Restore features removed by reduction¶
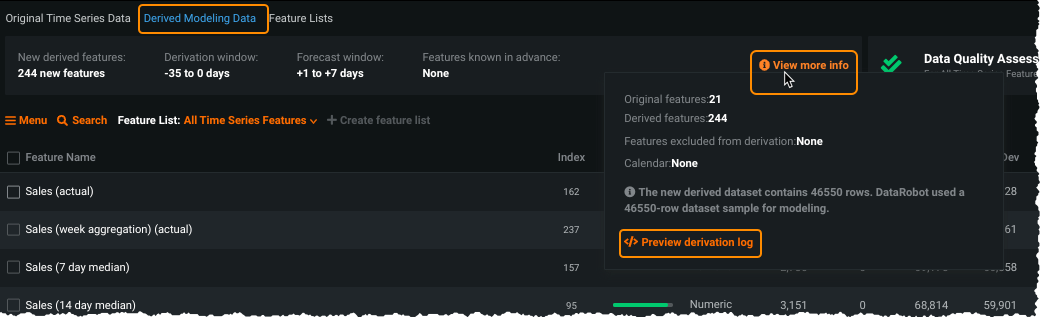
In any time series project, DataRobot generates derived features based on the window settings at project start. DataRobot then runs a feature reduction algorithm, removing features it detects as low impact. Sometimes, however, the algorithm may remove some important features during the feature reduction process—features that you want included in the generated feature lists or evaluated for feature impact. Some examples of this are certain calendar-derived features or a particular numeric statistic of a financial variable. After EDA2 completes, you can add these features back into your available derived modeling data.
Note
Even if you disable supervised reduction in advanced options, DataRobot may still remove features based on extractor priority. These features can also be restored with the restoration process.
Identify removed features¶
The easiest way to determine whether features were removed in the feature reduction process is to review the feature derivation log after EDA2 completes.
Depending on the dataset size, it is likely you need to download the log. This is because the reduction process runs last (is at the end of the file) and may be truncated from the preview.
Restore pruned features¶
The following describes how to restore removed features (identified from the derivation log) to the modeling dataset. You can use this option repeatedly, until you have restored all features or have reached the maximum supported features, which may be constrained by data ingest limits.
-
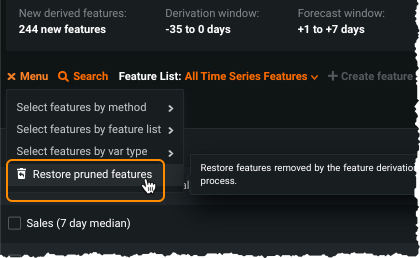
On the Data > Derived Modeling Data tab, select Restore pruned features from the menu:
-
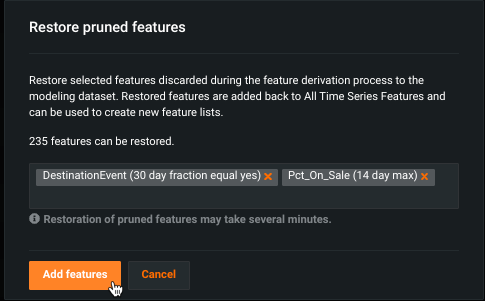
In the Restore pruned features window, begin typing to select features for restoration. DataRobot indicates the number of features that can be added back.
-
Click Add features when all desired features are listed. DataRobot reports progress:
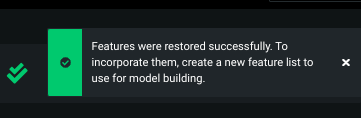
And then success:
-
To verify the restoration, click the index column. DataRobot re-sorts the features, listing the restored features first and marking them with a restoration icon (
 ).
).
Note
Feature restoration does not change the feature lists created during EDA2. To use the restored features for modeling, create new feature lists.
Create new feature lists¶
When features are restored, they are not added into existing feature lists. To use the new features as part of your modeling dataset you must create new feature list(s) that incorporates them. For example:
-
From the Derived Modeling Data tab, select the best performing feature list. Check the Feature Name box to select all features in that list.
-
Change to the All Time Series Features list (selections from the previous action are preserved).
-
Select the restored features you would like to add.
-
Click Create feature list to add the new list.
Once one or more new lists are created that contain the restored features, build models with them (individually or by rerunning Autopilot). Compare model performance between lists to see if there is value in including the restored features as part of the model to use for making predictions.
Deep dive: defining low impact¶
DataRobot's feature reduction algorithm removes features it detects as low impact. In other words, an internal algorithm sets a boundary for features to score a minimum of 80% for impact (in Quick mode). Additional calculations when creating the modeling dataset:
-
The total number (original and derived) of post-derivation features is limited to 10x the number of original features or 500 features, whichever is greater.
-
If the number of original features is under 50, DataRobot ensures that there is at least one derived feature for every original feature. If over 50 original features, this restriction is not applied and DataRobot discards all features determined to be not important.
Read more¶
To learn more about the topics discussed on this page, see:
- The time series feature engineering reference for a list of operators used and feature names created by the feature derivation process.
- Working with the modeling dataset.