Codespace scheduling¶
With the codespace scheduling capability, you can automate your code-based workflows by scheduling notebooks to run on a schedule in non-interactive mode.
See the associated considerations for important additional information.
Create a notebook job¶
Notebook scheduling is managed by notebook jobs. You can only create a new notebook job when your codespace is offline. If your codespace is currently open in an active session, you will need to first shut down this interactive session before you can create a new job for a notebook within the codespace.
To create a notebook job, start the codespace session and select the notebook for which you want scheduling. Then, select the calendar icon in the sidebar to access the Notebook jobs tab.
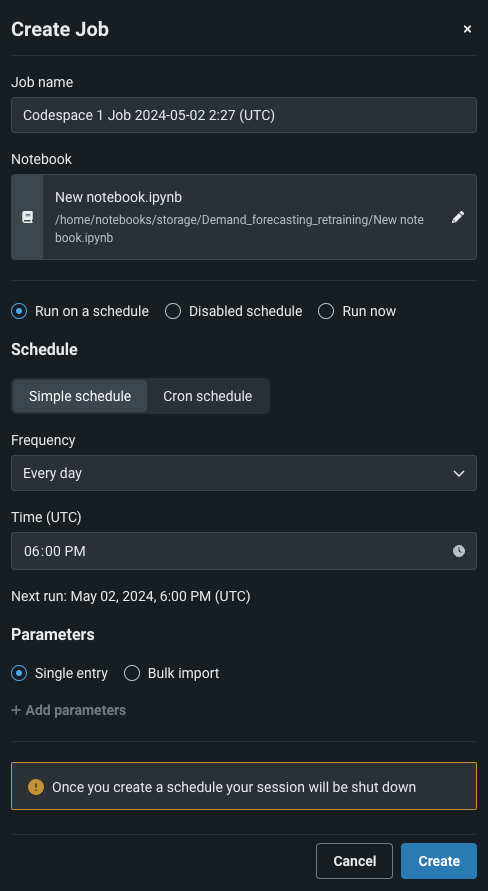
From the Notebook jobs tab, select Create notebook job. Then, configure the schedule from the notebook job modal.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
| Job name | Enter the name of the notebook job that you are creating. |
| Notebook | Select the notebook for which you want to create a schedule using the pencil icon. You can choose from any notebook in the codespace's file system. |
| Run mode | Set the run schedule for the notebook:
|
| Schedule type | Choose between a simple schedule or a cron schedule. A simple schedule only requires a frequency and a time to run the notebook. A cron schedule allows you to configure the exact time and date for the notebook to run, specifying the minute, hour, date, month, and day of the week. |
| Frequency | Set the rate at which you want to notebook to run (hourly, daily, monthly, etc.). |
| Time | Specify the time at which the notebook will run on the schedule. Select Cron schedule for more precise scheduling options. |
| Parameters | (Optional) Read more about parameterization below. Define parameters in the notebook to automatically provide their values at the time of the scheduled run instead of having to go into the notebook and manually change each value. Choose to add parameters as single entries or import them in bulk. |
When you have fully configured the notebook job, click Create. Once you’ve created the scheduled notebook job, DataRobot shuts down the codespace session (unless you’ve created the job in a disabled state). A codespace cannot be started in an interactive session while it has an enabled schedule on it in order to prevent unexpected behavior and filesystem conflicts. The newly created notebook job can be viewed from the Notebook jobs tab. When a notebook job runs, the results (cell outputs) are displayed in the notebook.
Notebook parameterization¶
You can parameterize a notebook to enhance the automation experience enabled by notebook scheduling. By defining certain values in a codespace as parameters, you can provide inputs for those parameters when a notebook job runs instead of having to continuously modify the notebook itself to change the values for each run. DataRobot supports parameterization for both scheduled notebook jobs as well as manual “Run now” notebook jobs in a codespace.
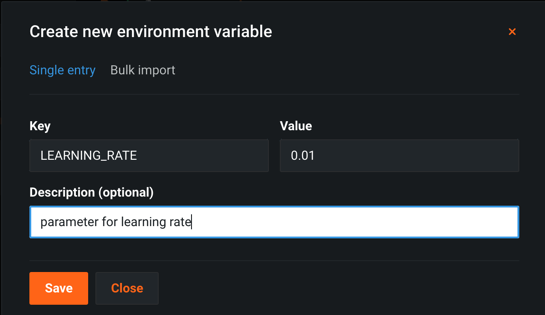
To parameterize certain values in a notebook, you must define the parameters as codespace environment variables. The value of the environment variable will serve as the default value of the parameter.
