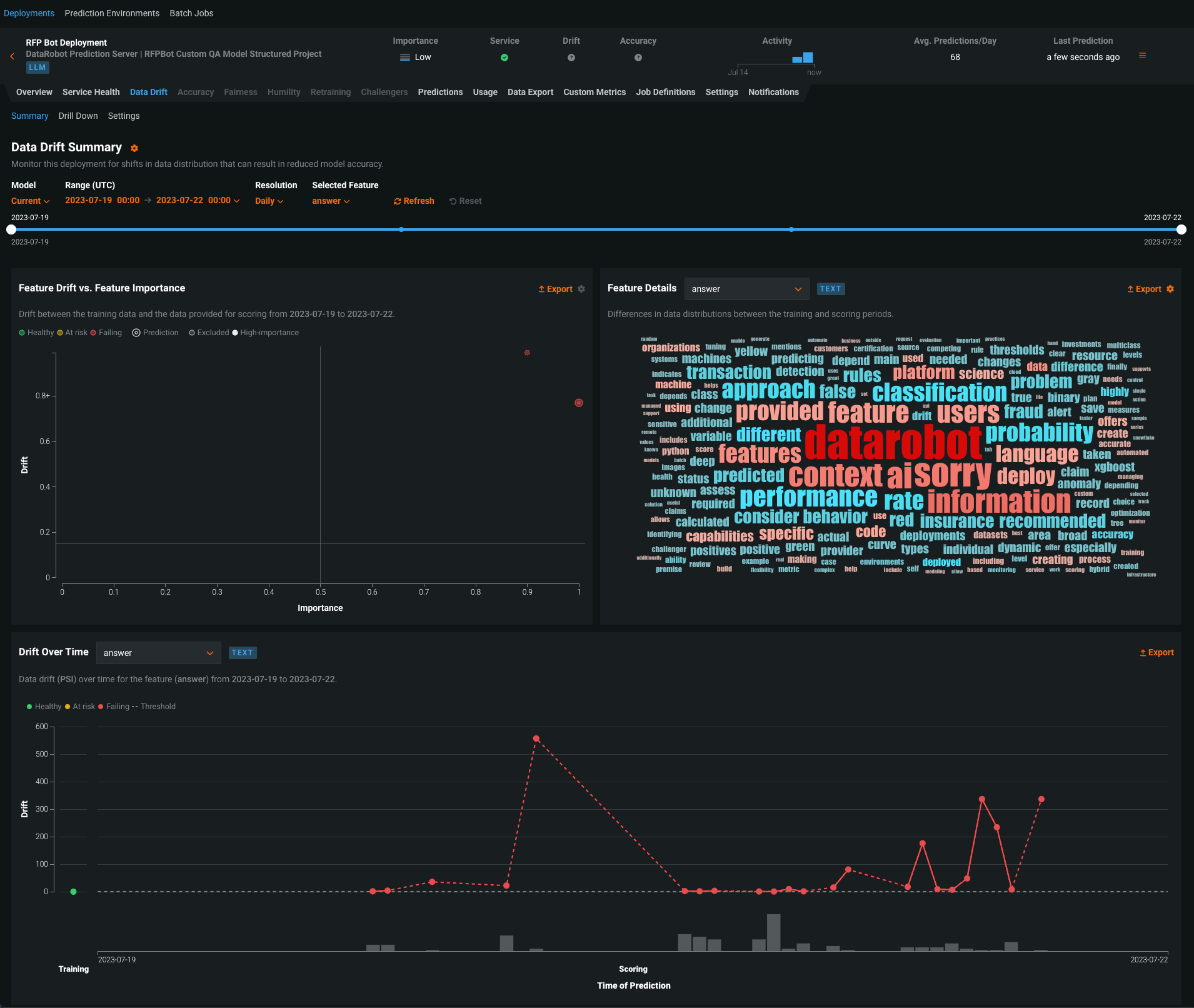
Monitoring support for generative models¶
Now available as a preview feature, the text generation target type for DataRobot custom and external models is compatible with generative Large Language Models (LLMs), allowing you to deploy generative models, make predictions, monitor service, usage, and data drift statistics, and create custom metrics. DataRobot supports LLMs through two deployment methods:
-
Create a text generation model as a custom inference model in DataRobot: Create and deploy a text generation model using DataRobot's Custom Model Workshop, calling the LLM's API to generate text instead of performing inference directly and allowing DataRobot MLOps to access the LLM's input and output for monitoring. To call the LLM's API, you should enable public network access for custom models.