Once defined, you can use this parameter in code by retrieving the corresponding environment variable, as shown below.
When a notebook job is executed, the session's environment variables will first be set according to codespace's environment variables; any parameters defined for the job will be set at the notebook kernel level and override the corresponding codespace environment variable's default value. Note that these runtime parameter values do not replace the codespace environment variables' stored values.
When adding parameters, you can add each one-by-one by adding key-value pairs, or define them in bulk. For bulk import, specify a new-line delimited key value pairs in the text field. Use the following format on each line in the field:
KEY=VALUE # DESCRIPTION
Manage notebook job definitions¶
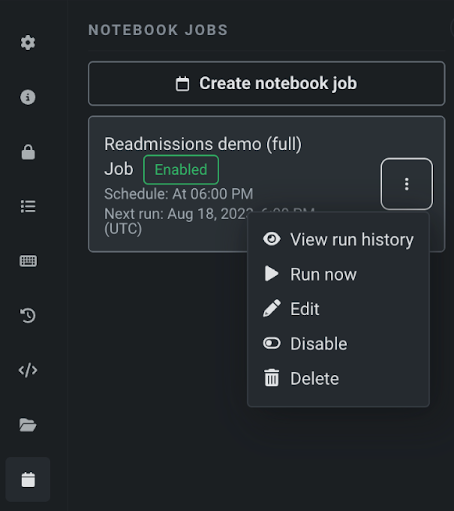
Scheduled job definitions for a notebook are displayed in the Notebook jobs tab. Click the Actions menu to access the list of actions you can perform on the job definition, such as viewing the run history or editing the job.
Note
Disabling a job definition pauses the schedule. No new automated runs of the scheduled job will be submitted until the schedule is re-enabled.
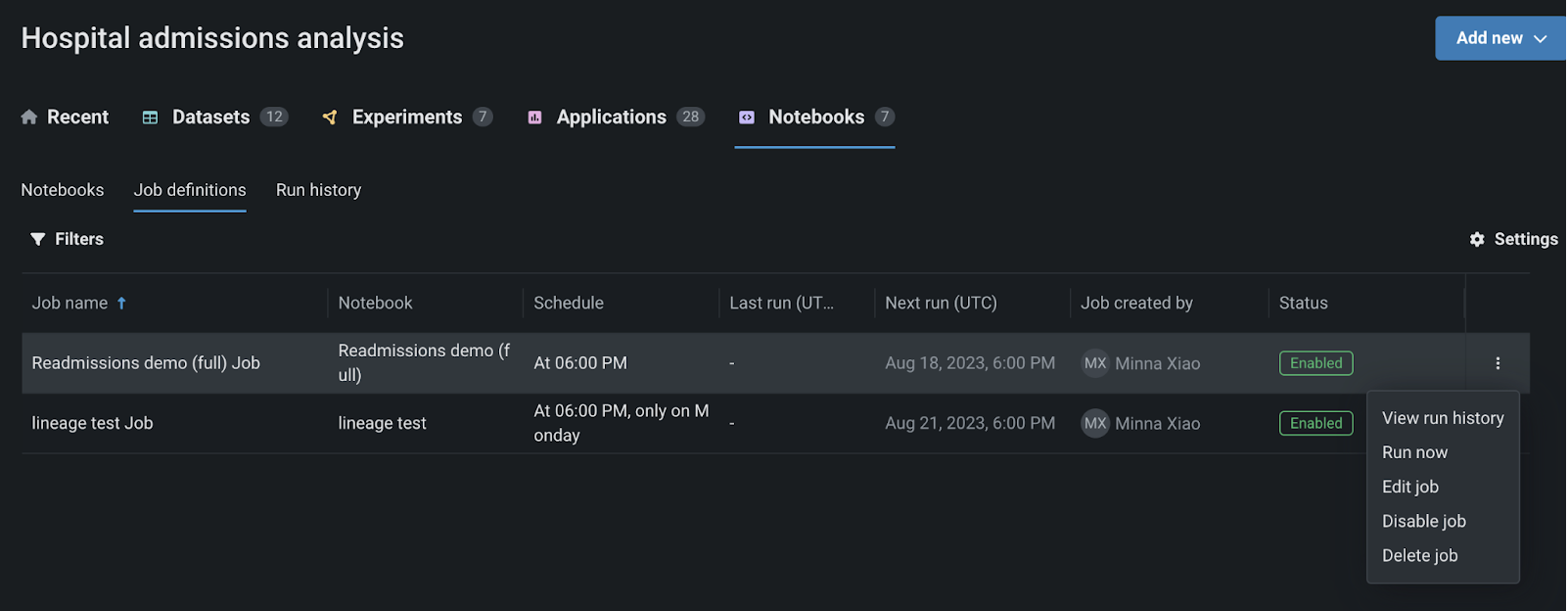