-
Monitor a text generation model running externally: Create and deploy a text generation model on your infrastructure (local or cloud), using the monitoring agent to communicate the input and output of your LLM to DataRobot for monitoring.
After you deploy a generative model, you can view service health and usage statistics, export deployment data, create custom metrics, and identify data drift. On the Data Drift tab for a generative model, you can view the Feature Drift vs. Feature Importance, Feature Details, and Drift Over Time charts.
Preview documentation.
Feature flags: Enable Monitoring Support for Generative Models
API enhancements¶
DataRobot REST API v2.31¶
New features¶
- New route to retrieve deployment fairness score over time:
GET /api/v2/deployments/(deploymentId)/fairnessScoresOverTime/- New route to retrieve deployment predictions stats over time:
GET /api/v2/deployments/(deploymentId)/predictionsOverTime/- New routes to calculate and retrieve sliced insights:
POST /api/v2/insights/featureEffects/GET /api/v2/insights/featureEffects/models/(entityId)/POST /api/v2/insights/featureImpact/GET /api/v2/insights/featureImpact/models/(entityId)/POST /api/v2/insights/liftChart/GET /api/v2/insights/liftChart/models/(entityId)/POST /api/v2/insights/residuals/GET /api/v2/insights/residuals/models/(entityId)/POST/api/v2/insights/rocCurve/GET GET /api/v2/insights/rocCurve/models/(entityId)/- New routes to create and manage data slices for use with sliced insights:
POST /api/v2/dataSlices/- :http:delete:
/api/v2/dataSlices/ DELETE /api/v2/dataSlices/(dataSliceId)/GET /api/v2/dataSlices/(dataSliceId)/GET /api/v2/projects/(projectId)/dataSlices/POST /api/v2/dataSlices/(dataSliceId)/sliceSizes/GET /api/v2/dataSlices/(dataSliceId)/sliceSizes/- New route to register a Leaderboard model:
POST /api/v2/modelPackages/fromLeaderboard/- New routes to create and manage Value Trackers (former Use Cases):
POST /api/v2/valueTrackers/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/PATCH /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/DELETE /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/activities/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/attachments/POST /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/attachments/DELETE /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/attachments/(attachmentId)/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/attachments/(attachmentId)/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/realizedValueOverTime/GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/sharedRoles/PATCH /api/v2/valueTrackers/(valueTrackerId)/sharedRoles/
API changes¶
- Added training and holdout data assignment to the custom model version creation endpoints:
POST /api/v2/customModels/(customModelId)/versions/-
PATCH /api/v2/customModels/(customModelId)/versions/ -
The Organization Administrator route for removing users from an organization,
DELETE /api/v2/organizations/(organizationId)/users/(userId)/has been removed. Instead, they should be deactivated, or a system administrator can move the user to a different organization. -
Adds the
useGpuoption/parameter. When GPU workers are enabled, this option controls whether the project should use GPU workers. The parameter is added to the following route:PATCH /api/v2/projects/(projectId)/aim/
-
The
useGpuoption/parameter will also be returned as a new field when project data is retrieved using route: -
GET /api/v2/projects/(projectId)/ -
The new optional parameters
modelBaselines,modelRegimeId,modelGroupIdfor OTV Time Series projects without FEAR are added to:PATCH /api/v2/projects/(projectId)/aim/. To use these fields, enable the feature flagForecasting Without Automated Feature Derivation.