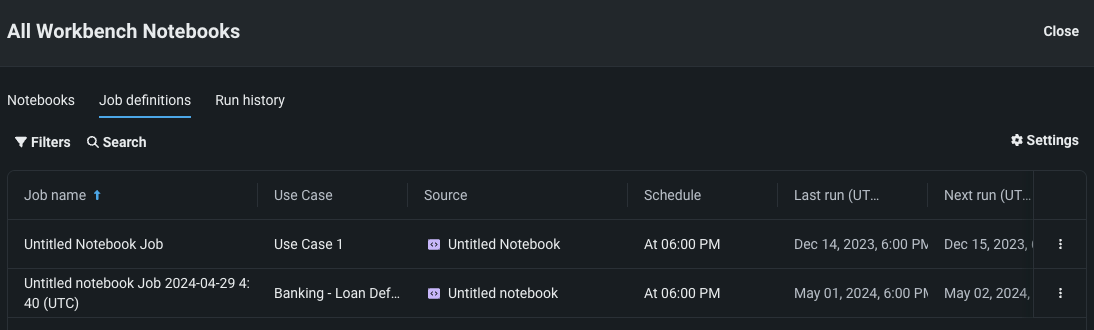
You can also view all scheduled job definitions across all the notebooks in a Use Case by navigating to the Job definitions section of the Notebooks tab in the Use Case home page.
Additionally, you can view notebook jobs configured across all Use Cases configured in Workbench. To do so, access a Use Case and navigate to its Notebooks tab. Then click All Workbench Notebooks.
This brings you to a page that displays all notebooks created across every Use Case that you have access to. From here, you can select the Job definitions tab to view all notebook jobs configured across these Use Cases.
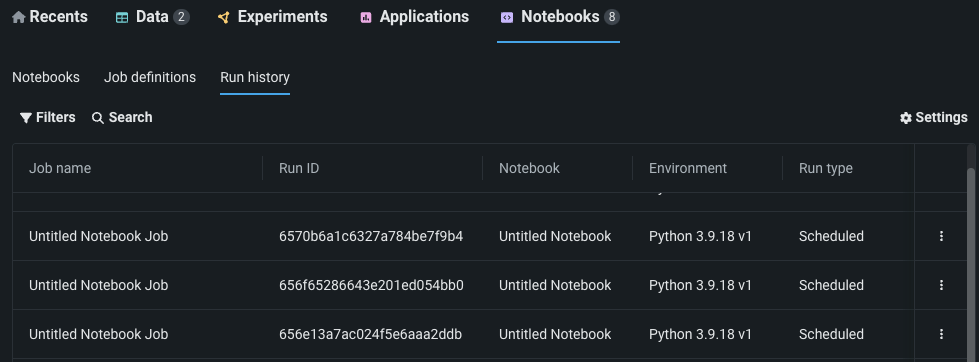
Monitor run history¶
DataRobot tracks the history and metadata of each automated run of a scheduled notebook and each manual run of a notebook triggered by the Run now action. To view the run history, navigate to the Run history section of the Notebooks tab on the Use Case home page. The Run history section displays metadata for each run including the run’s start time (UTC), end time (UTC), duration, and status.
Click the Actions menu to download run results or cancel a run. Select Settings to filter by the columns you wish to view and reorder them.