Deprecations¶
- The following custom inference models training data assignment endpoints are deprecated and will be removed in version 2.33:
PATCH /api/v2/customModels/(customModelId)/trainingData/-
PATCH /api/v2/customModels/(customModelId)/versions/withTrainingData/ -
The following route to register a Leaderboard model is deprecated in favor of
POST /api/v2/modelPackages/fromLeaderboard/and will be removed in v2.33: -
POST /api/v2/modelPackages/fromLearningModel/ -
The following use case manage endpoints are deprecated in favor of new
GET /api/v2/valueTrackers/based endpoints and will be removed in v2.33:POST /api/v2/useCases/GET /api/v2/useCases/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/PATCH /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/DELETE /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/activities/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/attachments/POST /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/attachments/DELETE /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/attachments/(attachmentId)/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/attachments/(attachmentId)/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/realizedValueOverTime/GET /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/sharedRoles/PATCH /api/v2/useCases/(useCaseId)/sharedRoles/
-
Current
useCases/endpoints are being renamed tovalueTracker/endpoints. CurrentuseCases/endpoints will sunset in two releases, API 2.33. In place of the currentuseCases/endpoints, please begin using thevalueTrackers/endpoints.
R client v2.31¶
Version v2.31 of the R client is now available for preview. It can be installed via GitHub.
This version of the R client addresses an issue where a new feature in the curl==5.0.1 package caused any invocation of datarobot:::UploadData (i.e., SetupProject) to fail with the error No method asJSON S3 class: form_file.
Enhancements¶
The unexported function datarobot:::UploadData now takes an optional argument fileName.
Bugfixes¶
Loading the datarobot package with suppressPackageStartupMessages() will now suppress all messages.
Deprecations¶
CreateProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureFithas been removed. UseCreateProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureEffectsinstead.ListProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureFithas been removed. UseListProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureEffectsinstead.ListProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureFitMetadatahas been removed. UseListProjectsDatetimeModelsFeatureEffectsMetadatainstead.CreateProjectsModelsFeatureFithas been removed. Use CreateProjectsModelsFeatureEffects instead.ListProjectsModelsFeatureFithas been removed. UseListProjectsModelsFeatureEffectsinstead.ListProjectsModelsFeatureFitMetadatahas been removed. UseListProjectsModelsFeatureEffectsMetadatainstead.
Dependency changes¶
Client documentation is now explicitly generated with Roxygen2 v7.2.3. Added Suggests: mockery to improve unit test development experience.
R client v2.18.3¶
Version v2.31 of the R client is now generally available. It can be accessed via CRAN.
The datarobot package is now dependent on R >= 3.5.
New features¶
-
The R client will now output a warning when you attempt to access certain resources (projects, models, deployments, etc.) that are deprecated or disabled by the DataRobot platform migration to Python 3.
-
Added support for comprehensive autopilot: use
mode = AutopilotMode.Comprehensive.
Enhancements¶
-
The function
RequestFeatureImpactnow accepts arowCountargument, which will change the sample size used for Feature Impact calculations. -
The un-exported function
datarobot:::UploadDatanow takes an optional argumentfileName.
Bugfixes¶
-
Fixed an issue where an undocumented feature in
curl==5.0.1is installed that caused any invocation ofdatarobot:::UploadData(i.e.,SetupProject) to fail with the errorNo method asJSON S3 class: form_file. -
Loading the
datarobotpackage withsuppressPackageStartupMessages()will now suppress all messages.
API changes¶
-
The functions
ListProjectsandas.data.frame.projectSummaryListno longer return fields related to recommender models, which were removed in v2.5.0. -
The function
SetTargetnow sets autopilot mode to Quick by default. Additionally, when Quick is passed, the underlying/aimendpoint will no longer be invoked with Auto.
Deprecations¶
-
The
quickrunargument is removed from the functionSetTarget. Users should setmode = AutopilotMode.Quickinstead. -
Compliance Documentation was deprecated in favor of the Automated Documentation API.
Dependency changes¶
-
The
datarobotpackage is now dependent on R >= 3.5 due to changes in the updated "Introduction to DataRobot" vignette. -
Added dependency on
AmesHousingpackage for updated "Introduction to DataRobot" vignette. -
Removed dependency on
MASSpackage. -
Client documentation is now explicitly generated with Roxygen2 v7.2.3.
Documentation changes¶
- Updated the "Introduction to DataRobot" vignette to use Ames, Iowa housing data instead of the Boston housing dataset.
All product and company names are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Use of them does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.