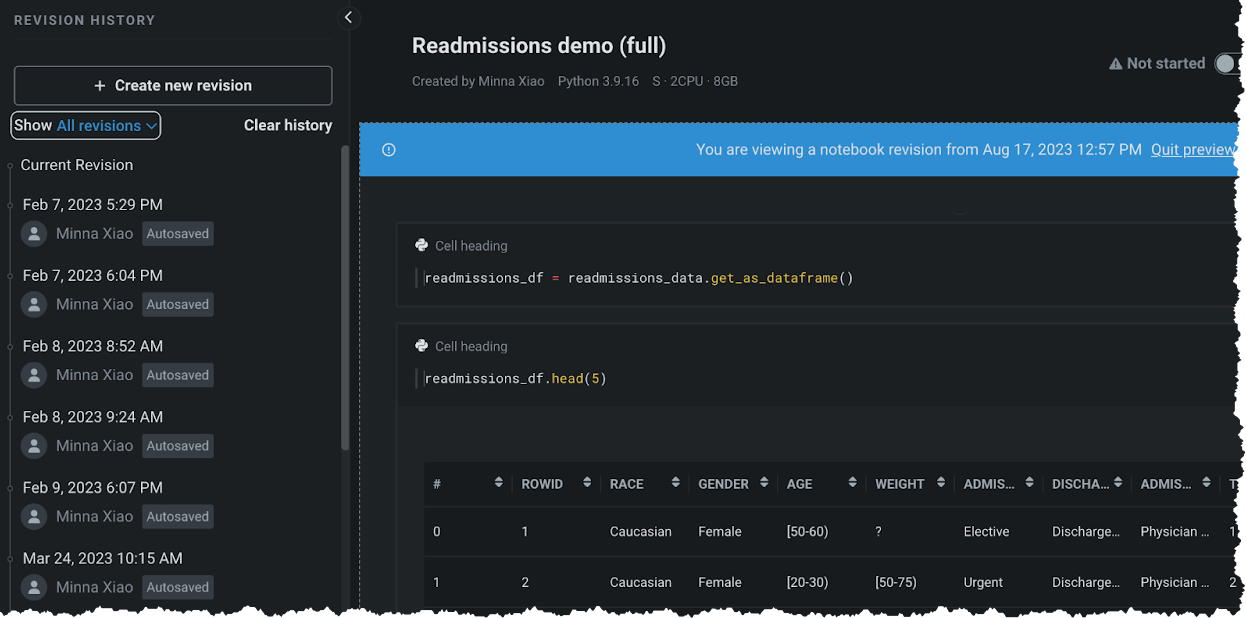
Each notebook run has a corresponding notebook revision, which is a snapshot of the notebook (and cell outputs) that DataRobot automatically collects at the end of each notebook job run. This allows you to go back and view the run results of previous notebook runs, even if the current version of the notebook has changed. The notebook revision is displayed in the Run results column in the Run history table. Click on a run in the table to open the notebook revision for that corresponding run.
Notifications¶
You can configure notifications for scheduled jobs to receive alerts on specific events. Notifications for scheduled notebook jobs are off by default. To set up notifications, leverage DataRobot’s notification system to first create a notification channel for delivering notifications. DataRobot supports webhook, email, Slack, and Microsoft Teams channels. Then, create a notification channel for your alert conditions. You can either create a policy for the event group, “Notebook-Schedule-related-events”, or for a single event. Events for notebook jobs include “Notebook Schedule Completed”, “Notebook Schedule Created”, and “Notebook Schedule Failure”.
An administrator is required to configure notification channels and policies, but notifications can be received by all subscribers. For more information on configuring notifications for scheduled jobs, see the Notification service documentation.
Notebook scheduling considerations¶
Review the following considerations before working with notebook scheduling:
-
Codespaces are limited to five active schedules. Additionally, each notebook can only have one active schedule at a time. Therefore, you can have up to five active schedules for five notebooks at a time in one codespace. If you do want to create another scheduled notebook job, you will need to disable an existing schedule from another notebook.
-
You cannot start a codespace in an interactive session if the codespace has an enabled scheduled job. In order to edit or execute your codespace in an interactive session, you will need to disable any enabled scheduled notebook job.
-
The smallest frequency you can specify for a schedule is hourly.
-
The max number of notebook jobs that can be executed in parallel is set at the organization level and defaults to two. This is a separate limit from the max number of interactive notebook sessions you can have running in parallel.
-
The max run time for a notebook job to execute is currently 24 hours. After that notebook execution limit is reached, the job will be terminated.
-
Getting input from the user from
stdin(such as when debuggers are used or other input prompts) is disabled when a codespace is in a scheduled job (or is non-interactively executed). This prevents the codespace from blocking indefinitely while waiting for interactive user input and allows the codespace job to execute to completion.